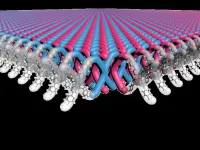
EVANSTON, Il. --- In a remarkable feat of chemistry, a Northwestern University-led research team has developed the first two-dimensional (2D) mechanically interlocked material.
Resembling the interlocking links in chainmail, the nanoscale material exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength. With further work, it holds promise for use in high-performance, light-weight body armor and other uses that demand lightweight, flexible and tough materials.
Publishing on Friday (Jan. 17) in the journal Science, the study marks several firsts for the field. Not only is it the first 2D mechanically interlocked polymer, but the novel material also contains 100 trillion mechanical bonds per 1 square centimeter — the highest density of mechanical bonds ever achieved. The researchers produced this material using a new, highly efficient and scalable polymerization process.
“We made a completely new polymer structure,” said Northwestern’s William Dichtel, the study’s corresponding author. “It’s similar to chainmail in that it cannot easily rip because each of the mechanical bonds has a bit of freedom to slide around. If you pull it, it can dissipate the applied force in multiple directions. And if you want to rip it apart, you would have to break it in many, many different places. We are continuing to explore its properties and will probably be studying it for years.”
Dichtel is the Robert L. Letsinger Professor of Chemistry at the Weinberg College of Arts and Sciences and a member of the International Institute of Nanotechnology (IIN) and the Paula M. Trienens Institute for Sustainability and Energy. Madison Bardot, a Ph.D. candidate in Dichtel’s laboratory and IIN Ryan Fellow, is the study’s first author.
Inventing a new process
For years, researchers have attempted to develop mechanically interlocked molecules with polymers but found it near impossible to coax polymers to form mechanical bonds.
To overcome this challenge, Dichtel’s team took a whole new approach. They started with X-shaped monomers — which are the building blocks of polymers — and arranged them into a specific, highly ordered crystalline structure. Then, they reacted these crystals with another molecule to create bonds between the molecules within the crystal.
“I give a lot of credit to Madison because she came up with this concept for forming the mechanically interlocked polymer,” Dichtel said. “It was a high-risk, high-reward idea where we had to question our assumptions about what types of reactions are possible in molecular crystals.”
The resulting crystals comprise layers and layers of 2D interlocked polymer sheets. Within the polymer sheets, the ends of the X-shaped monomers are bonded to the ends of other X-shaped monomers. Then, more monomers are threaded through the gaps in between. Despite its rigid structure, the polymer is surprisingly flexible. Dichtel’s team also found that dissolving the polymer in solution caused the layers of interlocked monomers to peel off each other.
“After the polymer is formed, there’s not a whole lot holding the structure together,” Dichtel said. “So, when we put it in solvent, the crystal dissolves, but each 2D layer holds together. We can manipulate those individual sheets.”
To examine the structure at the nanoscale, collaborators at Cornell University, led by Professor David Muller, used cutting-edge electron microscopy techniques. The images revealed the polymer’s high degree of crystallinity, confirmed its interlocked structure and indicated its high flexibility.
Dichtel’s team also found the new material can be produced in large quantities. Previous polymers containing mechanical bonds typically have been prepared in very small quantities using methods that are unlikely to be scalable. Dichtel’s team, on the other hand, made half a kilogram of their new material and assume even larger amounts are possible as their most promising applications emerge.
Adding strength to tough polymers
Inspired by the material’s inherent strength, Dichtel’s collaborators at Duke University, led by Professor Matthew Becker, added it to Ultem. In the same family as Kevlar, Ultem is an incredibly strong material that can withstand extreme temperatures as well as acidic and caustic chemicals. The researchers developed a composite material of 97.5% Ultem fiber and just 2.5% of the 2D polymer. That small percentage dramatically increased Ultem’s overall strength and toughness.
Dichtel envisions his group’s new polymer might have a future as a specialty material for light-weight body armor and ballistic fabrics.
“We have a lot more analysis to do, but we can tell that it improves the strength of these composite materials,” Dichtel said. “Almost every property we have measured has been exceptional in some way.”
Steeped in Northwestern history
The authors dedicated the paper to the memory of former Northwestern chemist Sir Fraser Stoddart, who introduced the concept of mechanical bonds in the 1980s. Ultimately, he elaborated these bonds into molecular machines that switch, rotate, contract and expand in controllable ways. Stoddart, who passed away last month, received the 2016 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for this work.
“Molecules don’t just thread themselves through each other on their own, so Fraser developed ingenious ways to template interlocked structures,” said Dichtel, who was a postdoctoral researcher in Stoddart’s lab at UCLA. “But even these methods have stopped short of being practical enough to use in big molecules like polymers. In our present work, the molecules are held firmly in place in a crystal, which templates the formation of a mechanical bond around each one.
“So, these mechanical bonds have deep tradition at Northwestern, and we are excited to explore their possibilities in ways that have not yet been possible.”
The study, “Mechanically interlocked two-dimensional polymers,” was primarily supported by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (contract number HR00112320041) and Northwestern’s IIN (Ryan Fellows Program).
END