(Press-News.org) New INFORMS Information Systems Research Study Key Takeaways:
The AI model achieves approximately 90% classification precision in predicting ICU length of stay, enabling hospitals to more effectively optimize resource management.
Clear, evidence-based explanations provided by the model empower ICU doctors to make better-informed decisions regarding patient care.
Real-world testing with ICU clinicians demonstrated the model’s potential to enhance care efficiency, reduce hospital costs and improve patient outcomes.
BALTIMORE, MD, January 16, 2025 – Intensive care units (ICUs) face mounting pressure to effectively manage resources while delivering optimal patient care. Groundbreaking research published in the INFORMS journal Information Systems Research highlights how a novel artificial intelligence (AI) model is revolutionizing ICU care by not only improving predictions of patient length of stay, but also equipping clinicians with clear, evidence-based insights to guide critical decisions.
“This model represents a major breakthrough in ICU care,” says Tianjian Guo, one of the study authors and a professor at the University of Texas at Austin. “By not only predicting ICU stays more accurately, but providing clear explanations based on real medical data, we’re giving clinicians the tools to make more informed, confident decisions about patient care.”
The AI model analyzes the complex relationships between various medical factors, such as patient age, medical history and current health conditions, to predict ICU length of stay.
Unlike traditional predictive models, this innovative system stands out for its explainable AI component, which offers healthcare providers clear, actionable insights into the factors driving its predictions. By ensuring transparency and fostering trust the model empowers clinicians to make more confident and informed decisions in high-stakes ICU environments.
“This explainable AI-driven approach has the potential to reduce ICU overcrowding, decrease the chances of readmission and ultimately cut down on hospital costs,” says Indranil Bardhan, study co-author and professor at the University of Texas at Austin. “By improving predictions and offering clear, evidence-based explanations of length of stay in the ICU, the model could make it easier for doctors to prioritize care and allocate resources more effectively, ensuring patients receive the best care possible during their ICU stay.”
The team behind the study, “An Explainable Artificial Intelligence Approach Using Graph Learning to Predict Intensive Care Unit Length of Stay,” is hopeful that hospitals around the world will begin adopting this new AI technology to enhance decision-making, increase efficiency and improve overall patient outcomes.
“As AI continues to transform healthcare, this approach represents an important step toward bridging the gap between advanced technology and the practical needs of medical professionals,” concluded Guo.
Link to full study.
About INFORMS and Information Systems Research
INFORMS is the world’s largest association for professionals and students in operations research, AI, analytics, data science and related disciplines, serving as a global authority in advancing cutting-edge practices and fostering an interdisciplinary community of innovation. Information Systems Research, an INFORMS journal, focuses on the utilization of information technology to enhance organizational efficiency. INFORMS helps its members advance research and practice through cutting-edge journals, conferences and resources. Learn more at www.informs.org or @informs.
###
Contact:
Ashley Smith
443-757-3578
asmith@informs.org
Subscribe and stay up to date on the latest from INFORMS.
Sign Up For Email Updates
END
Continental European snakes, geckos and Italian wall lizards are making their way to northern Europe undetected among imports of ornamental olive trees destined for gardens and green spaces.
These hitchhiking intruders can become invasive pests that cause extensive damage to the natural environment - as has happened in previously snake-free islands of the Mediterranean like Majorca.
They’re also a red flag for a bigger problem: the range of potentially serious agricultural and environmental pests being unwittingly imported to Britain and ...
Desert lizards are facing a ‘cost-of-living’ squeeze as global temperatures continue to rise, a new study finds.
For a lizard, the 'cost-of-living' is tightly linked to its body temperature, which dictates both how much food it needs and whether it can go outside to feed. Desert lizards are especially challenged because food is sparse, and it is often too hot to forage.
Published today in Science, the study found climate warming can ‘squeeze’ desert lizard energy budgets by increasing the food they need just ...
Stem Cell Reports, the peer-reviewed, open access, online journal of the International Society for Stem Cell Research (ISSCR) is seeking highly motivated and accomplished early career scientists to join the Early Career Scientist Editorial Board (ECEB). This group of distinguished early career scientists will have the opportunity to:
Advise on journal content and programming such as special Issues, podcast content, and other initiatives,
Receive mentoring from associate editors,
Attend the annual editorial board meeting
Build their professional network and connections, and
Serve as an ambassador ...
Our data-driven world demands more—more capacity, more efficiency, more computing power. To meet society’s insatiable need for electronic speed, physicists have been pushing the burgeoning field of spintronics.
Traditional electronics use the charge of electrons to encode, store and transmit information. Spintronic devices utilize both the charge and spin-orientation of electrons. By assigning a value to electron spin (up=0 and down=1), spintronic devices offer ultra-fast, energy-efficient platforms.
To develop viable spintronics, physicists must understand the quantum properties ...
The kids and grandkids of immigrants to the United States usually lose the ability to speak their heritage language fluently. Without access to the heritage language, second- and third-generation Americans may use distinct words and pronunciations in the dominant language, English, to assert their ethnic identities and connect to their communities.
Sociolinguists have long viewed these shifts as markers of cultural change. Like differences in food, clothing and religion, differences in language are subtle ways that groups distinguish themselves along ethnic boundaries. Recent work has pivoted from asking what are the differences to why are there differences? How are they using language to carve ...
Tufts Unvisity Assistant Professor Elizabeth Setren in the Department of Economics at the School of Arts and Sciences has received a Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers (PECASE) from President Joe Biden. PECASE recognition is the highest honor given by the U.S. government for outstanding scientists and engineers who are early in their careers
This year’s awardees are employed or funded by 14 governmental agencies. In Setren’s case, her recognition comes from the Department of Education’s Institute of Education Sciences, and ...
The proportion of babies dying before and during labor after 41 weeks of gestation has fallen by 47% in Sweden in a relatively short time. This is the result of a major national study. The reduction has occurred since the procedures around induction have changed.
A pregnancy normally lasts around 40 weeks. However, a fairly high proportion of women, 22%, pass their due date and are pregnant for 41 weeks or longer. Although Sweden generally has a very low risk of stillbirth and death within the first month of life, the risk increases the longer the pregnancy continues ...
Being lightweight is essential for space structures, particularly for tools used on already small, lightweight satellites. The ability to perform multiple functions is a bonus. To address these characteristics in a new way, researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign successfully integrated flexible electronics with a three-ply, self-deployable boom that weighs only about 20 grams.
“It's difficult to get commercial electronics integrated into these super thin structures,” said Xin Ning, an aerospace professor in The Grainger College of Engineering at U. of ...
A group of immune proteins called the inflammasome can help prevent blood stem cells from becoming malignant by removing certain receptors from their surfaces and blocking cancer gene activity, according to a preclinical study by Weill Cornell Medicine investigators.
The study, published Jan. 2 in Nature Immunology, may lead to therapies that target the earliest stages of cancer. The findings bolster the idea that the inflammasome has a dual role—it promotes inflammation associated with poor outcomes in late cancer stages, but early on, it can help prevent cells from becoming cancerous in the first ...
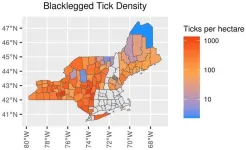
Across most of the Northeast, getting bitten by a blacklegged tick— also called a deer tick — is a risk during spring, summer, and fall. A new Dartmouth study, published in Parasites and Vectors, finds that 50% of adult blacklegged ticks carry the bacteria that causes Lyme disease while 20% to 25% of the younger (nymph) blacklegged ticks carry the bacteria.
A team of researchers from universities, health departments, and agricultural agencies from across the Northeast conducted a meta-analysis of data on how many blacklegged ticks there are and how many of them have the potential to pass pathogens ...