(Press-News.org) WHAT:
With support from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Office of the Assistant Secretary for Health (OASH), the National Institutes of Health (NIH) is leading the implementation of the Dr. Emmanuel Bilirakis and Honorable Jennifer Wexton National Plan to End Parkinson’s Act (P.L. 118-66), which was signed into law on July 2, 2024. This follows a delegation of authority from the Secretary of the Department of Health and Human Services to the NIH Director.
The act establishes a Federal Advisory Council on Parkinson’s Research, Care, and Services and calls for the creation and regular updating of a national plan to prevent, diagnose, treat, and cure Parkinson’s, ameliorate symptoms, and slow or stop progression. In addition to Parkinson’s disease, the national plan will also target other neurodegenerative Parkinsonisms, including multiple system atrophy, corticobasal degeneration, progressive supranuclear palsy, and Parkinson’s-related dementia.
The goals of the act are to coordinate Parkinson’s-related research and services across federal agencies; speed the development of safe and effective treatments; improve early diagnosis; facilitate coordination of care and treatment; reduce the impact of Parkinson’s on the physical, mental, and social health of individuals living with Parkinson’s and their caregivers and families; and increase international coordination.
In anticipation of implementing this act, NIH is seeking nominations for individuals to serve on the Federal Advisory Council on Parkinson’s Research, Care, and Services that will provide advice on Parkinson’s-related issues, including recommendations for priority actions to be included in the national plan. The council will include two patient advocates, including one individual who is living with young-onset PD; a family caregiver; a healthcare provider; two biomedical researchers with Parkinson’s related expertise; a movement disorders specialist who treats people with Parkinson’s; a dementia specialist who treats people with Parkinson’s; and two representatives from Parkinson’s-related nonprofit organizations. Additionally, the council will have representatives from 13 federal agencies that are involved in Parkinson’s research, clinical care, or care services. The council will be co-chaired by the director of the NIH’s National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke and the associate deputy director for the Office of Science and Medicine for HHS’ OASH.
More information about the act as well as the nomination process can be found here.
WHO:
Walter Koroshetz, M.D., director, NINDS, is available for comment. To arrange an interview, please contact NINDSPressTeam@ninds.nih.gov
###
About the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS): NINDS is the nation’s leading funder of research on the brain and nervous system. The mission of NINDS is to seek fundamental knowledge about the brain and nervous system and to use that knowledge to reduce the burden of neurological disease.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases.
END
NIH to lead implementation of National Plan to End Parkinson’s Act
Open call for participants to serve on Parkinson’s Advisory Council
2025-01-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Growth of private equity and hospital consolidation in primary care and price implications
2025-01-17
About The Study: In this cross-sectional study, nearly one-half of all primary care physicians (PCPs) were affiliated with hospitals, while private equity-affiliated PCPs were growing and concentrated in certain regional markets. Relative to PCPs in independent settings, hospital-affiliated PCPs and private equity-affiliated PCPs had higher prices for the same services.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Yashaswini Singh, PhD, MPA, email yashaswini_singh@brown.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2024.4935)
Editor’s ...
Online advertising of compounded glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists
2025-01-17
About The Study: This cross-sectional study showed websites that sell compounded glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) often partially informed and sometimes misinformed potential consumers. Compounded medications contain the same active ingredients as in branded medications but may contain different inactive ingredients. Most websites did not disclose that compounded GLP-1 RAs were not FDA approved, although some suggested these drugs were FDA approved. Many websites provided limited safety information and unauthorized efficacy claims. Some ...
Health care utilization and costs for older adults aging into Medicare after the affordable care act
2025-01-17
About The Study: This study found modest evidence of reductions in out-of-pocket costs and improvements in health among adults entering Medicare after the Affordable Care Act. Insurance coverage and financial assistance should be preserved and enhanced to improve health and health care access among vulnerable older adults.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Renuka Tipirneni, MD, MSc, email rtipirne@med.umich.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2024.5025)
Editor’s ...
Reading the genome and understanding evolution: Symbioses and gene transfer in leaf beetles
2025-01-17
With more than 50,000 described species, the leaf beetle family is distributed worldwide and represents about a quarter of the species diversity of all herbivores. Leaf beetles can be found to feed on almost all plant groups. They live in the rhizosphere, the canopy and even underwater. Many leaf beetles, such as the Colorado potato beetle, are notorious pests. Their species richness and global distribution highlight their evolutionary success, which is particularly astonishing given that leaves are a difficult food source to digest and provide unbalanced nutrients.
Researchers from the Department of Insect Symbiosis at the Max Planck Institute for Chemical ...
Brains of people with sickle cell disease appear older
2025-01-17
Individuals with sickle cell disease – a chronic illness where misshapen, sticky blood cells clump together, reducing oxygen delivery to organs – are at a higher risk for stroke and resulting cognitive disability. But even in the absence of stroke, many such patients struggle with remembering, focusing, learning and problem solving, among other cognitive problems, with many facing challenges in school and in the workplace.
Now a multidisciplinary team of researchers and physicians at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis has published a study that helps explain how the illness might affect cognitive performance ...
Elena Belova and Yevgeny Raitses recognized for groundbreaking plasma physics research
2025-01-17
The diversity of plasma research at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) was readily apparent when the PPPL 2024 Distinguished Research Fellows were recently announced. Elena Belova and Yevgeny Raitses were awarded the honor at the Lab’s annual State of the Laboratory event. Belova, a theoretical physicist, won for her work developing highly complex simulations of plasmas in different fusion experiments. Raitses, a managing principal research physicist, was honored for his experimental work on ...
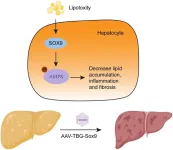
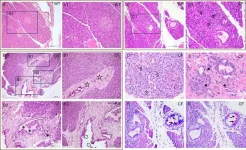
SOX9 overexpression ameliorates metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis through activation of the AMPK pathway
2025-01-17
Background and Aims
The transcription factor sex-determining region Y-related high-mobility group-box gene 9 (SOX9) plays a critical role in organ development. Although SOX9 has been implicated in regulating lipid metabolism in vitro, its specific role in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) remains poorly understood. This study aimed to investigate the role of SOX9 in MASH pathogenesis and explored the underlying mechanisms.
Methods
MASH models were established using mice fed either a methionine- and choline-deficient (MCD) diet or a high-fat, high-fructose diet. To evaluate the effects of SOX9, hepatocyte-specific SOX9 deletion or overexpression was performed. ...
Florescent probes illuminate cholesterol and Alzheimer’s research
2025-01-17
The search for answers to Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders remains one of the most pressing goals in brain research. Maciej J. Stawikowski, Ph.D., an assistant professor of chemistry and biochemistry at Florida Atlantic University’s Charles E. Schmidt College of Science, believes the key may lie in understanding how cholesterol and other lipids move through cells and affect their communication.
“It’s well known that lipids and Alzheimer’s are linked,” said Stawikowski, a member of the FAU Stiles-Nicholson Brain Institute. “Lipid imbalance may ...
Qigong significantly decreases chronic low back pain in US military veterans
2025-01-17
Chronic pain is widespread in the United States, particularly among military veterans, affecting between 40 to 70% of this population and serving as a leading cause of disability. Veterans experience chronic pain more often than civilians, with back pain being the most common. Up to 75% of older veterans report chronic pain, while younger veterans and those from recent conflicts face more severe pain.
Chronic low back pain in veterans affects not only physical health but also social and occupational functioning, often leading to job ...
New insights into pancreatic disease and diabetes
2025-01-17
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a life-threatening genetic disease affecting multiple organ systems, with pancreatic dysfunction representing a critical and often overlooked complication. A groundbreaking study published in eGastroenterology introduces young rabbits with CF as a novel and accessible model to study CF-related pancreatic endocrine pathology. This model offers an unprecedented opportunity to deepen our understanding of CF-related diabetes (CFRD), a condition affecting up to 50% of adults with CF.
CF is caused by mutations in the CF transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
[Press-News.org] NIH to lead implementation of National Plan to End Parkinson’s ActOpen call for participants to serve on Parkinson’s Advisory Council