(Press-News.org) Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a life-threatening genetic disease affecting multiple organ systems, with pancreatic dysfunction representing a critical and often overlooked complication. A groundbreaking study published in eGastroenterology introduces young rabbits with CF as a novel and accessible model to study CF-related pancreatic endocrine pathology. This model offers an unprecedented opportunity to deepen our understanding of CF-related diabetes (CFRD), a condition affecting up to 50% of adults with CF.
CF is caused by mutations in the CF transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene, resulting in abnormal chloride and sodium transport across epithelial cells. While advancements like Trikafta® have significantly improved pulmonary outcomes, pancreatic complications—especially endocrine dysfunction—continue to challenge patients’ quality of life. The present study, led by Dr. Jie Xu and colleagues, explores the spontaneous development of pancreatic lesions and glucose metabolism abnormalities in CF rabbits, offering new insights into the disease’s pathophysiology.
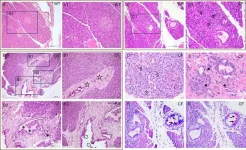
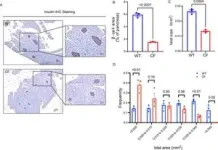
The team developed their CF rabbit model using CRISPR/Cas9 gene-editing technology. Rabbits with CF exhibited hallmark pancreatic changes, including fibrosis, vacuolar degeneration, and metaplasia of mucus-secreting epithelial cells. The size of insulin-producing pancreatic islets in these animals was significantly smaller than in wild-type controls, correlating with lower circulating insulin levels and compromised glucose metabolism.
“Our findings suggest that rabbits with CF replicate key aspects of CF pancreatic disease,” said Dr. Xu, corresponding author and a researcher at the University of Michigan Medical School. “This positions them as a valuable model for translational research on CFRD and related conditions.”
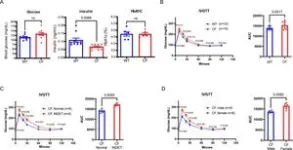
One of the study’s key outcomes was identifying an indeterminate glucose tolerance (INDET) stage in young CF rabbits, a precursor to CFRD observed in human patients. This stage featured delayed glucose clearance and reduced insulin secretion, paralleling early signs of diabetes progression in humans. Interestingly, female CF rabbits were more prone to INDET-like phenotypes, mirroring sex-based differences observed in human CFRD prevalence.
The implications of this work extend far beyond basic research. Rabbits with CF provide an alternative to existing large-animal models, such as pigs and ferrets, which are expensive and/or require specialized care. In contrast, rabbits are cost-effective, easier to handle, and widely used in laboratory settings, making them accessible to a broader range of researchers.
“As the CF community shifts its focus to age-related and metabolic complications, our rabbit model becomes increasingly relevant,” Dr. Xu explained. “With improved life expectancy due to CFTR modulators, understanding and mitigating CFRD will be critical for enhancing patients’ quality of life.”
The study also highlights the broader significance of CF-related pancreatic pathology. While exocrine dysfunction and pancreatic insufficiency are well-documented in CF, endocrine dysfunction—manifested as CFRD—presents unique challenges. CFRD combines features of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes, with insulin deficiency and resistance contributing to its progression. Current treatments focus primarily on symptom management, underscoring the urgent need for innovative therapeutic strategies.
By establishing rabbits as a viable model for CFRD research, the authors aim to facilitate the development of targeted interventions. Early-stage therapies, such as those addressing the INDET phase, could significantly delay or prevent the onset of full-blown diabetes in CF patients. Furthermore, this model allows for evaluating emerging treatments, including those designed to modulate pancreatic inflammation, fibrosis, and insulin production.
The study’s funding by the National Institutes of Health (grant DK134361) underscores its importance in addressing critical gaps in CF research. Future directions include exploring the long-term progression of pancreatic disease in CF rabbits and evaluating the impact of CFTR modulators like Trikafta® on endocrine outcomes.
In conclusion, this work represents a significant step forward in CF research. By leveraging the CF rabbit model's unique advantages, scientists can better understand the complex interplay between CFTR dysfunction and pancreatic disease. This knowledge promises to improve outcomes for thousands of patients living with CF and its complications.
See the article:
Liang X, Hou X, Chen YE, et al. Endocrine pathology in young rabbits with cystic fibrosis. eGastroenterology 2024;2:e100102. doi:10.1136/egastro-2024-100102
About eGastroenterology
eGastroenterology is a new, open-access, and open peer-reviewed BMJ Journal, which focuses on basic, clinical, translational, and evidence-based medicine research in all areas of gastroenterology (including hepatology, pancreatology, esophagology, and gastrointestinal surgery). eGastroenterology is now indexed by PubMed Central, Scopus, DOAJ, Dimensions, OpenAlex, ROAD, and COPE, with more to come!
For more information, please visit: egastroenterology.bmj.com and follow us on Twitter (@eGastro_BMJ).
Sign-up to Email Alerts for eGastroenterology: https://emails.bmj.com/k/Bmj/jausu/egastroenterology
END
Background and Aims
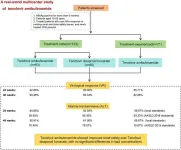
Chronic hepatitis B (CHB) remains a significant global health challenge, and effective antiviral therapies are essential for long-term management. This study aimed to evaluate the real-world effectiveness and safety of tenofovir amibufenamide (TMF) in a cohort of patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB).
Methods
In this multicenter, prospective, real-world cohort study, 194 CHB patients were recruited from four hospitals between August 2021 and August 2022. Patients were divided into treatment-naïve (TN, n = 123) and ...
Despite the success cardiac rehabilitation has shown at reducing heart-related deaths and hospital readmissions, higher out-of-pocket costs may prevent patients from participating in the program, a Michigan Medicine study suggests.
In a national study of over 40,000 people with Medicare and commercial insurance, 81.6% of patients did not have to pay for their initial cardiac rehabilitation session.
The medically supervised program lasts up to 36 sessions, which are often recommended for patients recovering from many conditions and procedures.
Among ...
European consortium for Solving the Unsolved Rare Diseases demonstrates the significance of international collaboration to address the unmet medical needs on rare diseases’ diagnosis
More than 500 European patients with unknown conditions have received a diagnosis through new genetic research. This includes patients with rare neurological disorders, severe intellectual disabilities, muscle diseases, and hereditary gastrointestinal cancer. These diagnoses were achieved through extensive European collaboration, led by researchers from the University of Tübingen, Radboud university medical center, and the National Center ...
Subtle changes in the brain, detectable through advanced imaging, blood and spinal fluid analysis, happen approximately twenty years before a clinical motor diagnosis in people with Huntington’s disease, finds a new study led by UCL researchers.
The research, published in Nature Medicine, was in collaboration with experts at the Universities of Glasgow, Gothenburg, Iowa, and Cambridge.
The team found that although functions such as movement, thinking or behaviour remained normal for a long time before the onset of symptoms in Huntington’s disease, subtle changes to the brain were taking place up to two decades earlier.
These findings pave the way for ...
Active galactic nuclei are supermassive black holes at the center of certain galaxies. As matter falls into these black holes, enormous amounts of energy are released, making active galactic nuclei, or AGN, one of the most energetic phenomena that can be observed in space. University of Arizona astronomers have now produced the highest resolution direct images ever taken of an AGN in the infrared, using the Large Binocular Telescope Interferometer.
Researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy in Germany were also involved in the study. The findings are published in the journal Nature Astronomy.
"The ...
Astrophysicists led by a team from Trinity College Dublin have – for the first time – imaged a large number of exocomet belts around nearby stars, and the tiny pebbles within them. The crystal-clear images show light being emitted from these millimetre-sized pebbles within the belts that orbit 74 nearby stars of a wide variety of ages – from those that are just emerging from birth to those in more mature systems like our own Solar System.
The REASONS (REsolved ALMA and SMA Observations of Nearby Stars) study ...
We have all been told to avoid direct sunlight between 12 noon and 3 p.m., seek out shade and put on sunscreen and a hat. Nevertheless, most of us have been experienced sunburn at least once. The skin turns bright red, feels irritated and needs cooling.
You may also have been told that sunburn damages the DNA. But that is not the full truth, the researchers responsible for a new study conducted at the University of Copenhagen and Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) explain.
“Sunburn damages the DNA, leading to cell death and inflammation. So the textbooks say. But in ...
UNDER STRICT EMBARGO UNTIL 5:00AM (UK TIME) ON FRIDAY 17TH JANUARY 2025
People who speak with accents perceived as ‘working-class’ including those from Liverpool, Newcastle, Bradford and London risk being stereotyped as more likely to have committed a crime, and becoming victims of injustice, a new study suggests.
Received pronunciation (RP) accent perceived as highest status and less likely to commit crimes with the exception of a sexual offence.
Liverpool’s accent most closely associated with criminal behaviour in general.
Welsh, Northern Irish and Scottish accents perceived more positively ...
The way you talk says a lot about you — but what people think it says may not be true. While no accent is better than any other, people use accents as markers for identifying and stereotyping social groups. In the justice system, these accent stereotypes could influence perceptions of guilt, leading to discrimination. Scientists collaborating on the Improving Voice Identification Procedures project explored this by testing participants’ perceptions of ten different accents heard around the UK. They found that speakers with accents considered lower-status were considered more ...
Perhaps you’ve heard the story of Peter Parker, raised by his aunt and uncle after the death of his parents only to see his uncle murdered by the same criminal the radioactive spider-bitten teen neglected to apprehend that very day. His guilt drives him to become Spider-Man.
But childhood trauma doesn’t always inspire super-heroics. Heath Ledger’s psychotic Joker, as seen in 2008 film The Dark Knight, recounts tales of horrific abuse by a father who disfigures him. It’s a stark contrast to his heroic nemesis Batman, who saw his parents gunned down in ...