Effectiveness and safety of tenofovir amibufenamide in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: A real-world, multicenter study
2025-01-17
(Press-News.org) Background and Aims
Chronic hepatitis B (CHB) remains a significant global health challenge, and effective antiviral therapies are essential for long-term management. This study aimed to evaluate the real-world effectiveness and safety of tenofovir amibufenamide (TMF) in a cohort of patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB).
Methods
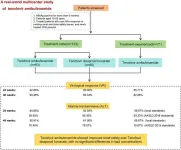
In this multicenter, prospective, real-world cohort study, 194 CHB patients were recruited from four hospitals between August 2021 and August 2022. Patients were divided into treatment-naïve (TN, n = 123) and treatment-experienced (TE, n = 71) groups. The TN group was further subdivided into TMF (n = 63) and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF, n = 60) subgroups. In the TE group, patients transitioned from prior antiviral therapies (entecavir or TDF) to TMF after meeting criteria for poor virological response or safety concerns. Treatment response was evaluated in terms of virological effectiveness and alanine transaminase normalization rates. Virological response (VR), ALT normalization rates, renal function markers, and lipid profiles were monitored.
Results
In the TN cohort, VR rates at 24 and 48 weeks were 42.86% and 90.48% for TMF, and 60.00% and 83.33% for TDF. ALT normalization rates at 24 and 48 weeks for TMF were 56.82% and 70.45% (according to AASLD 2018 standards). In the TE group, VR rates at 24 and 48 weeks were 83.1% and 91.55%, respectively. ALT normalization rates were 86.67% and 93.33% (local standards), and 66.67% and 76.67% (AASLD 2018 standards) (z = −2.822, P = 0.005). Additionally, TMF showed improved renal safety over TDF, with no significant differences in lipid concentrations.
Conclusions
TMF is comparable to TDF in terms of CHB treatment effectiveness, with better renal safety and no impact on lipid levels. In TE patients, transitioning to TMF therapy does not affect antiviral treatment outcomes.
Full text
https://www.xiahepublishing.com/2310-8819/JCTH-2024-00364
The study was recently published in the Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology.
The Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology (JCTH) is owned by the Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University and published by XIA & HE Publishing Inc. JCTH publishes high quality, peer reviewed studies in the translational and clinical human health sciences of liver diseases. JCTH has established high standards for publication of original research, which are characterized by a study’s novelty, quality, and ethical conduct in the scientific process as well as in the communication of the research findings. Each issue includes articles by leading authorities on topics in hepatology that are germane to the most current challenges in the field. Special features include reports on the latest advances in drug development and technology that are relevant to liver diseases. Regular features of JCTH also include editorials, correspondences and invited commentaries on rapidly progressing areas in hepatology. All articles published by JCTH, both solicited and unsolicited, must pass our rigorous peer review process.
Follow us on X: @xiahepublishing
Follow us on LinkedIn: Xia & He Publishing Inc.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-01-17
Despite the success cardiac rehabilitation has shown at reducing heart-related deaths and hospital readmissions, higher out-of-pocket costs may prevent patients from participating in the program, a Michigan Medicine study suggests.
In a national study of over 40,000 people with Medicare and commercial insurance, 81.6% of patients did not have to pay for their initial cardiac rehabilitation session.
The medically supervised program lasts up to 36 sessions, which are often recommended for patients recovering from many conditions and procedures.
Among ...
2025-01-17
European consortium for Solving the Unsolved Rare Diseases demonstrates the significance of international collaboration to address the unmet medical needs on rare diseases’ diagnosis
More than 500 European patients with unknown conditions have received a diagnosis through new genetic research. This includes patients with rare neurological disorders, severe intellectual disabilities, muscle diseases, and hereditary gastrointestinal cancer. These diagnoses were achieved through extensive European collaboration, led by researchers from the University of Tübingen, Radboud university medical center, and the National Center ...
2025-01-17
Subtle changes in the brain, detectable through advanced imaging, blood and spinal fluid analysis, happen approximately twenty years before a clinical motor diagnosis in people with Huntington’s disease, finds a new study led by UCL researchers.
The research, published in Nature Medicine, was in collaboration with experts at the Universities of Glasgow, Gothenburg, Iowa, and Cambridge.
The team found that although functions such as movement, thinking or behaviour remained normal for a long time before the onset of symptoms in Huntington’s disease, subtle changes to the brain were taking place up to two decades earlier.
These findings pave the way for ...
2025-01-17
Active galactic nuclei are supermassive black holes at the center of certain galaxies. As matter falls into these black holes, enormous amounts of energy are released, making active galactic nuclei, or AGN, one of the most energetic phenomena that can be observed in space. University of Arizona astronomers have now produced the highest resolution direct images ever taken of an AGN in the infrared, using the Large Binocular Telescope Interferometer.
Researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy in Germany were also involved in the study. The findings are published in the journal Nature Astronomy.
"The ...
2025-01-17
Astrophysicists led by a team from Trinity College Dublin have – for the first time – imaged a large number of exocomet belts around nearby stars, and the tiny pebbles within them. The crystal-clear images show light being emitted from these millimetre-sized pebbles within the belts that orbit 74 nearby stars of a wide variety of ages – from those that are just emerging from birth to those in more mature systems like our own Solar System.
The REASONS (REsolved ALMA and SMA Observations of Nearby Stars) study ...
2025-01-17
We have all been told to avoid direct sunlight between 12 noon and 3 p.m., seek out shade and put on sunscreen and a hat. Nevertheless, most of us have been experienced sunburn at least once. The skin turns bright red, feels irritated and needs cooling.
You may also have been told that sunburn damages the DNA. But that is not the full truth, the researchers responsible for a new study conducted at the University of Copenhagen and Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) explain.
“Sunburn damages the DNA, leading to cell death and inflammation. So the textbooks say. But in ...
2025-01-17
UNDER STRICT EMBARGO UNTIL 5:00AM (UK TIME) ON FRIDAY 17TH JANUARY 2025
People who speak with accents perceived as ‘working-class’ including those from Liverpool, Newcastle, Bradford and London risk being stereotyped as more likely to have committed a crime, and becoming victims of injustice, a new study suggests.
Received pronunciation (RP) accent perceived as highest status and less likely to commit crimes with the exception of a sexual offence.
Liverpool’s accent most closely associated with criminal behaviour in general.
Welsh, Northern Irish and Scottish accents perceived more positively ...
2025-01-17
The way you talk says a lot about you — but what people think it says may not be true. While no accent is better than any other, people use accents as markers for identifying and stereotyping social groups. In the justice system, these accent stereotypes could influence perceptions of guilt, leading to discrimination. Scientists collaborating on the Improving Voice Identification Procedures project explored this by testing participants’ perceptions of ten different accents heard around the UK. They found that speakers with accents considered lower-status were considered more ...
2025-01-17
Perhaps you’ve heard the story of Peter Parker, raised by his aunt and uncle after the death of his parents only to see his uncle murdered by the same criminal the radioactive spider-bitten teen neglected to apprehend that very day. His guilt drives him to become Spider-Man.
But childhood trauma doesn’t always inspire super-heroics. Heath Ledger’s psychotic Joker, as seen in 2008 film The Dark Knight, recounts tales of horrific abuse by a father who disfigures him. It’s a stark contrast to his heroic nemesis Batman, who saw his parents gunned down in ...
2025-01-17
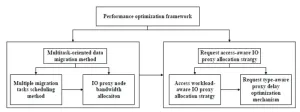
For the high-performance computing in a WAN environment, the geographical locations of national supercomputing centers are scattered and the network topology is complex, so it is difficult to form a unified view of resources. To aggregate the widely dispersed storage resources of national supercomputing centers in China, the team led by Zhisheng Huo have previously proposed a global virtual data space named GVDS. However, the GVDS suffers from performance bottlenecks in data migration and access across WANs.
To solve the problems, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Effectiveness and safety of tenofovir amibufenamide in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: A real-world, multicenter study