Astrophysicists reveal structure of 74 exocomet belts orbiting nearby stars in landmark survey
2025-01-17
(Press-News.org)
Astrophysicists led by a team from Trinity College Dublin have – for the first time – imaged a large number of exocomet belts around nearby stars, and the tiny pebbles within them. The crystal-clear images show light being emitted from these millimetre-sized pebbles within the belts that orbit 74 nearby stars of a wide variety of ages – from those that are just emerging from birth to those in more mature systems like our own Solar System.
The REASONS (REsolved ALMA and SMA Observations of Nearby Stars) study marks such a significant milestone in the study of exocometary belts because its images and analyses reveal where the pebbles, and hence the exocomets, are located. They are typically tens to hundreds of au (the distance from Earth to the Sun) from their central star.
In these regions, it is so cold (-250 to -150 degrees Celsius) that most compounds including water are frozen as ice on these exocomets. What the astrophysicists are therefore observing is where the ice reservoirs of planetary systems are located. REASONS is the first program to unveil the structure of these belts for a large sample of 74 exoplanetary systems.
The Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) is an array of 66 radio telescopes in the Atacama Desert of northern Chile, while the Submillimeter Array (SMA) is a similar eight-element array in Hawaii. Both observe electromagnetic radiation at millimetre and submillimetre wavelengths. This study used both to produce the images that have provided more information on populations of exocomets than ever before.
“Exocomets are boulders of rock and ice, at least 1 km in size, which smash together within these belts to produce the pebbles that we observe here with the ALMA and SMA arrays of telescopes. Exocometary belts are found in at least 20% of planetary systems, including our own Solar System,” said Luca Matrà, Associate Professor in Trinity’s School of Physics, and senior author of the research article that has just been published in leading international journal Astronomy and Astrophysics.
Dr Sebastián Marino, Royal Society University Research Fellow at the University of Exeter, and coauthor in this study, added: “The images reveal a remarkable diversity in the structure of belts. Some are narrow rings, as in the canonical picture of a ‘belt’ like our Solar System’s Edgeworth-Kuiper belt. But a larger number of them are wide, and probably better described as ‘disks’ rather than rings.”
Some systems have multiple rings/disks, some of which are eccentric, which provides evidence that yet undetectable planets are present and their gravity affects the distribution of pebbles in these systems.
“The power of a large study like REASONS is in revealing population-wide properties and trends,” explained Prof. Matrà.
“For example, it confirmed that the number of pebbles decreases for older planetary systems as belts run out of larger exocomets smashing together, but showed for the first time that this decrease in pebbles is faster if the belt is closer to the central star. It also indirectly showed – through the belts' vertical thickness – that unobservable objects as large as 140 km to Moon-size are likely present in these belts.
Dr David Wilner, Senior Astrophysicist at the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian, underlined:“Arrays like the ALMA and SMA used in this work are extraordinary tools that are continuing to give us incredible new insights into the universe and its workings. The REASONS survey required a large community effort and has an incredible legacy value, with multiple potential pathways for future investigation.
“For example, the REASONS dataset of belt and planetary system properties will enable studies of the birth and evolution of these belts, as well as follow-up observations across the wavelength range, from JWST to the next generation of Extremely Large Telescopes and ALMA’s upcoming ARKS Large Program to zoom even further onto the details of these belts.”
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:


ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-01-17
We have all been told to avoid direct sunlight between 12 noon and 3 p.m., seek out shade and put on sunscreen and a hat. Nevertheless, most of us have been experienced sunburn at least once. The skin turns bright red, feels irritated and needs cooling.
You may also have been told that sunburn damages the DNA. But that is not the full truth, the researchers responsible for a new study conducted at the University of Copenhagen and Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) explain.
“Sunburn damages the DNA, leading to cell death and inflammation. So the textbooks say. But in ...
2025-01-17
UNDER STRICT EMBARGO UNTIL 5:00AM (UK TIME) ON FRIDAY 17TH JANUARY 2025
People who speak with accents perceived as ‘working-class’ including those from Liverpool, Newcastle, Bradford and London risk being stereotyped as more likely to have committed a crime, and becoming victims of injustice, a new study suggests.
Received pronunciation (RP) accent perceived as highest status and less likely to commit crimes with the exception of a sexual offence.
Liverpool’s accent most closely associated with criminal behaviour in general.
Welsh, Northern Irish and Scottish accents perceived more positively ...
2025-01-17
The way you talk says a lot about you — but what people think it says may not be true. While no accent is better than any other, people use accents as markers for identifying and stereotyping social groups. In the justice system, these accent stereotypes could influence perceptions of guilt, leading to discrimination. Scientists collaborating on the Improving Voice Identification Procedures project explored this by testing participants’ perceptions of ten different accents heard around the UK. They found that speakers with accents considered lower-status were considered more ...
2025-01-17
Perhaps you’ve heard the story of Peter Parker, raised by his aunt and uncle after the death of his parents only to see his uncle murdered by the same criminal the radioactive spider-bitten teen neglected to apprehend that very day. His guilt drives him to become Spider-Man.
But childhood trauma doesn’t always inspire super-heroics. Heath Ledger’s psychotic Joker, as seen in 2008 film The Dark Knight, recounts tales of horrific abuse by a father who disfigures him. It’s a stark contrast to his heroic nemesis Batman, who saw his parents gunned down in ...
2025-01-17
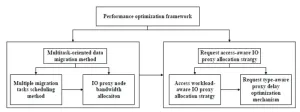
For the high-performance computing in a WAN environment, the geographical locations of national supercomputing centers are scattered and the network topology is complex, so it is difficult to form a unified view of resources. To aggregate the widely dispersed storage resources of national supercomputing centers in China, the team led by Zhisheng Huo have previously proposed a global virtual data space named GVDS. However, the GVDS suffers from performance bottlenecks in data migration and access across WANs.
To solve the problems, ...
2025-01-17
Excessive sugar consumption is linked to several non-communicable diseases, including obesity, cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome, and type 2 diabetes. Animals naturally crave sugar, and uncontrolled sugar preferences can lead to high sugar intake, raising the risk of hyperglycemia and metabolic diseases.
Previous research suggests that food cravings in humans are driven by signals from the gut to the brain, highlighting the gut's crucial role in shaping dietary preferences. However, the regulation of sugar preference is complex, and the specific influence of gut microbes remains unclear.
In a study published in Nature Microbiology, ...
2025-01-17
Megakaryocytes (MKs), known for their role in platelet production, have emerged as critical players in immune responses, showcasing versatility in both physiological and pathological contexts. Recent advances in technology have unveiled the diverse immune functions of MKs, which express immune sensors and participate in immune activities, thus expanding their traditional role beyond hemostasis and coagulation. This comprehensive review delves into the multifaceted immune roles of MKs, highlighting their distinct immunological roles under ...
2025-01-17
A new Cochrane review has found that calorie labelling of food on menus and products leads people to choose slightly fewer calories.
The research team, led by scientists from UCL, Bath Spa University, the University of Cambridge and the University of Oxford, examined evidence from 25 studies on the impact of calorie labelling on food selection and consumption. They found that calorie labels in supermarkets, restaurants and other food outlets led to a small reduction in the calories people selected and purchased. The average reduction was 1.8%, which would equate ...
2025-01-17
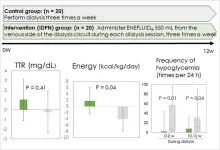
Niigata and Tokyo, Japan - In recent years, advancements in dialysis therapy and the growing number of elderly patients starting dialysis have contributed to the aging of the overall dialysis population. Consequently, malnutrition-related conditions such as sarcopenia, frailty, and protein energy wasting (PEW) have become significant issues for dialysis patients. Nutritional interventions, including nutritional counseling, oral supplements, and intradialytic parenteral nutrition (IDPN), are recommended to address these challenges. On dialysis days, patients tend to consume less ...
2025-01-17
New INFORMS Information Systems Research Study Key Takeaways:
The AI model achieves approximately 90% classification precision in predicting ICU length of stay, enabling hospitals to more effectively optimize resource management.
Clear, evidence-based explanations provided by the model empower ICU doctors to make better-informed decisions regarding patient care.
Real-world testing with ICU clinicians demonstrated the model’s potential to enhance care efficiency, reduce hospital costs and improve patient outcomes.
BALTIMORE, MD, January 16, 2025 – Intensive care units (ICUs) face mounting pressure to effectively manage resources while delivering ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Astrophysicists reveal structure of 74 exocomet belts orbiting nearby stars in landmark survey