Immunological face of megakaryocytes
2025-01-17
(Press-News.org)
Megakaryocytes (MKs), known for their role in platelet production, have emerged as critical players in immune responses, showcasing versatility in both physiological and pathological contexts. Recent advances in technology have unveiled the diverse immune functions of MKs, which express immune sensors and participate in immune activities, thus expanding their traditional role beyond hemostasis and coagulation. This comprehensive review delves into the multifaceted immune roles of MKs, highlighting their distinct immunological roles under inflammatory conditions and their interactions with the immune system.
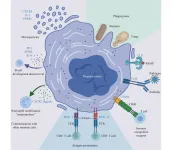
MKs exhibit cellular diversity, with subpopulations such as platelet-generating MKs, HSC niche MKs, and immune MKs, each with unique functional attributes. HSC niche MKs modulate HSC quiescence and proliferation, while immune MKs engage in immune responses. The review emphasizes the expression of immune receptors by MKs, such as toll-like receptors (TLRs), Fc gamma receptors (FcγRs), and CD40L, which enable them to detect pathogens and participate in innate and adaptive immunity. MKs also phagocytose fungi and bacteria, and can present antigens, suggesting their active role in immune surveillance.
Communication between MKs and other immune cells is a key aspect of their immune function. MKs secrete cytokines that influence B cell and plasma cell development, and they release microparticles that transport bioactive molecules, contributing to inflammation. The tissue-specific localization of MKs, such as in the lungs and spleen, shapes their immunological roles, with extramedullary MKs playing a role in immune surveillance and response.
In the context of inflammation, MKs serve as antiviral defenders and inflammation facilitators. They secrete interferons and upregulate IFN-induced transmembrane protein 3 (IFITM3), restricting viral entry and replication. However, an increased number of MKs correlates with disease severity in conditions like COVID-19, where they are associated with elevated cytokines and multiorgan injury. The dual role of MKs in viral infections underscores the balance between protective and pathogenic immune responses.
MKs also combat bacterial infections, with their numbers increasing in circulation during sepsis. They engage with bacteria both indirectly, through the release of pro-inflammatory platelets, and directly, through phagocytosis and the release of chromatin webs. The heterogeneity of MKs is further highlighted by the identification of an "immune MK" subpopulation, characterized by unique surface markers and gene expression profiles. This subpopulation is conserved across species, developmental stages, and tissues, and is involved in pathogen recognition, phagocytosis, and antigen presentation.
The review concludes by outlining future directions for "immune MK" research, including the exploration of the immune properties of platelets in relation to MK heterogeneity and the developmental origins of "immune MKs." The potential for "immune MKs" to influence disease outcomes and their interaction with other immune cells under various conditions is a promising area for future investigation. This review provides a thorough overview of the immunological face of megakaryocytes, emphasizing their complex and evolving role in immune responses and disease pathogenesis.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-01-17
A new Cochrane review has found that calorie labelling of food on menus and products leads people to choose slightly fewer calories.
The research team, led by scientists from UCL, Bath Spa University, the University of Cambridge and the University of Oxford, examined evidence from 25 studies on the impact of calorie labelling on food selection and consumption. They found that calorie labels in supermarkets, restaurants and other food outlets led to a small reduction in the calories people selected and purchased. The average reduction was 1.8%, which would equate ...
2025-01-17
Niigata and Tokyo, Japan - In recent years, advancements in dialysis therapy and the growing number of elderly patients starting dialysis have contributed to the aging of the overall dialysis population. Consequently, malnutrition-related conditions such as sarcopenia, frailty, and protein energy wasting (PEW) have become significant issues for dialysis patients. Nutritional interventions, including nutritional counseling, oral supplements, and intradialytic parenteral nutrition (IDPN), are recommended to address these challenges. On dialysis days, patients tend to consume less ...
2025-01-17
New INFORMS Information Systems Research Study Key Takeaways:
The AI model achieves approximately 90% classification precision in predicting ICU length of stay, enabling hospitals to more effectively optimize resource management.
Clear, evidence-based explanations provided by the model empower ICU doctors to make better-informed decisions regarding patient care.
Real-world testing with ICU clinicians demonstrated the model’s potential to enhance care efficiency, reduce hospital costs and improve patient outcomes.
BALTIMORE, MD, January 16, 2025 – Intensive care units (ICUs) face mounting pressure to effectively manage resources while delivering ...
2025-01-17
Continental European snakes, geckos and Italian wall lizards are making their way to northern Europe undetected among imports of ornamental olive trees destined for gardens and green spaces.
These hitchhiking intruders can become invasive pests that cause extensive damage to the natural environment - as has happened in previously snake-free islands of the Mediterranean like Majorca.
They’re also a red flag for a bigger problem: the range of potentially serious agricultural and environmental pests being unwittingly imported to Britain and ...
2025-01-16
Desert lizards are facing a ‘cost-of-living’ squeeze as global temperatures continue to rise, a new study finds.
For a lizard, the 'cost-of-living' is tightly linked to its body temperature, which dictates both how much food it needs and whether it can go outside to feed. Desert lizards are especially challenged because food is sparse, and it is often too hot to forage.
Published today in Science, the study found climate warming can ‘squeeze’ desert lizard energy budgets by increasing the food they need just ...
2025-01-16
Stem Cell Reports, the peer-reviewed, open access, online journal of the International Society for Stem Cell Research (ISSCR) is seeking highly motivated and accomplished early career scientists to join the Early Career Scientist Editorial Board (ECEB). This group of distinguished early career scientists will have the opportunity to:
Advise on journal content and programming such as special Issues, podcast content, and other initiatives,
Receive mentoring from associate editors,
Attend the annual editorial board meeting
Build their professional network and connections, and
Serve as an ambassador ...
2025-01-16
Our data-driven world demands more—more capacity, more efficiency, more computing power. To meet society’s insatiable need for electronic speed, physicists have been pushing the burgeoning field of spintronics.
Traditional electronics use the charge of electrons to encode, store and transmit information. Spintronic devices utilize both the charge and spin-orientation of electrons. By assigning a value to electron spin (up=0 and down=1), spintronic devices offer ultra-fast, energy-efficient platforms.
To develop viable spintronics, physicists must understand the quantum properties ...
2025-01-16
The kids and grandkids of immigrants to the United States usually lose the ability to speak their heritage language fluently. Without access to the heritage language, second- and third-generation Americans may use distinct words and pronunciations in the dominant language, English, to assert their ethnic identities and connect to their communities.
Sociolinguists have long viewed these shifts as markers of cultural change. Like differences in food, clothing and religion, differences in language are subtle ways that groups distinguish themselves along ethnic boundaries. Recent work has pivoted from asking what are the differences to why are there differences? How are they using language to carve ...
2025-01-16
Tufts Unvisity Assistant Professor Elizabeth Setren in the Department of Economics at the School of Arts and Sciences has received a Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers (PECASE) from President Joe Biden. PECASE recognition is the highest honor given by the U.S. government for outstanding scientists and engineers who are early in their careers
This year’s awardees are employed or funded by 14 governmental agencies. In Setren’s case, her recognition comes from the Department of Education’s Institute of Education Sciences, and ...
2025-01-16
The proportion of babies dying before and during labor after 41 weeks of gestation has fallen by 47% in Sweden in a relatively short time. This is the result of a major national study. The reduction has occurred since the procedures around induction have changed.
A pregnancy normally lasts around 40 weeks. However, a fairly high proportion of women, 22%, pass their due date and are pregnant for 41 weeks or longer. Although Sweden generally has a very low risk of stillbirth and death within the first month of life, the risk increases the longer the pregnancy continues ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Immunological face of megakaryocytes