(Press-News.org) Excessive sugar consumption is linked to several non-communicable diseases, including obesity, cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome, and type 2 diabetes. Animals naturally crave sugar, and uncontrolled sugar preferences can lead to high sugar intake, raising the risk of hyperglycemia and metabolic diseases.
Previous research suggests that food cravings in humans are driven by signals from the gut to the brain, highlighting the gut's crucial role in shaping dietary preferences. However, the regulation of sugar preference is complex, and the specific influence of gut microbes remains unclear.
In a study published in Nature Microbiology, a research team led by Prof. LIANG Xinmiao from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, collaborating with Prof. ZHU Shenglong and Prof. CHEN Yongquan from Jiangnan University, identified an intestinal bacterium that can reduce dietary sugar intake, opening up new avenues for the therapies of obesity and metabolic diseases.
Researchers analyzed the blood of 18 mice with induced diabetes and 60 patients with type 2 diabetes. They identified low levels of free fatty acid receptor 4 (FFAR4) in the blood cells of both diabetic mice and humans, alongside an increased sugar preference in individuals with FFAR4 mutations. They also found that reduced gut FFAR4 levels significantly affect the abundance of the gut microbe Bacteroides vulgatus and its key metabolite, pantothenic acid. Pantothenic acid activated the GLP-1-FGF21 hormone axis.
These results revealed a novel mechanism of the gut-liver-brain interaction. In mouse models, researchers validated this complex interaction. Bacteroides vulgatus and pantothenic acid were administered to diabetic mice, which demonstrated their effects on sugar preference in mice.
The findings revealed a novel regulatory mechanism underlying sugar preference, and that intestinal fatty acid receptors play a crucial role in regulating sugar intake behavior.
This study provides a promising strategy for diabetes prevention. The development of tissue-specific FFAR4 agonists or targeting Bacteroides vulgatus provides new approaches for preventing diabetes. Future clinical studies are essential to validate the application of the gut-liver-brain interaction as a nutrient-sensing pathway for managing metabolic diseases.
END
Researchers reveal novel mechanism for intrinsic regulation of sugar cravings
2025-01-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Immunological face of megakaryocytes
2025-01-17
Megakaryocytes (MKs), known for their role in platelet production, have emerged as critical players in immune responses, showcasing versatility in both physiological and pathological contexts. Recent advances in technology have unveiled the diverse immune functions of MKs, which express immune sensors and participate in immune activities, thus expanding their traditional role beyond hemostasis and coagulation. This comprehensive review delves into the multifaceted immune roles of MKs, highlighting their distinct immunological roles under ...
Calorie labelling leads to modest reductions in selection and consumption
2025-01-17
A new Cochrane review has found that calorie labelling of food on menus and products leads people to choose slightly fewer calories.
The research team, led by scientists from UCL, Bath Spa University, the University of Cambridge and the University of Oxford, examined evidence from 25 studies on the impact of calorie labelling on food selection and consumption. They found that calorie labels in supermarkets, restaurants and other food outlets led to a small reduction in the calories people selected and purchased. The average reduction was 1.8%, which would equate ...
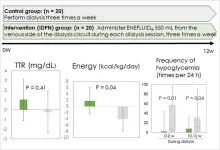
The effectiveness of intradialytic parenteral nutrition with ENEFLUID???? infusion
2025-01-17
Niigata and Tokyo, Japan - In recent years, advancements in dialysis therapy and the growing number of elderly patients starting dialysis have contributed to the aging of the overall dialysis population. Consequently, malnutrition-related conditions such as sarcopenia, frailty, and protein energy wasting (PEW) have become significant issues for dialysis patients. Nutritional interventions, including nutritional counseling, oral supplements, and intradialytic parenteral nutrition (IDPN), are recommended to address these challenges. On dialysis days, patients tend to consume less ...
New study reveals AI’s transformative impact on ICU care with smarter predictions and transparent insights
2025-01-17
New INFORMS Information Systems Research Study Key Takeaways:
The AI model achieves approximately 90% classification precision in predicting ICU length of stay, enabling hospitals to more effectively optimize resource management.
Clear, evidence-based explanations provided by the model empower ICU doctors to make better-informed decisions regarding patient care.
Real-world testing with ICU clinicians demonstrated the model’s potential to enhance care efficiency, reduce hospital costs and improve patient outcomes.
BALTIMORE, MD, January 16, 2025 – Intensive care units (ICUs) face mounting pressure to effectively manage resources while delivering ...
Snakes in potted olive trees ‘tip of the iceberg’ of ornamental plant trade hazards
2025-01-17
Continental European snakes, geckos and Italian wall lizards are making their way to northern Europe undetected among imports of ornamental olive trees destined for gardens and green spaces.
These hitchhiking intruders can become invasive pests that cause extensive damage to the natural environment - as has happened in previously snake-free islands of the Mediterranean like Majorca.
They’re also a red flag for a bigger problem: the range of potentially serious agricultural and environmental pests being unwittingly imported to Britain and ...
Climate change driving ‘cost-of-living' squeeze in lizards
2025-01-16
Desert lizards are facing a ‘cost-of-living’ squeeze as global temperatures continue to rise, a new study finds.
For a lizard, the 'cost-of-living' is tightly linked to its body temperature, which dictates both how much food it needs and whether it can go outside to feed. Desert lizards are especially challenged because food is sparse, and it is often too hot to forage.
Published today in Science, the study found climate warming can ‘squeeze’ desert lizard energy budgets by increasing the food they need just ...
Stem Cell Reports seeks applications for its Early Career Scientist Editorial Board
2025-01-16
Stem Cell Reports, the peer-reviewed, open access, online journal of the International Society for Stem Cell Research (ISSCR) is seeking highly motivated and accomplished early career scientists to join the Early Career Scientist Editorial Board (ECEB). This group of distinguished early career scientists will have the opportunity to:
Advise on journal content and programming such as special Issues, podcast content, and other initiatives,
Receive mentoring from associate editors,
Attend the annual editorial board meeting
Build their professional network and connections, and
Serve as an ambassador ...
‘Brand new physics’ for next generation spintronics
2025-01-16
Our data-driven world demands more—more capacity, more efficiency, more computing power. To meet society’s insatiable need for electronic speed, physicists have been pushing the burgeoning field of spintronics.
Traditional electronics use the charge of electrons to encode, store and transmit information. Spintronic devices utilize both the charge and spin-orientation of electrons. By assigning a value to electron spin (up=0 and down=1), spintronic devices offer ultra-fast, energy-efficient platforms.
To develop viable spintronics, physicists must understand the quantum properties ...
Pacific Islander teens assert identity through language
2025-01-16
The kids and grandkids of immigrants to the United States usually lose the ability to speak their heritage language fluently. Without access to the heritage language, second- and third-generation Americans may use distinct words and pronunciations in the dominant language, English, to assert their ethnic identities and connect to their communities.
Sociolinguists have long viewed these shifts as markers of cultural change. Like differences in food, clothing and religion, differences in language are subtle ways that groups distinguish themselves along ethnic boundaries. Recent work has pivoted from asking what are the differences to why are there differences? How are they using language to carve ...
White House honors Tufts economist
2025-01-16
Tufts Unvisity Assistant Professor Elizabeth Setren in the Department of Economics at the School of Arts and Sciences has received a Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers (PECASE) from President Joe Biden. PECASE recognition is the highest honor given by the U.S. government for outstanding scientists and engineers who are early in their careers
This year’s awardees are employed or funded by 14 governmental agencies. In Setren’s case, her recognition comes from the Department of Education’s Institute of Education Sciences, and ...