(Press-News.org) In the decades following the launch of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers have tallied over 1 trillion galaxies in the universe. But only one galaxy stands out as the most important nearby stellar island to our Milky Way — the Andromeda Galaxy. It can be seen with the naked eye on clear autumn nights as a faint oval object roughly the size of the moon.
A century ago, astronomer Edwin Hubble first established that this so-called "spiral nebula" was approximately 2.5 million light years away from our own Milky Way galaxy.
Now, the space telescope named after Hubble has accomplished the most comprehensive survey of this galaxy. The work yields new clues to the evolutionary history of Andromeda — and it looks markedly different from the Milky Way's history.
University of Washington astronomers presented the findings Jan. 16 in Maryland at a meeting of the American Astronomical Society, and in an accompanying paper published the same date in The Astrophysical Journal.
Without Andromeda as an example of a spiral galaxy, astronomers would know much less about the structure and evolution of our own Milky Way. That's because Earth is embedded inside the Milky Way. This is like trying to understand the layout of New York City by standing in the middle of Central Park.
"With Hubble we can get into enormous detail about what's happening on a holistic scale across the entire disk of the galaxy. You can't do that with any other large galaxy," said principal investigator Benjamin Williams, a UW research associate professor of astronomy.
Hubble's sharp imaging capabilities can resolve more than 200 million stars in the Andromeda galaxy, detecting only stars brighter than our Sun. They look like grains of sand across the beach. But the telescope can’t capture everything. Andromeda's total population is estimated to be 1 trillion stars, with many less massive stars falling below Hubble's sensitivity limit.
Photographing Andromeda was a Herculean task because the galaxy is a much bigger target in the sky than the galaxies Hubble routinely observes, which are often billions of light years away. The full mosaic was carried out under two Hubble programs. In total it required over 1,000 Hubble orbits, spanning more than a decade.
This panorama started about a decade ago with the Panchromatic Hubble Andromeda Treasury program. Images were obtained at near-ultraviolet, visible and near-infrared wavelengths using instruments aboard Hubble to photograph the northern half of Andromeda.
This has now been followed by the newly published Panchromatic Hubble Andromeda Southern Treasury. This phase added images of approximately 100 million stars in the southern half of Andromeda. This region is structurally unique and more sensitive to the galaxy's merger history than the northern disk mapped earlier.
Combined, the two programs collectively cover the entire disk of Andromeda, which is seen almost edge on — tilted by 77 degrees relative to the view we see from Earth. The galaxy is so large that the mosaic is assembled from approximately 600 separate fields of view. The mosaic image is made up of at least 2.5 billion pixels.
“The asymmetry between the two halves — now visually evident in this image — is incredibly intriguing,” said Zhuo Chen, a UW postdoctoral researcher in astronomy and lead author of the accompanying paper. “It’s fascinating to see the detailed structures of an external spiral galaxy mapped over such a large, contiguous area.”
The complementary Hubble survey programs provide information about the age, heavy-element abundance and stellar masses inside Andromeda. This will allow astronomers to distinguish between competing scenarios where Andromeda merged with one or more galaxies. Hubble's detailed measurements constrain models of Andromeda's merger history and disk evolution.
“This ambitious photography of the Andromeda galaxy sets a new benchmark for precision studies of large spiral galaxies,” Chen said.
Though the Milky Way and Andromeda galaxies formed presumably around the same time many billions of years ago, observational evidence shows that they have very different evolutionary histories, despite growing up in the same cosmological neighborhood. Andromeda seems to be more highly populated with younger stars and unusual features like coherent streams of stars, researchers say. This implies it has a more active recent star formation and interaction history than the Milky Way.
"This detailed look at the resolved stars will help us to piece together the galaxy's past merger and interaction history," Williams said.
This research was funded by NASA and the Simons Foundation. A full list of co-authors is listed with the paper.
For more information, contact Williams at benw1@uw.edu or Chen at zczhuo@uw.edu.
END
Panorama of our nearest galactic neighbor unveils hundreds of millions of stars
2025-01-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A chain reaction: HIV vaccines can lead to antibodies against antibodies
2025-01-17
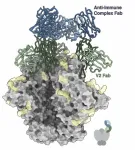
LA JOLLA, CA—Many vaccines work by introducing a protein to the body that resembles part of a virus. Ideally, the immune system will produce long-lasting antibodies recognizing that specific virus, thereby providing protection.
But Scripps Research scientists have now discovered that for some HIV vaccines, something else happens: after a few immunizations the immune system begins to produce antibodies against immune complexes already bound to the viral protein alone. They don’t yet know whether this chain reaction, described in Science ...
Bacteria in polymers form cables that grow into living gels
2025-01-17
Scientists at Caltech and Princeton University have discovered that bacterial cells growing in a solution of polymers, such as mucus, form long cables that buckle and twist on each other, building a kind of "living Jell-O."
The finding could be particularly important to the study and treatment of diseases such as cystic fibrosis, in which the mucus that lines the lungs becomes more concentrated, often causing bacterial infections that take hold in that mucus to become life threatening. This discovery ...
Rotavirus protein NSP4 manipulates gastrointestinal disease severity
2025-01-17
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and collaborating institutions have improved our understanding of how rotavirus, the most common cause of acute gastroenteritis in children, makes people sick. The study published in Science Advances is among the first to show that the rotavirus protein NSP4 is both necessary and sufficient for multiple aspects of rotavirus infection by disrupting calcium signaling not only within infected cells but also in nearby uninfected cells. These disruptions in calcium signaling affect rotavirus disease severity, providing new insights into how ...
‘Ding-dong:’ A study finds specific neurons with an immune doorbell
2025-01-17
Interleukin-1 (IL-1) is a key molecule involved in inflammation and plays an important role in both healthy and diseased states. In disease, high levels of IL-1 in the brain are linked to neuroinflammation, which can disrupt the body’s stress response, cause sickness-like behaviors, worsen inflammation by activating brain immune cells, and allow immune cells from the body to enter the brain. It also can lead to brain damage by causing support cells to produce harmful molecules. Elevated IL-1 levels are associated with mood disorders, ...
A major advance in biology combines DNA and RNA and could revolutionize cancer treatments
2025-01-17
Our genes contain all the instructions our body needs to function, but their expression must be finely regulated to guarantee that each cell performs its role optimally. This is where DNA and RNA epigenetics comes in: a series of mechanisms that act as "markers" on genes, to control their activity without modifying the DNA or RNA sequence itself.
Until now, DNA and RNA epigenetics were studied as independent systems. These two mechanisms seemed to function separately, each playing its own role in distinct stages of the gene regulation process.
Perhaps that was a mistake.
In a publication ...
Neutrophil elastase as a predictor of delivery in pregnant women with preterm labor
2025-01-17
Background and objectives
No previous study has been conducted in Nigeria on the role of neutrophil elastase in predicting preterm birth. The present study aimed to determine the role of the neutrophil elastase test in predicting birth in women with preterm labor.
Methods
The present prospective cohort study recruited 83 pregnant women with preterm labor between 28 and 36+6 weeks of gestation, and followed up these subjects for 14 days. The controls comprised 85 pregnant women without preterm labor. The cervicovaginal fluid was collected and tested using the neutrophil elastase test. Then, the sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive parameters were determined. ...
NIH to lead implementation of National Plan to End Parkinson’s Act
2025-01-17
WHAT:
With support from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Office of the Assistant Secretary for Health (OASH), the National Institutes of Health (NIH) is leading the implementation of the Dr. Emmanuel Bilirakis and Honorable Jennifer Wexton National Plan to End Parkinson’s Act (P.L. 118-66), which was signed into law on July 2, 2024. This follows a delegation of authority from the Secretary of the Department of Health and Human Services to the NIH Director.
The act establishes a Federal ...
Growth of private equity and hospital consolidation in primary care and price implications
2025-01-17
About The Study: In this cross-sectional study, nearly one-half of all primary care physicians (PCPs) were affiliated with hospitals, while private equity-affiliated PCPs were growing and concentrated in certain regional markets. Relative to PCPs in independent settings, hospital-affiliated PCPs and private equity-affiliated PCPs had higher prices for the same services.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Yashaswini Singh, PhD, MPA, email yashaswini_singh@brown.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2024.4935)
Editor’s ...
Online advertising of compounded glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists
2025-01-17
About The Study: This cross-sectional study showed websites that sell compounded glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) often partially informed and sometimes misinformed potential consumers. Compounded medications contain the same active ingredients as in branded medications but may contain different inactive ingredients. Most websites did not disclose that compounded GLP-1 RAs were not FDA approved, although some suggested these drugs were FDA approved. Many websites provided limited safety information and unauthorized efficacy claims. Some ...
Health care utilization and costs for older adults aging into Medicare after the affordable care act
2025-01-17
About The Study: This study found modest evidence of reductions in out-of-pocket costs and improvements in health among adults entering Medicare after the Affordable Care Act. Insurance coverage and financial assistance should be preserved and enhanced to improve health and health care access among vulnerable older adults.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Renuka Tipirneni, MD, MSc, email rtipirne@med.umich.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2024.5025)
Editor’s ...