(Press-News.org) Maital Neta, professor of psychology at the University of Nebraska–Lincoln, has received the Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers, the highest honor bestowed by the U.S. government on outstanding scientists and engineers early in their careers.
Neta, Carl A. Happold Professor of Psychology, directs the Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience Lab and is resident faculty of the Center for Brain, Biology and Behavior.
Neta said she was “very grateful” for the honor, announced Jan. 14 by President Biden. “And I’m grateful to all my mentors and mentees, and the support from my village that helped me get here,” she said.
Neta’s lab pursues novel research exploring how people process and cope with uncertainty and tests interventions that promote psychological well-being. Her research has also included a partnership with Nebraska Athletics to examine the factors relating to concussions and traumatic brain injuries using the latest technology available to the center. Her partnership with Nebraska Athletics was featured recently on the Big Ten Network.
Neta’s work has earned federal research funding from the National Science Foundation and the National Institutes of Health. In 2018, Neta earned an NSF Faculty Early Career Development Program award, a highly prestigious honor for pre-tenure faculty. As part of her CAREER project, Neta investigated how people’s emotional responses to uncertainty evolve over time. That work provided a foundation for additional research about how positive valence bias — the tendency for the brain to process positive information more quickly than negative information — improves with age, giving older adults a more optimistic disposition.
David DiLillo, chair of the psychology department, said “Dr. Neta winning this award is a testament to her groundbreaking contributions and exceptional dedication to advancing science and innovation."
Neta received her Bachelor of Science in psychobiology from the University of California, Los Angeles, and her doctoral degree in cognitive neuroscience from Dartmouth College. She joined the Nebraska faculty in 2014 and has earned multiple awards, including the Harold and Esther Edgerton Junior Faculty Award for creative research, outstanding teaching and academic promise.
Neta is one of nearly 400 scientists and engineers across the country who received the White House honor.
Established by President Clinton in 1996, the award recognizes scientists and engineers who show exceptional potential for leadership early in their research careers. The award recognizes innovative and far-reaching developments in science and technology, expands awareness of careers in science and engineering, recognizes the scientific missions of participating agencies, enhances connections between research and impacts on society, and highlights the importance of science and technology for the nation’s future.
This year’s awardees are employed or funded by 14 participating agencies within the Departments of Agriculture, Commerce, Defense, Education, Energy, Health and Human Services, Interior, Transportation, and Veterans Affairs and the Environmental Protection Agency, the intelligence community, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration, the National Science Foundation and the Smithsonian Institution.
Neta is the second Husker to earn the honor. Angela Pannier, Swarts Family Chair in Biological Systems Engineering, received a PECASE award in 2019.
END
Nebraska psychology professor recognized with Presidential Early Career Award
Maital Neta explores how people cope with uncertainty
2025-01-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New data shows how ‘rage giving’ boosted immigrant-serving nonprofits during the first Trump Administration
2025-01-17
As Donald Trump prepares to take office for a second term as President, research led by the University of California, Santa Cruz is demonstrating the important role nonprofits played during Trump’s first term as a counterforce that channeled public resistance to anti-immigrant policies.
The new study, published in the journal International Migration Review, shows how nonprofits that provide legal services for immigrants ended up receiving increases in public contributions in the wake of Trump's attacks on immigrants.
Previously, there had been many reported examples of this backlash effect, sometimes called ...
Unique characteristics of a rare liver cancer identified as clinical trial of new treatment begins
2025-01-17
Like many rare diseases, fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma (FLC) mounts a ferocious attack against an unlucky few—in this case, children, adolescents, and young adults. Because its symptoms can vary from person to person, it’s often missed or misdiagnosed until it has metastasized and becomes lethal. Moreover, drug therapies for common liver cancers are not just useless for FLC patients but actually harmful.
But new insights about the disease, coupled with a just-launched clinical trial of a promising drug treatment, could significantly improve health outcomes. Researchers in Rockefeller University’s Laboratory of Cellular Biophysics, headed by Sanford ...
From lab to field: CABBI pipeline delivers oil-rich sorghum
2025-01-17
Researchers at the Center for Advanced Bioenergy and Bioproducts Innovation (CABBI) have developed a new sorghum variant that can outperform soybeans in oil production, with great potential as a clean source of renewable fuel.
Scientists have long worked to create new sustainable sources of vegetable oils, known as triacylglycerols (TAG), to meet the growing demand for renewable fuels like sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) and renewable diesel.
Currently, oil palm and oilseeds such as soybeans provide most TAG for renewable ...
Stem cell therapy jumpstarts brain recovery after stroke
2025-01-17
SAN FRANCISCO—Every 40 seconds, someone in the United States has a stroke. For survivors of the most common type of stroke, called an ischemic stroke, only about 5 percent fully recover. Most others suffer from long-term problems, including weakness, chronic pain, or epilepsy.
Now, scientists at Gladstone Institutes and the regenerative medicine company SanBio have shown that a cell therapy derived from stem cells can restore normal patterns of brain activity after a stroke. While most stroke treatments must be administered in the immediate hours ...
Polymer editing can upcycle waste into higher-performance plastics
2025-01-17
Polymer editing can upcycle waste into higher-performance plastics
By editing the polymers of discarded plastics, chemists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory have found a way to generate new macromolecules with more valuable properties than those of the starting material. Upcycling may help remedy the roughly 450 million tons of plastic discarded worldwide annually, of which only 9% gets recycled; the rest is incinerated or winds up in landfills, oceans or elsewhere.
ORNL’s ...
Research on past hurricanes aims to reduce future risk
2025-01-17
Tropical storms like hurricanes are not only terrifying, but also incredibly costly for coastal regions across the United States, Mexico, Central America and the Caribbean. Beyond the immediate devastation, these storms contribute to significant economic losses and human displacement. In 2023 alone, climate migration linked to such events saw 2.5 million individuals attempt to cross the U.S. southern land border.
New research led by The University of Texas at Arlington emphasizes that studying ...
UT Health San Antonio, UTSA researchers receive prestigious 2025 Hill Prizes for medicine and technology
2025-01-17
SAN ANTONIO, Jan. 17, 2025 – On the eve of a historic merger between The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio and The University of Texas at San Antonio, researchers from the two institutions have been honored with highly prestigious 2025 Hill Prizes, in medicine and technology.
The prizes are awarded by the Texas Academy of Medicine, Engineering, Science and Technology (TAMEST), and Lyda Hill Philanthropies, which fund the awards to “propel high-risk, high-reward ideas and innovations that demonstrate very significant potential for real-world impact and can lead ...
Panorama of our nearest galactic neighbor unveils hundreds of millions of stars
2025-01-17
In the decades following the launch of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers have tallied over 1 trillion galaxies in the universe. But only one galaxy stands out as the most important nearby stellar island to our Milky Way — the Andromeda Galaxy. It can be seen with the naked eye on clear autumn nights as a faint oval object roughly the size of the moon.
A century ago, astronomer Edwin Hubble first established that this so-called "spiral nebula" was approximately 2.5 million light years away from our own Milky Way galaxy.
Now, the space telescope named ...
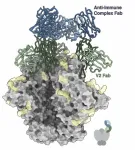
A chain reaction: HIV vaccines can lead to antibodies against antibodies
2025-01-17
LA JOLLA, CA—Many vaccines work by introducing a protein to the body that resembles part of a virus. Ideally, the immune system will produce long-lasting antibodies recognizing that specific virus, thereby providing protection.
But Scripps Research scientists have now discovered that for some HIV vaccines, something else happens: after a few immunizations the immune system begins to produce antibodies against immune complexes already bound to the viral protein alone. They don’t yet know whether this chain reaction, described in Science ...
Bacteria in polymers form cables that grow into living gels
2025-01-17
Scientists at Caltech and Princeton University have discovered that bacterial cells growing in a solution of polymers, such as mucus, form long cables that buckle and twist on each other, building a kind of "living Jell-O."
The finding could be particularly important to the study and treatment of diseases such as cystic fibrosis, in which the mucus that lines the lungs becomes more concentrated, often causing bacterial infections that take hold in that mucus to become life threatening. This discovery ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tiny flows, big insights: microfluidics system boosts super-resolution microscopy
Pennington Biomedical researcher publishes editorial in leading American Heart Association journal
New tool reveals the secrets of HIV-infected cells
HMH scientists calculate breathing-brain wave rhythms in deepest sleep
Electron microscopy shows ‘mouse bite’ defects in semiconductors
Ochsner Children's CEO joins Make-A-Wish Board
Research spotlight: Exploring the neural basis of visual imagination
Wildlife imaging shows that AI models aren’t as smart as we think
Prolonged drought linked to instability in key nitrogen-cycling microbes in Connecticut salt marsh
Self-cleaning fuel cells? Researchers reveal steam-powered fix for ‘sulfur poisoning’
Bacteria found in mouth and gut may help protect against severe peanut allergic reactions
Ultra-processed foods in preschool years associated with behavioural difficulties in childhood
A fanged frog long thought to be one species is revealing itself to be several
Weill Cornell Medicine selected for Prostate Cancer Foundation Challenge Award
Largest high-precision 3D facial database built in China, enabling more lifelike digital humans
SwRI upgrades facilities to expand subsurface safety valve testing to new application
Iron deficiency blocks the growth of young pancreatic cells
Selective forest thinning in the eastern Cascades supports both snowpack and wildfire resilience
A sea of light: HETDEX astronomers reveal hidden structures in the young universe
Some young gamers may be at higher risk of mental health problems, but family and school support can help
Reduce rust by dumping your wok twice, and other kitchen tips
High-fat diet accelerates breast cancer tumor growth and invasion
Leveraging AI models, neuroscientists parse canary songs to better understand human speech
Ultraprocessed food consumption and behavioral outcomes in Canadian children
The ISSCR honors Dr. Kyle M. Loh with the 2026 Early Career Impact Award for Transformative Advances in Stem Cell Biology
The ISSCR honors Alexander Meissner with the 2026 ISSCR Momentum Award for exceptional work in developmental and stem cell epigenetics
The ISSCR honors stem cell COREdinates and CorEUstem with the 2026 ISSCR Public Service Award
Minimally invasive procedure effectively treats small kidney cancers
SwRI earns CMMC Level 2 cybersecurity certification
Doctors and nurses believe their own substance use affects patients
[Press-News.org] Nebraska psychology professor recognized with Presidential Early Career AwardMaital Neta explores how people cope with uncertainty