Development of a high-performance AI device utilizing ion-controlled spin wave interference in magnetic materials
2025-01-17
(Press-News.org)
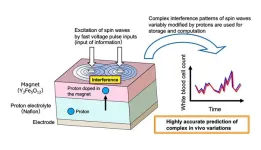
A research team from NIMS and the Japan Fine Ceramics Center (JFCC) has developed a next-generation AI device—a hardware component for AI systems—that incorporates an iono-magnonic reservoir. This reservoir controls spin waves (collective excitations of electron spins in magnetic materials), ion dynamics and their interactions. The technology demonstrated significantly higher information processing performance than conventional physical reservoir computing devices, underscoring its potential to transform AI technologies.
As AI devices become increasingly sophisticated, demand for energy-efficient, high-performance solutions continues to grow. The newly developed device generates spin waves using antennas integrated with yttrium iron garnet (YIG) magnets, a material critical to its operation. The interference patterns of these spin waves can be fine-tuned by applying voltage to the magnets and adjusting the number of ions introduced into them. The device is able to perform computations by leveraging these dynamic interference patterns through an iono-magnonic reservoir. This approach delivers performance far surpasses conventional physical reservoir computing devices.
This device demonstrated exceptional performance in time-series predictions, achieving error rates less than one tenth those of conventional devices. Its prediction accuracy was evaluated using a standard testing method based on the Mackey–Glass equations, which are commonly used to model complex variations in biological systems.
This technology can be implemented in both magnetic thin films and single crystals, while being miniaturized without performance degradation, making it potentially suitable for various industrial applications. When integrated with different sensors, it has the potential to enable energy-efficient, high-precision AI devices for a wide range of purposes.
###
This project was carried out by a research team consisting of Takashi Tsuchiya (Group Leader, Neuromorphic Devices Group (NDG), Research Center for Materials Nanoarchitectonics (MANA), NIMS), Wataru Namiki (Postdoctoral Researcher, NDG, MANA, NIMS at the time of this project; currently Researcher, MANA, NIMS), Daiki Nishioka (Trainee, NDG, MANA, NIMS at the time of this project; currently Research Fellow, International Center for Young Scientists, NIMS), Kazuya Terabe (Group Leader, Ionic Devices Group, MANA, NIMS), Yuki Nomura (Senior Researcher, Nanostructures Research Laboratory (NRL), JFCC) and Kazuo Yamamoto (Group Leader, NRL, JFCC).
This work was supported by funding from the National Security Technology Research Promotion Fund of the Acquisition, Technology & Logistics Agency, Ministry of Defense.
This research was published in Advanced Science, an open access journal, on November 17, 2024.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-01-17
By Shawn Ballard
The complexity of the human brain – 86 billion neurons strong with more than 100 trillion connections – enables abstract thinking, language acquisition, advanced reasoning and problem-solving, and the capacity for creativity and social interaction. Understanding how differences in brain signaling and dynamics produce unique cognition and behavior in individuals has long been a goal of neuroscience research, yet many phenomena remain unexplained.
A study from neuroscientists and ...
2025-01-17
As the atmosphere continues to fill with greenhouse gases from human activities, many proposals have surfaced to “geoengineer” climate-saving solutions, that is, alter the atmosphere at a global scale to either reduce the concentrations of carbon or mute its warming effect.
One recent proposal seeks to infuse the atmosphere with hydrogen peroxide, insisting that it would both oxidize methane (CH4), an extremely potent greenhouse gas while improving air quality.
Too good to be true?
University of Utah atmospheric scientists Alfred Mayhew and Jessica Haskins were skeptical, so they set out to test the claims behind this proposal. Their results, published on ...
2025-01-17
WASHINGTON, D.C. – Today, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) announced it is accepting applications for the 2025 DOE Office of Science Early Career Research Program to support the research of outstanding scientists early in their careers. The program will support over 80 early career researchers for five years at U.S. academic institutions, DOE national laboratories, and Office of Science user facilities.
“The vision, creativity, and effort of early career faculty drive innovation in the basic science enterprise. The Department of Energy’s Office of Science is dedicated to ...
2025-01-17
University of Virginia School of Engineering and Applied Science faculty members James T. Burns, Coleen Carrigan and Liheng Cai received the Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers (PECASE) on Tuesday, as did two UVA Engineering alumni, Ashutosh Giri and Ryan Johnson.
PECASE is the highest honor bestowed by the U.S. government on outstanding scientists and engineers early in their careers. According to the release from the White House, this award recognizes “innovative and far-reaching developments in science and technology.”
“This award year has been extraordinary not ...
2025-01-17
ARLINGTON, Va.—A favorite childhood memory for Dr. Sandra Chapman was visiting the USS Arizona Memorial in Pearl Harbor with her father. They hung out at the memorial so often that they memorized lines to the movie playing prior to the boat ride to the memorial.
So it’s appropriate that Chapman — a program officer in the Office of Naval Research’s (ONR) Warfighter Performance Department — is passionate about her involvement in the development of an innovative technology recently applied to efforts to preserve the area around the USS Arizona ...
2025-01-17
Images
EAST LANSING, Mich. – Our sun is essentially a searing hot sphere of gas. Its mix of primarily hydrogen and helium can reach temperatures between 10,000 and 3.6 million degrees Fahrenheit on its surface and its atmosphere’s outermost layer. Because of that heat, the blazing orb constantly oozes a stream of plasma, made up of charged subatomic particles — mainly protons and electrons. The sun’s gravity can’t contain them because they hold so much energy as heat, so they drift away into space as solar wind. Understanding how charged particles ...
2025-01-17
Maital Neta, professor of psychology at the University of Nebraska–Lincoln, has received the Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers, the highest honor bestowed by the U.S. government on outstanding scientists and engineers early in their careers.
Neta, Carl A. Happold Professor of Psychology, directs the Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience Lab and is resident faculty of the Center for Brain, Biology and Behavior.
Neta said she was “very grateful” for the honor, announced ...
2025-01-17
As Donald Trump prepares to take office for a second term as President, research led by the University of California, Santa Cruz is demonstrating the important role nonprofits played during Trump’s first term as a counterforce that channeled public resistance to anti-immigrant policies.
The new study, published in the journal International Migration Review, shows how nonprofits that provide legal services for immigrants ended up receiving increases in public contributions in the wake of Trump's attacks on immigrants.
Previously, there had been many reported examples of this backlash effect, sometimes called ...
2025-01-17
Like many rare diseases, fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma (FLC) mounts a ferocious attack against an unlucky few—in this case, children, adolescents, and young adults. Because its symptoms can vary from person to person, it’s often missed or misdiagnosed until it has metastasized and becomes lethal. Moreover, drug therapies for common liver cancers are not just useless for FLC patients but actually harmful.
But new insights about the disease, coupled with a just-launched clinical trial of a promising drug treatment, could significantly improve health outcomes. Researchers in Rockefeller University’s Laboratory of Cellular Biophysics, headed by Sanford ...
2025-01-17
Researchers at the Center for Advanced Bioenergy and Bioproducts Innovation (CABBI) have developed a new sorghum variant that can outperform soybeans in oil production, with great potential as a clean source of renewable fuel.
Scientists have long worked to create new sustainable sources of vegetable oils, known as triacylglycerols (TAG), to meet the growing demand for renewable fuels like sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) and renewable diesel.
Currently, oil palm and oilseeds such as soybeans provide most TAG for renewable ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Development of a high-performance AI device utilizing ion-controlled spin wave interference in magnetic materials