(Press-News.org) A collision happens. Someone is hurt, a head injury, a concussion. Just as the first responders arrive to help the person, inside the brain, another “crew” of responders is busy clearing debris and repairing injured tissue.
This crew is called the microglia - the immune cells of the central nervous system. Microglia are imperative to maintaining neuronal function by clearing toxins in the brain and central nervous system. But if they are overactive, they can damage neurons instead and, in some cases, have been found to promote the progression of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
During development, there are known sex-related differences in how microglia function. But into adulthood, there was thought to be less variation in how they behave. New research from the Del Monte Institute for Neuroscience at the University of Rochester finds that microglia function may not be as similar across sex as once thought. This discovery could have broad implications for how diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's are approached and studied, and points to the necessity of having gender specific research. It is already known that more women are diagnosed with Alzheimer’s and more men are diagnosed with Parkinson’s but it’s unclear as to why.
“It is a fortuitous finding that has repercussions for what people are doing in the field, but also helps us understand microglia biology in a way that people may not have been expecting,” said Ania Majewska, PhD, professor of Neuroscience and the senior author of a study out today in Cell Reports that shows how microglia respond differently in adult male versus female mice when given an enzyme inhibitor to block its microglia survival receptor. “This research has a lot of ramifications for microglia biology and as a result all these diseases where microglia are important in a sex specific manner.”
Pexidartinib or PLX3397 is an enzyme inhibitor commonly used to remove microglia in the lab setting to help researchers better understand the role of these cells in brain health, function, and disease. PLX3397 is also used to treat the rare disease tenosynovial giant cells tumors (TGCT) a condition that causes benign tumors to grow rapidly in the joints.
Researchers in the Majewska Lab were using PLX3397 in male versus female experiments but continued to run into difficulties, so they decided to take a different approach with the inhibitor. Instead of using it to ask other questions, they decided to better understand how microglia were responding to the drug in males versus females.
Linh Le, PhD (‘24), currently a Research Scientist, SetPoint Medical Corp was a graduate student in the Majewska Lab and is first author of this study, found the expected response from microglia to PLX3397 in male mice—it blocked the receptor that signals microglial survival and depleted the microglia. However, Le, et al, were surprised to find that female microglia responded with a different signaling strategy that resulted in increased microglial survival and less depletion.
“These findings are crucial in the rapidly emerging field of developing disease-modifying therapies that target microglia,” said Majewska. “We do not yet know why the microglia are acting differently in the two sexes. I think we'd like to understand how the signaling through this receptor is regulated in different conditions, i.e. hormonal changes, basal state, inflammatory, or an anti-inflammatory state.”
Additional authors include Sophia Eliseeva, Elizabeth Plunk, Kallam Kara-Pabani, Herman Li, Felix Yarovinsky, PhD, of the University of Rochester. This work was supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, the Department of Defense, and the Goodman award, and the Kilian J. and Caroline F. Schmitt Foundation through Del Monte Institute for Neuroscience Pilot Program.
END
Brain immune cells may also be from Mars and Venus
Researchers find that microglia function differently in males versus females, potentially having broad implications for how neurological diseases are studied
2025-01-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Effect of pediatric obesity treatment on long-term health
2025-01-21
About The Study: This cohort study demonstrated that good response to pediatric obesity treatment was associated with reduced long-term morbidity, such as type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia, and hypertension. Additionally, a link between pediatric obesity treatment effectiveness and lower incidences of mortality in young adulthood was observed; however, effective pediatric obesity treatment was not associated with adult depression or anxiety, highlighting their distinct nature despite frequent coexistence.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Emilia Hagman, PhD, email emilia.hagman@ki.se
To access the embargoed study: Visit our ...
Factors associated with semaglutide initiation among adults with obesity
2025-01-21
About The Study: This cohort study found that key sociodemographic, health care, and clinical factors are associated with receipt of semaglutide, a novel glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist medication, in those without diabetes. These findings suggest that insurance plan type and structure may be a crucial intervention point for improving equity in obesity treatment access.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Andrew C. Stokes, PhD, email acstokes@bu.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.55222)
Editor’s ...
Ten group leaders awarded EMBO Installation Grants
2025-01-21
EMBO announces that ten life scientists have been selected to receive EMBO Installation Grants. These grants support group leaders, who are in the early stages of setting up their laboratories, to strengthen the life sciences in countries participating in the scheme. Two new installation grantees will establish laboratories in Croatia, one in Czechia, one in Estonia, two in Greece, three in Poland and one in Portugal.
“EMBO Installation Grants offer flexible funding, extensive networking opportunities and practical support for life scientists pursuing ambitious research projects,” says EMBO Director Fiona Watt. ”We ...
Telephone therapy reduces fatigue interference with activities, mood and cognition for metastatic breast cancer survivors
2025-01-21
INDIANAPOLIS -- With medical advances, more than 169,000 people in the United States are living with metastatic breast cancer. Addressing debilitating symptoms has become increasingly crucial. Fatigue remains a significant challenge, affecting up to 63 percent of patients and severely impacting daily functioning.
A study demonstrates the effectiveness of telephone-delivered acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT) in reducing fatigue’s interference with functioning and improving the quality of life for survivors of metastatic breast cancer. ACT is a behavioral intervention that has shown promise in pilot studies in advanced cancer. ...
COPD is the sixth leading cause of death in the United States
2025-01-21
Miami (January 21, 2025) – Chronic lower respiratory diseases, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), are the sixth leading cause of death in the United States, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). The CDC’s National Center for Health Statistics released its “Deaths: Leading Causes for 2022” final report, ranking the 10 leading causes of death.
COPD comprises several conditions, including chronic bronchitis and emphysema, and can be caused by genetics and irritants like smoke or pollution. Symptoms ...
Mass shootings increase alcohol sales
2025-01-21
Alcohol sales spike after a public mass shooting, according to a study. The increase in alcohol consumption could further increase firearm-related violence in affected communities.
Nicholas R. Buttrick and colleagues analyzed data from 35,000 alcohol retailers, covering more than half of all American grocery and drug-store purchases from 2006–2019, and found that a public mass shooting in a community predicts a 3.5%–5.5% increase in weekly alcohol sales for at least two years. The effect is found for public shootings; mass shootings in private homes did not affect alcohol sales. The authors attribute ...
Peptides to clean up microplastics
2025-01-21
Researchers have identified peptides that can help remove microplastics from the environment by combining biophysical modeling, molecular dynamics, quantum computing, and reinforcement learning. The ultimate goal of the work is peptide-based technologies that can find, capture, and destroy microscopically tiny plastic particles.
Microplastics, plastic particles smaller than 5 mm, are ubiquitous pollutants, found everywhere from human breastmilk to Antarctic snow. Fengqi You and colleagues used a range of tools to identify peptides ...
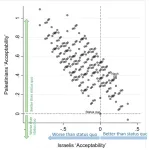
Surveys reveal zone of possible agreement for Israeli–Palestinian peace agreement
2025-01-21
A 2022 survey of Palestinians and Israelis identifies a set of peace deals that would be preferable to the status quo for majorities on both sides of the conflict.
Between March and May of 2022, Elisa Cavatorta and colleagues asked nationally representative samples of 1,197 Palestinians and 679 Israelis to rank hypothetical peace agreements. Each agreement consisted of eight components, varied in a controlled manner. This methodology enabled the calculation of the strength of preference for each component and the overall acceptability of 256 potential ...
Water as a waste management source: SEOULTECH researchers revolutionize catalytic plastic recycling
2025-01-21
Plastics are undeniably useful materials that have found their way into virtually all human activities. However, with yearly global plastic production exceeding 400 million tons, the environmental threat posed by increased plastic consumption and disposal, contributing to its pollution, is also bigger than ever. Considering that only one-tenth of all plastic waste is recycled, new technologies that can help tackle this growing problem are urgently required.
Catalytic recycling techniques, such as hydrogenolysis and hydrocracking, are emerging chemical processes that can break down plastic waste into simpler components ...
Antibiotics, vaccinations and anti-inflammatory medication linked to reduced risk of dementia
2025-01-21
Antibiotics, antivirals, vaccinations and anti-inflammatory medication are associated with reduced risk of dementia, according to new research that looked at health data from over 130 million individuals.
The study, led by researchers from the universities of Cambridge and Exeter, identified several drugs already licensed and in use that have the potential to be repurposed to treat dementia.
Dementia is a leading cause of death in the UK and can lead to profound distress in the individual and among those caring for them. It has been estimated to have a worldwide economic cost in excess of US$1 trillion dollars.
Despite intensive ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AAI appoints Anand Balasubramani as Chief Scientific Programs Officer
Prior authorization may hinder access to lifesaving heart failure medications
Scholars propose transparency, credit and accountability as key principles in scientific authorship guidelines
Jeonbuk National University researchers develop DDINet for accurate and scalable drug-drug interaction prediction
IEEE researchers achieve 20x signal boost in cerebral blood flow monitoring with next-generation interferometric diffusing wave spectroscopy
IEEE researchers achieve low-power ultrashort mid-IR pulse compression
Deep-sea natural compound targets cancer cells through a dual mechanism
Antibiotics can affect the gut microbiome for several years
Study: Electrical stimulation can restore ability to move limbs, receive sensory feedback after spinal cord injury
Rice scientists unveil new tool to watch quantum behavior in action
Gene-based therapies poised for major upgrade thanks to Oregon State University research
Extreme heat has extreme effects r—but some like it hot
Blood marker for Alzheimer’s may also be useful in heart and kidney diseases
Climate extremes hinder early development in young birds
Climate policies: The swing voters that determine their fate
Building protection against infectious diseases with nanostructured vaccines
Oval orbit casts new light on black hole - neutron star mergers
Does online sports gambling affect substance use behaviors?
How do rapid socio-environmental transitions reshape cancer risk?
Do abortion bans affect birth rates and food-assistance costs?
Can artificial intelligence help reduce the carbon footprint of weather forecasting models?
Mangrove forests are short of breath
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
[Press-News.org] Brain immune cells may also be from Mars and VenusResearchers find that microglia function differently in males versus females, potentially having broad implications for how neurological diseases are studied