(Press-News.org) Alcohol sales spike after a public mass shooting, according to a study. The increase in alcohol consumption could further increase firearm-related violence in affected communities.
Nicholas R. Buttrick and colleagues analyzed data from 35,000 alcohol retailers, covering more than half of all American grocery and drug-store purchases from 2006–2019, and found that a public mass shooting in a community predicts a 3.5%–5.5% increase in weekly alcohol sales for at least two years. The effect is found for public shootings; mass shootings in private homes did not affect alcohol sales. The authors attribute the increase in alcohol consumption to the trauma or dislocation felt by members of the public in communities where shootings occurred. According to the authors, the result may underestimate the effects of shooting-related trauma on alcohol sales because the data do not include bodegas, independent liquor stores and wineshops, bars, or restaurants. Ironically, high levels of alcohol use are associated with firearm violence, which could in turn produce yet more trauma, in what the authors term “negative spirals of violence.” The authors call for whole-community approaches to addressing the trauma of mass shootings.
END
Mass shootings increase alcohol sales
2025-01-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Peptides to clean up microplastics
2025-01-21
Researchers have identified peptides that can help remove microplastics from the environment by combining biophysical modeling, molecular dynamics, quantum computing, and reinforcement learning. The ultimate goal of the work is peptide-based technologies that can find, capture, and destroy microscopically tiny plastic particles.
Microplastics, plastic particles smaller than 5 mm, are ubiquitous pollutants, found everywhere from human breastmilk to Antarctic snow. Fengqi You and colleagues used a range of tools to identify peptides ...
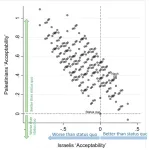
Surveys reveal zone of possible agreement for Israeli–Palestinian peace agreement
2025-01-21
A 2022 survey of Palestinians and Israelis identifies a set of peace deals that would be preferable to the status quo for majorities on both sides of the conflict.
Between March and May of 2022, Elisa Cavatorta and colleagues asked nationally representative samples of 1,197 Palestinians and 679 Israelis to rank hypothetical peace agreements. Each agreement consisted of eight components, varied in a controlled manner. This methodology enabled the calculation of the strength of preference for each component and the overall acceptability of 256 potential ...
Water as a waste management source: SEOULTECH researchers revolutionize catalytic plastic recycling
2025-01-21
Plastics are undeniably useful materials that have found their way into virtually all human activities. However, with yearly global plastic production exceeding 400 million tons, the environmental threat posed by increased plastic consumption and disposal, contributing to its pollution, is also bigger than ever. Considering that only one-tenth of all plastic waste is recycled, new technologies that can help tackle this growing problem are urgently required.
Catalytic recycling techniques, such as hydrogenolysis and hydrocracking, are emerging chemical processes that can break down plastic waste into simpler components ...
Antibiotics, vaccinations and anti-inflammatory medication linked to reduced risk of dementia
2025-01-21
Antibiotics, antivirals, vaccinations and anti-inflammatory medication are associated with reduced risk of dementia, according to new research that looked at health data from over 130 million individuals.
The study, led by researchers from the universities of Cambridge and Exeter, identified several drugs already licensed and in use that have the potential to be repurposed to treat dementia.
Dementia is a leading cause of death in the UK and can lead to profound distress in the individual and among those caring for them. It has been estimated to have a worldwide economic cost in excess of US$1 trillion dollars.
Despite intensive ...
Study links popular herbicide to problems with infant health
2025-01-21
EUGENE, Ore. — Jan. 21, 2025 — Increased exposure to glyphosate, one of the most widely used herbicides in the United States and much of the world, harms infant health in U.S. agricultural counties, according to a new study by two University of Oregon economists.
In a paper published Jan. 14 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Emmett Reynier and Edward Rubin showed that a dramatic increase in the use of glyphosate in U.S. counties most suitable for genetically engineered crops lowered ...
Why you should (not) get a dog: the pros and cons of dog ownership
2025-01-21
Are dogs really the key to better health and a happier life? In this new study, dog owners were invited to describe the biggest benefits and challenges of dog ownership. The commitments and responsibilities of having a dog were found to be both a joy and a burden, highlighting the importance of making a conscious adoption choice.
The pet dog population has been growing worldwide. Often benefiting from good press in mainstream media, dog ownership is generally assumed to improve human lives, providing companionship and boosting well-being. While bringing a dog into the family does come with ...
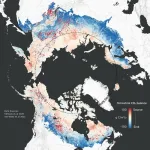
After millennia as carbon dioxide sink, more than one-third of Arctic-boreal region is now a source
2025-01-21
After millennia as a carbon deep-freezer for the planet, regional hotspots and increasingly frequent wildfires in the northern latitudes have nearly canceled out that critical storage capacity in the permafrost region, according to a new study published in Nature Climate Change.
An international team led by Woodwell Climate Research Center found that a third (34 percent) of the Arctic-boreal zone (ABZ)—the treeless tundra, boreal forests, and wetlands that make up Earth’s northern latitudes—is now a source of carbon to the atmosphere. That balance sheet is made up of carbon dioxide (CO₂) uptake from plant photosynthesis and CO₂ ...
The reversal of lipoprotein alterations in patients with ischaemic stroke offers new perspectives for cardiovascular disease research and management
2025-01-21
A study recently published by researchers from the Sant Pau Research Institute (IR Sant Pau) and the Stroke Unit of Sant Pau Hospital in the Journal of Lipid Research provides new evidence on the essential role of the qualitative properties of lipoproteins, such as LDL and HDL, in the pathophysiology of cardiovascular diseases, including ischaemic stroke. The findings underscore the importance of going beyond traditional quantitative cholesterol levels to evaluate the risk of these pathologies.
Dr ...
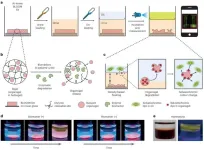
Early diagnosis of bladder cancer, now conveniently at home
2025-01-21
Bladder cancer has a cure rate of over 90% when detected early, but it has a high recurrence rate of 70%, necessitating continuous monitoring. Late detection often requires major surgeries such as bladder removal followed by artificial bladder implantation or the use of a urine pouch, significantly lowering the patient’s quality of life. However, existing urine test kits have low sensitivity, and cystoscopy, which involves inserting a catheter into the urethra for internal bladder examination, is both painful and burdensome. This highlights the urgent need for a simple yet accurate diagnostic technology for patients.
The research team led by Dr. Youngdo Jeong of the Center for Advanced ...
People who are autistic and transgender/gender diverse have poorer health and health care
2025-01-21
Researchers at the Autism Research Centre at Cambridge University found that these individuals also report experiencing lower quality healthcare than both autistic and non-autistic people whose gender identity matches their sex assigned at birth (cisgender).
The findings have important implications for the healthcare and support of autistic transgender/gender diverse (TGD) individuals. This is the first large-scale study on the experiences of autistic TGD people and the results are published today in Molecular Autism.
Previous research suggests that both autistic people and TGD people separately have poorer healthcare experiences ...