(Press-News.org) Many companies are making substantial investments in artificial intelligence (AI), which can enhance decision-making processes, foster innovation, increase productivity, and have other advantages. New research published in the Journal of Management Studies shows that company employees’ perceptions of how well AI performs (cognitive trust) and feelings towards AI (emotional trust) vary, and that these perceptions can affect AI performance and adoption in organizations.
Interviews with employees of a medium-sized software development firm revealed four different trust configurations: full trust (high cognitive/high emotional), full distrust (low cognitive/low emotional), uncomfortable trust (high cognitive/low emotional), and blind trust (low cognitive/high emotional).
Employees exhibited distinct behaviors under these different trust configurations: some responded by detailing their digital footprints, while others engaged in manipulating, confining, or withdrawing them. These behaviors triggered a “vicious cycle,” where biased and unbalanced data inputs degraded AI performance, further eroding trust and stalling adoption.
The findings could provide insights into how managers should introduce AI into the workplace.
“AI adoption isn’t just a technological challenge—it’s a leadership one. Success hinges on understanding trust, addressing emotions, and meeting employees where they are,” said corresponding author Natalia Vuori, DSc, of Aalto University, in Finland. “Without this human-centered approach, even the smartest AI will fail to deliver on its promise.”
URL upon publication: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/JOMS.13177
Additional Information
NOTE: The information contained in this release is protected by copyright. Please include journal attribution in all coverage. For more information or to obtain a PDF of any study, please contact: Sara Henning-Stout, newsroom@wiley.com.
About the Journal
The Journal of Management Studies is a globally respected, multidisciplinary business and management journal with a long-established history of excellence in management research. We publish innovative empirical and conceptual articles which advance the fields of management and organization, welcoming contributions relevant to organization theory, organizational behaviour, human resource management, strategy, international business, entrepreneurship, innovation and critical management studies. We have an inclusive ethos and open to a wide range of methodological approaches and philosophical underpinnings.
About Wiley
Wiley is one of the world’s largest publishers and a trusted leader in research and learning. Our industry-leading content, services, platforms, and knowledge networks are tailored to meet the evolving needs of our customers and partners, including researchers, students, instructors, professionals, institutions, and corporations. We empower knowledge-seekers to transform today’s biggest obstacles into tomorrow’s brightest opportunities. For more than two centuries, Wiley has been delivering on its timeless mission to unlock human potential. Visit us at Wiley.com. Follow us on Facebook, X, LinkedIn and Instagram.
END
How employee trust in AI drives performance and adoption
2025-01-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Does sleep apnea treatment influence patients’ risk of getting into car accidents?
2025-01-22
Sleepiness at the wheel is a significant contributing factor to motor vehicle accidents. A new analysis published in Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery reveals that for people with sleep apnea, getting surgery for their condition may lessen their risk of such accidents compared with using a Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) device at night or receiving no treatment.
In the analysis of data on 2,832,437 patients with obstructive sleep apnea, 3.4% of patients who underwent surgery were in a car accident at any point following their diagnosis, compared with 6.1% of those using a CPAP and 4.7% of those not receiving any treatment.
Patients ...
Do minimum wage hikes negatively impact students’ summer employment?
2025-01-22
New research in Contemporary Economic Policy indicates that rising minimum wages in a state are associated with reduced summer employment for college students, the time when students tend to work the most.
The study, which involved data from a public university and quarterly work records from Washington State, found that college students’ employment and hours worked decrease as minimum wages rise in the summer quarter. Students experiencing the largest reductions are those with little or no work experience ...
Exposure to stress during early pregnancy affects offspring into adulthood
2025-01-22
Maternal stress hormone levels during early pregnancy can have a lasting effect on the stress system of the offspring. The results of a long-term study on wild Assamese macaques in Thailand indicate that maternal stress in the first half of pregnancy is particularly relevant. Elevated stress hormones later during pregnancy or after birth did not have the same effects. The long-term study conducted by the University of Göttingen and the German Primate Center – Leibniz Institute for Primate Research provides important insights into the ...
Curious blue rings in trees and shrubs reveal cold summers of the past — potentially caused by volcanic eruptions
2025-01-22
When the going gets cold, even tough trees struggle with growing. Trees need a certain number of warm days in their growing seasons to grow properly; otherwise, the cell walls of new growth don’t lignify properly, creating ‘blue rings’ that appear when wood samples are dyed. Since trees and shrubs can live for hundreds of years, identifying these blue rings allows us to spot cold summers in the past. By looking at pine trees and juniper shrubs from northern Norway, scientists identified two extremely cold summers in 1902 and 1877, possibly caused by the eruptions of Mount Pelée on the island of Martinique and ...
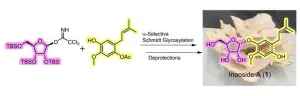
New frontiers in organic chemistry: Synthesis of a promising mushroom-derived compound
2025-01-22
Natural compounds from plants and animals have long been used in drug development, but mushrooms remain underexplored despite their rich chemical potential. Now, researchers from Japan have successfully developed the first method to synthesize inaoside A, a compound derived from the edible mushroom Laetiporus cremeiporus. This achievement will help better understand more of its bioactive properties and pave the way for similar mushroom-derived compounds in pharmaceuticals and functional foods.
Natural compounds derived from plants and animals have long been a source of inspiration when developing drugs and dietary supplements. Many well-established medical ...
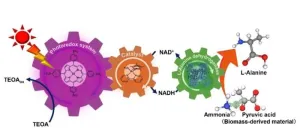
Biodegradable nylon precursor produced through artificial photosynthesis
2025-01-22
Nylon, the durable and elastic material, is like other plastics made from chemicals found in fossil fuels. Biodegradable plastics based on biomass-derived compounds are attracting attention as an alternative to conventional plastics, and Osaka Metropolitan University scientists have now synthesized biodegradable nylon precursors.
Professor Yutaka Amao’s team at the Research Center for Artificial Photosynthesis previously reported on a method for producing raw materials for biodegradable plastics from biomass-derived compounds. ...
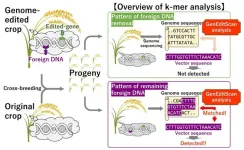
GenEditScan: novel k-mer analysis tool based on next-generation sequencing for foreign DNA detection in genome-edited products
2025-01-22
Genetic changes have the ability to alter crop characteristics, and some crop breeding techniques take advantage of this. Conventionally, genetic engineering has relied on natural or artificial mutations. In recent years, genome editing technology has been grabbing attention. Genome editing technology can target and cut specific DNA sequences, causing mutations in target genes. This makes it possible to develop new cultivars efficiently.
A common method for creating genome-edited crops involves introducing foreign DNA temporarily that produces an enzyme to cut the target ...
Survey: While most Americans use a device to monitor their heart, few share that data with their doctor
2025-01-22
RELEASE EMBARGOED UNTIL JAN. 22, 12:01 A.M. ET
Note to editor: photos and videos are available for download: https://bit.ly/4jkgIqT
Survey: While most Americans use a device to monitor their heart, few share that data with their doctor
Taking action with your doctor is critical for a proper diagnosis, action plan
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Advances in technology have made it increasingly easier for people to self-monitor their heart health whether it’s via a smart device on their wrist or finger or a blood pressure monitor. However, a new national survey commissioned by The Ohio State University Wexner Medical ...
Dolphins use a 'fat taste' system to get their mother’s milk
2025-01-22
Juvenile dolphins were found to have specialized receptors for fatty acids on their tongues, offering new insights into their growth and feeding habits.
Scientists have discovered that juvenile bottlenose dolphins have specialized receptors for detecting the fatty acids in their mother’s milk. These findings, published in the journal Marine Mammal Science, offer important insights into how these marine mammals grow, feed, and communicate.
The new findings challenge previous assumptions about cetacean sensory systems. Unlike land mammals, dolphins and other marine mammals have limited olfactory capabilities – their sense of smell is largely ...
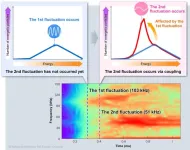
Clarifying the mechanism of coupled plasma fluctuations using simulations
2025-01-22
Background
In nature, phenomena in which multiple fluctuations occur in a coupled manner are frequently observed. For example, in large earthquakes, cases of them occurring consecutively in adjacent regions have been reported. When multiple fluctuations occur in this coupled way, compared to a single fluctuation, the coupled ones release more energy, leading to larger-scale phenomena. In fusion plasmas, fluctuations caused by energetic particles exist and are known to degrade the confinement of energetic particles. ...