(Press-News.org) Juvenile dolphins were found to have specialized receptors for fatty acids on their tongues, offering new insights into their growth and feeding habits.
Scientists have discovered that juvenile bottlenose dolphins have specialized receptors for detecting the fatty acids in their mother’s milk. These findings, published in the journal Marine Mammal Science, offer important insights into how these marine mammals grow, feed, and communicate.
The new findings challenge previous assumptions about cetacean sensory systems. Unlike land mammals, dolphins and other marine mammals have limited olfactory capabilities – their sense of smell is largely nonfunctional in aquatic environments. Researchers have therefore speculated that dolphins had other ways of sensing their surroundings and detecting food.
Fat plays an essential role in providing energy and supporting brain development in dolphin calves, which are entirely dependent on their mother’s milk during their early stages of life.
"We looked at the tongue of a young Indo-Pacific bottlenose dolphin and confirmed special structures that may help it detect fat," says the study’s first author Hinako Katsushima of the Graduate School of Environmental Science at Japan’s Hokkaido University. "At the back of the tongue, there's a V-shaped row of taste receptors that are specifically tuned to pick up fatty acids. These receptors also have enzymes that help break down the fat, making it easier for the dolphin to sense and process it."
In a second experiment, the team gave young dolphins a choice between two liquids: one containing milk and the other a cloudy solution. The dolphin showed an unexpected preference for the cloudy solution. This reinforces the finding that dolphins can distinguish between the two liquids, but the researchers are unsure why they avoided the milk. One possibility is that they found the milk unfamiliar – it was a mixture of milk from two females – and so avoided it from a fear of new foods, a habit called neophobia.
“Our findings suggest that the ability to detect fatty acids in their mother's milk is part of a specialized ‘fat taste’ system that could help dolphins assess the nutritional value of their food,” says Assistant Professor Takashi Hayakawa from the Faculty of Environmental Earth Science at Hokkaido University, who led the study. “In the wild, where fat-rich diets are critical for survival, this capability may provide dolphins with an evolutionary advantage, allowing them to select high-quality milk from their mothers and later evaluate the nutritional content of their prey.”
The new study opens new avenues for understanding how marine mammals perceive and interact with their environment, as well as how they communicate and forage in the wild. Further research will be necessary to explore the full scope of this "fat taste" system and how it functions in other marine species.
END
Dolphins use a 'fat taste' system to get their mother’s milk
2025-01-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
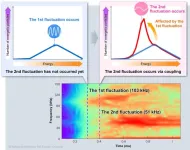
Clarifying the mechanism of coupled plasma fluctuations using simulations
2025-01-22
Background
In nature, phenomena in which multiple fluctuations occur in a coupled manner are frequently observed. For example, in large earthquakes, cases of them occurring consecutively in adjacent regions have been reported. When multiple fluctuations occur in this coupled way, compared to a single fluctuation, the coupled ones release more energy, leading to larger-scale phenomena. In fusion plasmas, fluctuations caused by energetic particles exist and are known to degrade the confinement of energetic particles. ...
Here’s what’s causing the Great Salt Lake to shrink, according to PSU study
2025-01-22
The Great Salt Lake, the largest saltwater lake in the Western Hemisphere, reached historic low levels in 2022, raising economic, ecological and public health concerns for Utah. New research from Portland State is believed to be the first peer-reviewed study that quantifies the contributing factors to the record low water volume levels, which the researchers say is important for anticipating and managing future lake changes.
“The lake has a lot of social and economic relevance for the region and Utah,” said Siiri Bigalke, the lead author and a Ph.D. candidate in PSU’s Earth, ...
Can DNA-nanoparticle motors get up to speed with motor proteins?
2025-01-22
DNA-nanoparticle motors are exactly as they sound: tiny artificial motors that use the structures of DNA and RNA to propel motion by enzymatic RNA degradation. Essentially, chemical energy is converted into mechanical motion by biasing the Brownian motion. The DNA-nanoparticle motor uses the "burnt-bridge" Brownian ratchet mechanism. In this type of movement, the motor is being propelled by the degradation (or "burning") of the bonds (or "bridges") it crosses along the substrate, essentially biasing its motion forward.
These nano-sized motors are highly programmable and can be ...
Childhood poverty and/or parental mental illness may double teens’ risk of violence and police contact
2025-01-22
Living with persistent poverty and/or parental mental illness throughout childhood may double the risk of carrying and/or using a weapon and getting on the wrong side of the law by the age of 17, suggests research published online in the Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health.
These factors may account for nearly 1 in 3 cases of weapon use or carriage and more than a quarter of all police contact among 17 year olds, nationwide, estimate the researchers.
Youth crime and violence are common around the world, they note. In England and Wales, for example, around 104,400 first-time offenders were ...
Fizzy water might aid weight loss by boosting glucose uptake and metabolism
2025-01-22
Fizzy water might aid weight loss by boosting blood glucose uptake and metabolism—the rate at which the body uses and converts energy—but the effects are so small, drinking it can’t be relied on alone to shed the pounds, concludes a brief analysis published in the open access journal BMJ Nutrition Prevention & Health.
There are no quick fixes to slimming down and keeping off the weight, says the author: regular physical activity and a healthy balanced diet are still essential, added to which the long term effects of drinking large amounts of carbonated water aren’t known.
Because ...
Muscular strength and good physical fitness linked to lower risk of death in people with cancer
2025-01-22
Muscular strength and good physical fitness are linked to a significantly lower risk of death from any cause in people with cancer, finds a pooled data analysis of the available evidence, published online in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
Tailored exercise to boost muscle strength and cardiorespiratory fitness in patients with cancer may help boost their chances of survival, suggest the researchers.
In 2022 alone, 20 million people were diagnosed with cancer worldwide, and nearly ...
Recommendations for studying the impact of AI on young people's mental health proposed by Oxford researchers
2025-01-22
A new peer-reviewed paper from experts at the Oxford Internet Institute, University of Oxford, highlights the need for a clear framework when it comes to AI research, given the rapid adoption of artificial intelligence by children and adolescents using digital devices to access the internet and social media.
Its recommendations are based on a critical appraisal of current shortcomings in the research on how digital technologies’ impact young people’s mental health, and an in-depth analysis of the challenges underlying those shortcomings.
The paper, “From ...
Trump clusters: How an English lit graduate used AI to make sense of Twitter bios
2025-01-22
An English literature graduate turned data scientist has developed a new method for large language models (LLMs) used by AI chatbots to understand and analyse small chunks of text, such as those on social media profiles, in customer responses online or for understanding online posts responding to disaster events.
In today’s digital world, such use of short text has become central to online communication. However, analysing these snippets is challenging because they often lack shared words or context. This lack of context makes it difficult for AI to find patterns ...
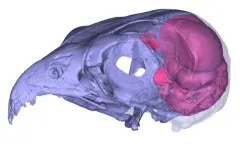
Empty headed? Largest study of its kind proves ‘bird brain’ is a misnomer
2025-01-22
It’s difficult to know what birds ‘think’ when they fly, but scientists in Australia and Canada are getting some remarkable new insights by looking inside birds' heads.
Evolutional biologists at Flinders University in South Australia and neuroscience researchers at the University of Lethbridge in Canada have teamed up to explore a new approach to recreating the brain structure of extinct and living birds by making digital ‘endocasts’ from the area inside a bird skeleton’s empty cranial space.
Published today in Biology Letters, the study led by the ‘Bones and Diversity Lab’ at Flinders and the Iwaniuk Lab at the University ...
Wild baboons not capable of visual self-awareness when viewing their own reflection
2025-01-22
Published today in Proceedings of the Royal Society B, the study found that while the baboons noticed and responded to a laser mark shone on their arms, legs and hands, they did not react when they saw, via their mirror reflection, the laser on their faces and ears.
It was the first time a controlled laser mark test has been done on these animals in a wild setting and strengthens the evidence from other studies that monkeys don’t recognise their own reflection.
The researchers observed 120 Chacma ...