(Press-News.org) A new study suggests that countries with stronger commitments to protect the natural environment—regardless of national oil dependence or other economic interests—are more likely to see the establishment of counter climate change groups that aim to obstruct climate change action. Jared Furuta and Patricia Bromley of Stanford University, U.S., present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS One on January 22, 2025.
Prior research has highlighted how the fossil fuel industry and conservative think tanks and philanthropists have stoked climate change skepticism in the U.S. in order to serve their economic and political interests. However, in the past several decades, the counter climate change movement has become international and now includes eclectic organizations whose views are not straightforwardly tied to economic or political self-interest.
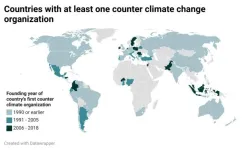
To better understand the factors influencing the growing international counter climate change movement, Furuta and Bromley conducted a statistical analysis of data on more than 160 countries and hundreds of counter climate organizations around the world.
Their analysis suggests that counter climate organizations are more likely to arise in countries that have stronger policies and structures aimed at protecting the natural environment. Notably, factors related to a country’s economic interests—such as greenhouse gas emissions or reliance on oil resources—did not have a significant association with the development of counter climate change organizations. Nor did several other alternative factors also explored by the researchers, such as a country’s level of economic development, level of income inequality, its ties to the U.S., or the ideology of its political leadership.
These findings support the idea that reactionary and oppositional dynamics shape counter climate change movements as part of a process that is intertwined with the evolution of pro-environmental efforts.
On the basis of their findings, the researchers outline potential directions for future research and policymaking, suggesting, for instance, that climate change policymakers and environmental organizations might consider routinely investigating the ways in which their efforts could possibly trigger counterproductive reactionary movements, and adjust their efforts accordingly.
The authors add: “More than fifty countries around the world are now home to at least one counter climate change organization: nonprofits that work to undermine climate science and policy. These organizations have long been active in the US, but in recent years they have evolved to form a global movement; they arise especially in countries with the strongest environmental policies and institutions, rather than in countries with the highest levels of greenhouse gas emissions or industrial activity.”
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS One: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0315012
Citation: Furuta J, Bromley P (2025) Globalizing opposition to pro-environmental institutions: The growth of counter climate change organizations around the world, 1990 to 2018. PLoS ONE 20(1): e0315012. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0315012
Author countries: U.S.
Funding: The author(s) received no specific funding for this work.
END
Anti-climate action groups tend to arise in countries with stronger climate change efforts
Study suggests counter climate groups emerge as a form of backlash to stronger environmental policies and institutions
2025-01-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
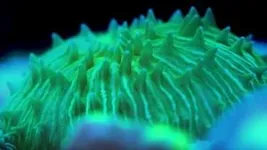
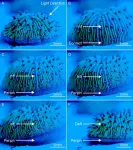
Some coral "walk" towards blue or white light, using rolling, sliding or pulsing movements to migrate, per experiments with free-living mushroom coral Cycloseris cyclolites
2025-01-22
Some coral "walk" towards blue or white light, using rolling, sliding or pulsing movements to migrate, per experiments with free-living mushroom coral Cycloseris cyclolites
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0315623
Article title: Walking coral: Complex phototactic mobility in the free-living coral Cycloseris cyclolites
Author countries: Australia, Saudi Arabia
Funding: The authors declare the research was funded by an Australian Research ...
Discovery of the significance of birth in the maintenance of quiescent neural stem cells
2025-01-22
A research group led by Kazunobu Sawamoto, a professor at Nagoya City University and National Institute for Physiological Sciences, and Koya Kawase, a pediatric doctor at Nagoya City University Hospital, has elucidated the significance of birth in the maintenance of neural stem cells (NSCs).
Birth is one of the most significant life events for animals. The transition from the intrauterine to the extrauterine environment causes various metabolic changes in individuals. Despite its significance, the role of birth in the developmental process remains incompletely understood. In the adult mammalian brain, NSCs are retained in the ...
Severe weather and major power outages increasingly coincide across the US
2025-01-22
An understanding of the relationship between severe weather and power outages in our changing climate will be critical for hazard response plans, according to a study published January 22, 2025 in the open-access journal PLOS Climate by Vivian Do of Columbia University, New York and colleagues.
Throughout the United States, large-scale power outages commonly occur alongside severe weather events. These combined events can be associated with major economic costs and health risks, as loss of power can disrupt medical equipment, heating or air conditioning, and other important systems. As severe weather ...
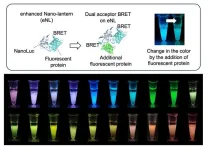
Bioluminescent cell imaging gets a glow-up
2025-01-22
Osaka, Japan – Imaging live cells with fluorescent proteins has long been a crucial technique for understanding cellular behavior. While bioluminescent proteins offer several advantages over fluorescent proteins, the limited availability of color variants has made it difficult to observe multiple targets simultaneously. Now, researchers from SANKEN (The Institute of Scientific and Industrial Research) at Osaka University have developed a groundbreaking method to expand the color palette of bioluminescent protein to 20 distinct colors, enabling advanced simultaneous multi-color imaging.
Cells are the fundamental building blocks of life. Understanding how they function is essential ...
Float like a jellyfish: New coral mobility mechanisms uncovered
2025-01-22
When it comes time to migrate, QUT research has found how a free-living coral ignores the classic advice and goes straight towards the light.
The research – led by Dr Brett Lewis from the QUT School of Atmospheric and Earth Sciences and Reef Restoration and Adaptation Program, and published in PLOS One – investigated how the free-living mushroom coral Cycloseris cyclolites moves, navigates and responds to light in its natural environments.
“Not all corals are attached to the substrate; some are solitary and free-living, allowing them to migrate into preferred habitats,” ...
Severe weather and major power outages increasingly coincide across the U.S.
2025-01-22
An understanding of the relationship between severe weather and power outages in our changing climate will be critical for hazard response plans, according to a study led by a researcher at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health. The study is published in the open-access journal PLOS Climate.
Throughout the U.S., large-scale power outages commonly occur alongside severe weather events. These combined events can be associated with major economic costs and health risks, as loss of power can disrupt medical equipment, heating or air conditioning, and other important systems. As severe weather events increase in severity and frequency ...
Who to vaccinate first? Penn engineers answer a life-or-death question with network theory
2025-01-22
Engineering and medical researchers at Penn have developed a groundbreaking framework that can determine the best and most computationally optimized distribution strategy for COVID-19 vaccinations in any given community. Published in PLOS One, this study addresses one of the most critical challenges in pandemic response — how to prioritize vaccination efforts in communities with individuals of different risk levels when supplies are scarce and the stakes are high.
The research team, comprised of Saswati Sarkar, Professor ...
Research shows PTSD, anxiety may affect reproductive health of women firefighters
2025-01-22
TUCSON, Arizona — A new study led by University of Arizona Mel and Enid Zuckerman College of Public Health researchers in collaboration with fire service partners and other researchers around the country through the Fire Fighter Cancer Cohort Study showed that post-traumatic stress disorder and anxiety are associated with lower levels of anti-Müllerian hormone, a marker of ovarian reserve, among women firefighters.
The ovarian reserve is the number of healthy eggs in a woman’s ovaries that ...
U of M Medical School research team receives $1.2M grant to study Tourette syndrome treatment
2025-01-22
MINNEAPOLIS/ST. PAUL (1/22/2025) — A research team from the University of Minnesota Medical School recently received a three-year, $1.2 million grant from the National Institutes of Health to study the use of transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) as a treatment for youth with Tourette syndrome and other tic disorders.
These conditions affect one in every 50 children and are characterized by involuntary movements or sounds called “tics.” Tics are often painful, distressing and interfere with daily life activities. In some cases, tics can be quite disabling.
The research team recently completed the first phase of this clinical trial ...
In the hunt for new and better enzymes, AI steps to the fore
2025-01-22
Enzymes are crucial to life. They are nature’s little catalysts. In the gut, they help us digest food. They can enhance perfumes or get laundry cleaner with less energy. Enzymes also make potent drugs to treat disease. Scientists naturally are eager to create new enzymes. They imagine them doing everything from drawing greenhouse gases out of the skies to degrading harmful toxins in the environment.
That age-old quest for new enzymes just got a whole lot easier. A team of bioengineers and synthetic biologists has developed a computational workflow that can design thousands of new enzymes, predict how they will behave in the real world, and test their performance ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
[Press-News.org] Anti-climate action groups tend to arise in countries with stronger climate change effortsStudy suggests counter climate groups emerge as a form of backlash to stronger environmental policies and institutions