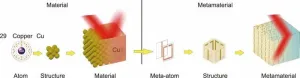
Interpreting metamaterials from an artistic view
2025-01-23
(Press-News.org)
Two leading experts in the field of metamaterials from Tsinghua University co-authored a review article on this emerging scientific field in Engineering recently. Unlike traditional review articles, the authors interpret metamaterials from an artistic perspective. By drawing parallels with art, they reflect on significant achievements made over the past two decades and offer insights into the future development of the field. Their work introduces readers to the novel concept of metamaterials as “the art in materials science.”
Metamaterials refer to artificially engineered materials composed of structural units designed to exhibit extraordinary properties not found in natural materials. Although the field has only developed for just over 20 years, it has expanded into numerous areas of physics and significantly influenced engineering applications. The two scholars compare metamaterials to the “art of materials science” because research in this field is inherently creative. Just as art comes from life but goes beyond it, metamaterials are composed of natural materials but can exhibit properties beyond those found in nature. The article emphasizes that the key to metamaterials research lies in achieving the “meta”—a process akin to artistic creation, breaking conventions, embracing freedom, and fully leveraging human ingenuity to design materials with extraordinary, enhanced properties, and super functionalities. On a micro level, the design methods and concepts exhibited during the development of metamaterials, as well as the overarching development patterns observed over its thriving 20-year history on macro level, show remarkable similarities to the evolution of artistic creation. From a results perspective, metamaterials have enabled realizations of concepts that had existed only in the realm of art for millennia but were previously unattainable—such as the “invisibility cloak.” Finally, the authors provide an outlook on the future development of metamaterials, addressing foundational research, intelligent systems, artificial intelligence, and engineering applications. They stress the necessity of advancing metamaterials toward practical applications while addressing existing challenges. The article proposes transitioning metamaterials from “art pieces” to “craftworks”—from intricate laboratory creations to industrial-scale mass production. This transformation is expected to revolutionize productivity and drive societal progress.
The paper “Metamaterials: The Art in Materials Science,” authored by Jingbo Sun, Ji Zhou. Full text of the open access paper: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2024.12.011. For more information about the Engineering, follow us on X (https://twitter.com/EngineeringJrnl) & like us on Facebook (https://www.facebook.com/EngineeringJrnl).
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-01-23
Researchers at University of California San Diego analyzed cannabis smoking practices in San Diego County to assess whether in-home smoking was associated with cannabis detection in children. The study, published in the Jan. 23, 2025, online edition of the Journal of the American Medical Association Network Open, found that in-home cannabis smoking increased the odds of child exposure to cannabis smoke.
Smoking is the most common method of cannabis use and is known to generate emissions that are harmful to those exposed. Cannabis is often smoked indoors, putting non-smokers such as children at risk for exposure.
“While the long-term health consequences of cannabis smoke are not ...
2025-01-23
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Adam Leroy, a professor of astronomy at The Ohio State University, has been named the recipient of the 2025 Henry Draper Medal.
The oldest medal awarded by the National Academy of Sciences, the Henry Draper Medal celebrates those who have made “a recent, original investigation in astronomical physics, of sufficient importance and benefit to science to merit such recognition.” It is awarded every four years.
Leroy’s work was selected for pathbreaking efforts that have characterized, “in unprecedented detail, the physical ...
2025-01-23
Non-white communities had significantly less access to opioid medications commonly prescribed for moderate to severe pain than white communities over the decade beginning in 2011, according to a study by Weill Cornell Medicine researchers.
The findings, published Jan. 23 in Pain, stretched across all socioeconomic groups, and suggest that communities of color may be especially vulnerable to the unintended consequences of efforts to reduce unsafe use of opioid analgesics.
From 2011 to 2021, prescription opioid use dropped by about 50% ...
2025-01-23
The prevalence of diagnosed disorders from recurrent use of sedative, hypnotic and antianxiety medications in adolescents and young adults has increased sharply since 2001, according to Rutgers Health researchers.
Their study, published in Addiction, examined diagnoses of these disorders in adolescents and young adults between 2001 to 2019.
Sedative, hypnotic and antianxiety medications are used to treat a variety of conditions, including sleep and anxiety disorders. According to Harvard Health, consistent use of these drugs can lead to a higher tolerance for their effects, meaning patients require higher doses to achieve the intended effects.
For ...
2025-01-23
A recent study by researchers from Peking University demonstrates the potential of nuclear electric resonance to control the nuclear spins of nitrogen atoms in DNA using electric field gradients, thereby achieving artificial intervention to manipulate DNA for computation. Utilizing molecular dynamics simulations, quantum chemical computations and theoretical analyses, the research reveals how electric field gradient orientation patterns vary with DNA bases and nitrogen atom sites, encoding genetic and structural information into the direction of nitrogen nuclear spins. The research was published Dec. 12 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner ...
2025-01-23
“It has been postulated that the clinical benefit of adding POM results from enhanced immunocompetency.”
BUFFALO, NY - January 23, 2025 – A new editorial was published in Oncoscience’s Volume 12 on January 14, 2025, titled “Pomalidomide improved immune profiles in myeloma."
The editorial by researchers Hannah Seah, Vaishnavi Reddy Bade, Lakshmi Bhavani Potluri, Srikanth Talluri, and Rao H. Prabhala from Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, VA Boston Healthcare System, and Harvard Medical School, discuss how the drug pomalidomide (POM) can help improve the immune system ...
2025-01-23
The PREPSOIL project, a pivotal initiative within the EU's Mission Soil framework, will host an engaging webinar on February 13, 2025, focusing on the importance of soil literacy among young people. The event highlights the vital connection between young citizens and soil health, offering educators innovative ways to integrate soil-related topics into their curriculum.
As part of the Mission Soil's eight goals, increasing soil literacy across Member States aims to foster greater awareness, involvement, and proactive behavior toward soil health. By embedding soil health education in school curriculums, the initiative seeks to empower the next generation to take informed ...
2025-01-23
WASHINGTON, Jan. 23, 2025 – Many science fiction authors try to incorporate scientific principles into their work, but Ian Tregillis, who is a contributing author of the Wild Cards book series when he’s not working as a physicist at Los Alamos National Laboratory, took it one step further: He derived a formula to describe the dynamics of the fictional universe’s viral system.
In independent research published in the American Journal of Physics, from AIP Publishing, Tregillis and George R.R. Martin derive a formula for viral behavior in the Wild Cards universe.
Wild Cards is a science fiction series written by a collection of authors and ...
2025-01-23
The remains of the earliest dinosaurs may lie undiscovered in the Amazon and other equatorial regions of South America and Africa, suggests a new study led by UCL (University College London) researchers.
Currently, the oldest known dinosaur fossils date back about 230 million years and were unearthed further south in places including Brazil, Argentina and Zimbabwe. But the differences between these fossils suggest dinosaurs had already been evolving for some time, pointing to an origin millions of years earlier.
The new study, published in the journal Current Biology, accounted for gaps in ...
2025-01-23
About The Study: The results of this retrospective cohort study of 44,000 individuals suggest that fasting plasma glucose level, age, body mass index (BMI), and male sex were all associated with development of diabetes, with significant interaction between these variables. These data contribute to understanding the clinical course of diabetes and highlight the substantial individual variation in diabetes risk according to commonly measured clinical variables. The findings facilitate lifestyle and pharmacologic interventions to treat those at highest risk of diabetes to reduce future morbidity and mortality. Further work is needed to validate this risk ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Interpreting metamaterials from an artistic view