(Press-News.org) Battery-powered electric vehicles are now more reliable and can match the lifespans of traditional cars and vans with petrol and diesel engines - marking a pivotal moment in the drive towards sustainable transportation, a new study reveals.
Researchers used nearly 300 million UK Ministry of Transport (MOT) test records charting the ‘health’ of every vehicle on the United Kingdom’s roads between 2005 and 2022 to estimate vehicle longevity and provide a comprehensive analysis of survival rates for different powertrains.
The international research team found that, although early Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) were less reliable than internal combustion engine vehicles (ICEVs), rapid advances in technology have enabled newer BEVs to achieve comparable lifespans, even under more intensive use.
Researchers found that BEVs demonstrated the most rapid improvement in reliability, with a 12% lower likelihood of failure (hazard rate) for each successive year of production, compared to 6.7% for petrol and 1.9% for diesel vehicles.
Publishing their findings today (24 Jan) in Nature Energy, researchers from the University of Birmingham, London School of Economics and Political Science (LSE), University of California San Diego, and University of Bern, Switzerland, reveal that, on average, BEVs now have a lifespan of 18.4 years and can travel up to 124,000 miles, surpassing traditional petrol cars in mileage.
They also identify top-performing brands in terms of vehicle longevity. Tesla leads among BEVs. For petrol and diesel vehicles, Audi and Skoda are the best performers, respectively.
Co-author Dr Viet Nguyen-Tien, from the LSE, commented: “Our findings provide critical insights into the lifespan and environmental impact of electric vehicles. No longer just a niche option, BEVs are a viable and sustainable alternative to traditional vehicles - a significant step towards achieving a net-zero carbon future.”
Co-author Robert Elliott, Professor of Economics at the University of Birmingham, commented: "BEVs offer significant environmental benefits, especially as Europe switches to a more renewable energy mix. Despite higher initial emissions from production, a long-lasting electric vehicle can quickly offset its carbon footprint, contributing to the fight against climate change - making them a more sustainable long-term option.
"Our findings offer consumers reliable data to make informed decisions about their vehicle purchases, whilst policymakers can use our insights to shape regulations and incentives that promote the adoption of durable and environmentally friendly vehicles and plan ahead their end-of-life treatment."
The study highlights the importance of advances in technology in promoting the adoption of BEVs. It also provides valuable insights for fleet replacement strategies and planning how to effectively recycle electric vehicles at the end of their working life.
ENDS
For more information, interviews or an embargoed copy of the research paper, please contact Tony Moran, International Communications Manager, University of Birmingham, tel: +44 (0)7827 832312: email: t.moran@bham.ac.uk
Notes to editor:
The University of Birmingham is ranked amongst the world’s top 100 institutions. Its work brings people from across the world to Birmingham, including researchers, teachers and more than 8,000 international students from over 150 countries.
‘The Closing Longevity Gap between Battery Electric Vehicles and Internal Combustion Vehicles in Great Britain’ - Viet Nguyen-Tien, Chengyu Zhang, Eric Strobl, and Robert J R Elliott is published by Nature Energy.
END
Battery-powered electric vehicles now match petrol and diesel counterparts for longevity
2025-01-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
MIT method enables protein labeling of tens of millions of densely packed cells in organ-scale tissues
2025-01-24
A new technology developed at MIT enables scientists to label proteins across millions of individual cells in fully intact 3D tissues with unprecedented speed, uniformity, and versatility. Using the technology, the team was able to richly label whole rodent brains and other large tissue samples in a single day. In their new study in Nature Biotechnology, they also demonstrate that the ability to label proteins with antibodies at the single-cell level across whole brains can reveal insights left hidden by other widely used labeling methods.
Profiling the proteins that cells are making is a staple of studies in biology, neuroscience and related fields because the ...
Calculating error-free more easily with two codes
2025-01-24
Computers also make mistakes. These are usually suppressed by technical measures or detected and corrected during the calculation. In quantum computers, this involves some effort, as no copy can be made of an unknown quantum state. This means that the state cannot be saved multiple times during the calculation and an error cannot be detected by comparing these copies. Inspired by classical computer science, quantum physics has developed a different method in which the quantum information is distributed across several entangled quantum bits and stored redundantly in this ...
Dissolving clusters of cancer cells to prevent metastases
2025-01-24
Certain tumour types do not remain at their point of origin but spread throughout the body and form metastases. This is because the primary tumour continuously releases cancer cells into the blood. These circulating tumour cells (CTCs) can join together into small clusters of up to a dozen cells and settle in other organs. There, the clusters grow into larger tumours, known as metastases. Metastatic tumours are still a major medical problem: every year, around seven million people worldwide die from them.
One example of such a spreading tumour is breast cancer. As soon ...
A therapeutic HPV vaccine could eliminate precancerous cervical lesions
2025-01-24
PHILADELPHIA – A therapeutic vaccine targeting human papillomavirus type 16 (HPV16) induced regression in high-grade precancerous cervical lesions, according to the results from a phase II clinical trial published in Clinical Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
“Nearly all premalignant cervical lesions and cervical cancers are caused by HPV infection, with HPV16 implicated in the majority of cases,” said Refika Yigit, MD, principal investigator and oncological gynecologist at University Medical Centre Groningen in the ...
Myth busted: Healthy habits take longer than 21 days to set in
2025-01-24
We’re nearly one month into 2025, but if you’re struggling to hold onto your New Year’s resolution, stay strong, as University of South Australia research shows that forming a healthy habit can take longer than you expect.
In the first systematic review of its kind, UniSA researchers found that new habits can begin forming within about two months (median of 59–66 days) but can take up to 335 days to establish.
It’s an important finding that could inform health interventions to ...
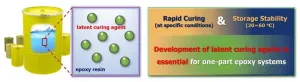
Development of next-generation one-component epoxy with high-temperature stability and flame retardancy
2025-01-24
Two-component epoxies, which require mixing resin and curing agent before use, often suffer from issues such as mixing ratio errors, limited working times, and inconsistent curing. Additionally, they must be used immediately after mixing, leading to wasted residue. To address these challenges, one-component epoxies have gained attention. One-component epoxies come pre-mixed, making them easy to use, reducing processing time, and ensuring consistent quality without mixing. In particular, using latent curing agents allows curing to be triggered only under specific conditions (e.g., heat or UV exposure), significantly improving storage stability. However, ...
Scaling up neuromorphic computing for more efficient and effective AI everywhere and anytime
2025-01-24
Neuromorphic computing—a field that applies principles of neuroscience to computing systems to mimic the brain’s function and structure—needs to scale up if it is to effectively compete with current computing methods. In a review published Jan. 22 in the journal Nature, 23 researchers, including two from the University of California San Diego, present a detailed roadmap of what needs to happen to reach that goal. The article offers a new and practical perspective toward approaching the cognitive capacity of the human brain with comparable form factor and power consumption.
“We ...
Make it worth Weyl: engineering the first semimetallic Weyl quantum crystal
2025-01-24
An international team of researchers led by the Strong Correlation Quantum Transport Laboratory of the RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science (CEMS) has demonstrated, in a world’s first, an ideal Weyl semimetal, marking a breakthrough in a decade-old problem of quantum materials.
Weyl fermions arise as collective quantum excitations of electrons in crystals. They are predicted to show exotic electromagnetic properties, attracting intense worldwide interest. However, despite the careful study of thousands of crystals, most ...
Exercise improves brain function, possibly reducing dementia risk
2025-01-24
A study led by scientists at Rutgers University-New Brunswick has shown that specialized cells involved in how the body responds to insulin are activated in the brain after exercise, suggesting that physical activity may directly improve brain function.
A study, published in Aging Cell, a journal focused on the biology of aging, indicates that therapies targeting this insulin action may be developed to offset or even prevent dementia progression.
“We believe this work is important because it suggests exercise may work to improve cognition and memory by improving the abilities of insulin to act on the brain,” ...
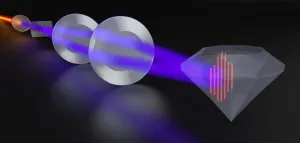
Diamonds are forever—But not in nanodevices
2025-01-24
Ultrawide-bandgap semiconductors—such as diamond—are promising for next-generation electronics due to a larger energy gap between the valence and conduction bands, allowing them to handle higher voltages, operate at higher frequencies, and provide greater efficiency compared to traditional materials like silicon. However, their unique properties make it challenging to probe and understand how charge and heat move on nanometer-to-micron scales. Visible light has a very limited ability to probe nanoscale properties, and moreover, it is not absorbed ...