New dyes pave way for better photothermal cancer treatment and diagnosis
Second near-IR absorbing chemical ring structure promises deeper tissue access
2025-01-25
(Press-News.org)
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have developed a new dye that can strongly absorb second near-IR radiation and transform it to heat. Starting with a dye from the bile pigment family, they designed a unique ring structure which can bind rhodium and iridium. Measurements and modeling revealed strong second near-IR absorptions and exceptional photostability. Second near-IR waves easily penetrate human tissue; the new dye may be applied in deep tissue therapies and imaging.
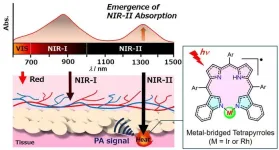
The second near-IR region of the electromagnetic spectrum (1000-1700 nanometers) is a potentially important wavelength range for medical science. In this range, light is not as strongly scattered or absorbed by biological tissue. This transparency makes it ideal for delivering energy into deeper parts of the body, whether for imaging or treatments. An important example of such a therapy is photoacoustic imaging in cancer diagnosis and treatment. When a contrast agent injected into the body is hit with light, it emits heat which creates tiny ultrasonic shocks which can either be detected for imaging, or itself used to damage cancerous cells.
The efficacy of this approach hinges on the availability of stable contrast agents which can efficiently absorb light at these wavelengths. The majority of contrast agents, however, are more sensitive in the first near-IR range (700 – 1000 nanometers), where scattering effects are stronger, and energy delivery is less efficient.
Now, a team of researchers led by Associate Professor Masatoshi Ichida from Tokyo Metropolitan University have developed a new chemical compound which overcomes this Achilles’ heel. Starting with a dye from the bile pigment family called bilatriene, they applied a method known as N-confusion chemistry to modify the ring structure of bilatriene to accept the binding of metal ions. In their most recent work, they successfully incorporated rhodium and indium ions onto the ring via nitrogen atoms.
The team’s new dye showed its strongest light absorption at a wavelength of 1600 nanometers under normal conditions, which is well inside the second near-IR region. It was also shown to be very photostable, meaning that it won’t break apart easily on exposure to light. Detailed measurements of how the molecule responds to magnetic fields, and numerical calculations using density functional theory (DFT) both showed how the unique distribution of electrons in a cloud encompassing the whole, intricate structure of the metal-binding molecule (also known as a pi-radicaloid) gave rise to absorbances which are not possible in existing, similar compounds.
Since the second near-IR is not as strongly absorbed by tissues, regions sensitized with the dye may be exposed more strongly to light, allowing for clearer imaging and better delivery of heat for therapies. The team hopes their molecule will open the door to new approaches to deep tissue medicine, as well as more general applications to chemical catalysis.
This work was supported by JSPS Grant Numbers JP20H00406 and JP22K19937, JST PRESTO Grant Number JPMJPR2103, the Izumi Science and Technology Foundation, Advanced Research Infrastructure for Materials and Nanotechnology in Japan (ARIM) of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) under proposal Number JPMXP1222MS1802, the Cooperative Research Program of NJRC Mater. & Dev., and a Tokyo Global Partner fellowship from Tokyo Metropolitan University.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-01-25
Researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus have found a promising drug candidate that could help restore vision in individuals with multiple sclerosis (MS) and other neurological conditions that damage neurons.
The study was published this week in the journal Nature Communications.
The drug, LL-341070, enhances the brain's ability to repair damaged myelin— the protective sheath around nerve fibers. Damage to myelin is a hallmark of diseases like MS, as well as a natural consequence of aging, often resulting in vision loss, loss of motor skills, ...
2025-01-24
Complex organisms, thousands of times smaller than a grain of sand, can shape massive ecosystems and influence the fate of Earth's climate, according to a new study.
Researchers from Arizona State University, along with their colleagues from the National University of the Peruvian Amazon, have identified an unknown family of microbes uniquely adapted to the waterlogged, low-oxygen conditions of tropical peatlands in Peru’s northwestern Amazonian rainforest.
The new research shows these microbes have a dual role in the carbon cycle and the potential to either ...
2025-01-24
CLEVELAND – University Hospitals is now offering endoscopic spine surgery for patients needing treatment for back pain due to herniated discs in their spine. Xiaofei (Sophie) Zhou, MD, completed Arthrex's Endoscopic Spine Training course to bring this advanced procedure to the health system and recently completed the first endoscopic discectomy utilizing Arthrex technology at UH. The health system is the only one in the greater Cleveland area offering this type of ultra-minimally invasive surgery.
Arthrex's technology allows surgeons to remove the ...
2025-01-24
Reston, VA (January 24, 2025)—The Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) and the European Association of Nuclear Medicine (EANM) have issued a new procedure standard/practice guideline for the use of fibroblast activation protein (FAP) PET. Published in the January issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine, the procedure standard/practice guideline was developed to assist providers in recommending and performing FAP PET, as well as interpreting and reporting results of the imaging studies.
FAP is a transmembrane protein expressed on both cancer-associated fibroblasts and on normal activated fibroblasts involved in wound healing and ...
2025-01-24
The National Science Foundation Convergence Accelerator Program has granted $5 million dollars to Phase 2 of the project “Securing critical material supply chains by enabling phOtovoltaic circuLARity (SOLAR).”
SOLAR’s goal is to proactively ensure circularity of solar panels by providing solutions to barriers throughout the end-to-end supply chain. The intent is to make solar panels recyclable and find a solution to remanufacturing them at a competitive cost. Achieving this will help promote a clean and resilient energy system in the United States.
The three-year project is led by Battelle Memorial Institute ...
2025-01-24
NEW YORK, NY, January 24, 2025 — A team of scientists has developed a groundbreaking approach using specially designed peptides to improve drug formulations. This innovative method significantly enhances anti-tumor efficacy, as demonstrated in leukemia models. The study, published in the journal Chem, was led by researchers at the Advanced Science Research Center at the CUNY Graduate Center (CUNY ASRC) and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center.
Drug delivery systems often face two critical challenges: poor solubility and inefficient delivery within the body. Many drugs do not dissolve well, making it difficult for them to reach ...
2025-01-24
ST. LOUIS, MO, January 24, 2025 - A new collaborative research team of leading plant scientists are developing sorghums with nitrogen-saving traits by utilizing the genetic diversity of wild relatives to improve resilience and productivity for grain sorghum producers.
The project is part of a $38 million investment in nine projects by the U.S. Department of Energy, DOE, Advanced Research Projects Agency-Energy, ARPA-E, to develop advanced technologies for plants to increase nitrogen-use efficiency and reduce nitrogen pollution from U.S. bioenergy feedstocks.
Veena Veena, PhD, MBA, principal investigator and director of the Plant Transformation ...
2025-01-24
Researchers from Mass General Brigham and collaborating institutions have developed a non-invasive approach to manipulate cardiac tissue activity by using light to stimulate an innovative ink incorporated into bioprinted tissue. Their goal is to develop a technique that can be used to repair the heart. Their findings in preclinical models, published in Science Advances, show the transformative potential of non-invasive therapeutic methods to control electrically active tissues.
“We showed for the first time that with this optoelectronically active ink, we can print scaffolds that allow remote control of engineered heart tissues,” said co-corresponding ...
2025-01-24
Boston – Dana-Farber Cancer Institute researchers have identified factors that determine whether donor lymphocyte infusion (DLI), a standard therapy for patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) who have relapsed after allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplant, will successfully move the patient into remission. The team identified that a key cell type in the DLI product and features of the tumor microenvironment in patients both play a role.
The findings were published in Science Immunology.
“Relapse of AML after stem cell transplant is a major challenge,” says first author Katie ...
2025-01-24
LOS ANGELES—January 24, 2025—In patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), a novel analysis evaluating surgeon preference for multi- versus single-arterial grafting may help explain the differing results between prior retrospective analyses and randomized controlled trials regarding long-term survival.
A study presented this week at The Society of Thoracic Surgeons’ 61st Annual Meeting explores findings in more than a million U.S. Medicare beneficiaries who underwent CABG from 2001 to 2019. The researchers found that patients who received multi-arterial grafting (MAG) had improved survival over those who ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New dyes pave way for better photothermal cancer treatment and diagnosis
Second near-IR absorbing chemical ring structure promises deeper tissue access