Relapse is common when someone is trying to quit, regardless of whether they’re giving up opioids or alcohol or cigarettes.
To better inform treatment, researchers with the Fralin Biomedical Research Institute at VTC’s Addiction Recovery Research Center wanted to better understand how the experience of quitting differed across substances.
“When we talk about intervention for addiction, we know that we are far from the ideal model of treatment,” said Rafaela Fontes, a research scientist at the Fralin Biomedical Research Institute and first author on the study, “Beyond the first try: How many quit attempts are necessary to achieve substance use cessation?”
For the study, “quitting” was based on a yes or no response to a survey question that asked whether participants still used a specific substance. Researchers noted that because substance use is a chronically relapsing disorder, the number of quit attempts reported might not be final, although for all participants across all substances, the average time in abstinence was more than seven years.
The work, scheduled for publication in the Feb. 1 issue of Drug and Alcohol Dependence, found that:
Substance use disorder is a chronically relapsing condition that often requires multiple quit attempts before successful abstinence.
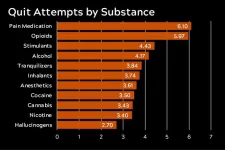
The number of quit attempts varies by substance, with opioids and pain medication requiring significantly more attempts than all other substances.
Hallucinogens are less challenging to quit, requiring fewer attempts.
People who meet the criteria of having a more severe or longer history of substance use disorder might need more attempts before achieving abstinence.
“We treat addiction as an acute disorder, even though we know that it is a chronically relapsing condition,” Fontes said. “When we’re talking about addiction, we need to understand that it’s not one size fits all. There are some substances that are harder to quit than others, and it’s not equally easy or equally hard for everyone. We cannot use the same strategy for everything, because it might not work.”
The findings suggest that early intervention improves success and reduces relapses, according to Allison Tegge, corresponding author on the study and a research associate professor at the Fralin Biomedical Research Institute at VTC.
“What makes this research stand out is that, not only did we consider the substance, but we asked additional questions to look at the individual experience in context,” Tegge said.
What they did
Researchers recruited study participants from the International Quit & Recovery Registry, a tool created to advance scientific understanding of success in overcoming addiction. Sponsored by the Fralin Biomedical Research Institute, it was developed by Professor Warren Bickel, an addiction expert who died in September. Bickel was an author and principal investigator on the substance use cessation research.
“These findings highlight the relevance of the registry and the work started by Dr. Bickel to understand addiction recovery,” Fontes said. “He was a visionary, and his registry continues to help us gain a deeper and better understanding of recovery trajectories.”
The study ultimately drew its findings from 344 registry participants who completed surveys on the substances they had used, the age of first use, the number of quit attempts, and current substance use. Only participants who reported successful abstinence from at least one substance were included.
Participants were asked which they had used 10 or more times: nicotine, alcohol, cannabis, cocaine, opioids, stimulants, prescription pain relievers, hallucinogens, anesthetics, tranquilizers, inhalants, or “other.” They were also asked about length and severity of use, based on criteria from the American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders.
What they found
Participants reported more difficulty quitting pain medication and opioids, substances with high relapse rates and for which short-term treatment effectiveness is low. Both alcohol and stimulants had more quit attempts than cannabis, cocaine, hallucinogens, and nicotine.
Hallucinogens, which have a different clinical profile than other commonly misused substances, required fewer quit attempts. Researchers also found that tranquilizers had a substantially higher number of quit attempts than hallucinogens.
Notably, substances with a higher number of quit attempts were also those that can bring on severe physical symptoms of withdrawal, such as pain, nausea, and anxiety.
The researchers hope their work informs treatment, with a goal of avoiding high rates of relapse and readmission.
“This information can help provide the necessary support for someone moving through recovery,” Tegge said.
Why it matters
The research corroborates the chronic nature of substance use disorder and expands on previous research by showing that the number of quit attempts varies depending on the substance.
Additionally, recognizing that it takes multiple attempts, and understanding how some substances may be more challenging to quit than others, is the first step. “If people in recovery knew the average number of attempts it might take to quit a particular drug, rather than see relapse as a failure they might view it as a step on the journey,” Tegge said. “Understanding that relapse is part of recovery can help people stay engaged.”
The challenges of substances’ physiological effects combined with individual circumstances allows treatment providers to create personalized plans. Knowing different factors that affect relapse can help inform interventions.
In addition to helping inform providers, Fontes also hopes it helps people who are trying to quit. “Maybe they can see that failure is part of the process,” she said, “and think: ‘I just need to keep trying, and eventually I'm going to get there.’”
Authors:
Rafaela Fontes, research scientist, Fralin Biomedical Research Institute at VTC
Allison Tegge, research associate professor, Fralin Biomedical Research Institute at VTC and Department of Basic Science Education, Virginia Tech Carilion School of Medicine
Roberta Freitas-Lemos, assistant professor, Fralin Biomedical Research Institute at VTC and Department of Psychology, College of Science
Daniel Cabral, postdoctoral associate, Fralin Biomedical Research Institute at VTC
Warren Bickel, professor, Fralin Biomedical Research Institute at VTC; Department of Psychology, College of Science; and psychiatry and behavioral medicine, Virginia Tech Carilion School of Medicine END