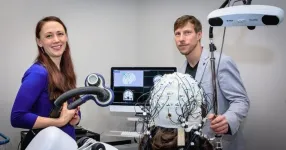
(Press-News.org) In an international effort, researchers at Western University, the University of Maryland School of Dentistry (UMSOD) and Neuroscience Research Australia (NeuRA) uncovered how specific patterns in brain activity can predict an individual’s sensitivity to pain, expanding opportunities for improved pain management strategies.
The new study was published Jan. 27 in JAMA Neurology. It found the combination of two biomarkers in the brain – corticomotor excitability (CME), excitability in the region of the brain that controls movement, and peak alpha frequency (PAF), a neural marker associated with cognitive performance – can accurately and reliably distinguish high- and low-pain sensitive individuals during prolonged pain.
“The burden of chronic pain is massive. Having objective biomarkers would greatly assist with decision making in the diagnosis, prevention and treatment of chronic pain,” said senior author and Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry professor David Seminowicz, who started this study while he was a professor at UMSOD.
For people who suffer from prolonged or chronic pain, this means they could be more effectively treated according to their level of pain sensitivity.
According to recent data from the Global Burden of Disease study, approximately 1.7 billion people around the world live with musculoskeletal conditions, typically characterized by persistent pain, including pain in muscles, bones, joints, ligaments and tendons. Living with prolonged pain can be debilitating and affect a person’s ability to work or socialize. Currently, there is a lack of effective treatments for chronic pain and a gap in understanding the transition from acute to chronic pain.
“For the first time we have something that looks like it could predict pain outcome for people,” said Siobhan Schabrun, co-author and professor at Western’s School of Physical Therapy.
The researchers looked specifically at jaw pain typically attributed to problems with the joint or muscles in the jaw, also known as temporomandibular disorders.
The study involved 150 participants in Australia, aged 18 to 44. PAF, the brain biomarker associated with cognitive performance, was measured using electroencephalography (EEG) recording, which records electrical activity in the brain using electrodes. CME, the biomarker related to excitability, was measured through transcranial magnetic stimulation, where nerve cells in the brain are stimulated using magnetic fields.
This research was a collaborative effort between Nahian Chowdhury, research fellow at NeuRA, who led the data collection; a statistical team led by University of Maryland School of Medicine postdoctoral fellow Chuan Bi and professor Shuo Chen; and principal investigator of the UMSOD site, assistant professor Joyce Teixeira Da Silva.
Slow PAF and low CME indicates higher pain sensitivity
“Our results suggest individuals who have slow PAF prior to a prolonged pain episode and reduced CME shortly after the onset of a prolonged pain episode are more likely to experience higher pain days or weeks later.” explained Seminowicz.
Additional findings from complementary studies indicate individuals with low levels of CME during the acute stages of low back pain were more likely to develop chronic pain after six months.
The new research also shows potential to measure PAF and CME in pre-operative and post-injury settings to identify whether a patient has high- or low-pain sensitivity.
Based on previous literature that found higher acute pain can predict the development of chronic pain, the researchers suggest these biomarkers, PAF and CME, could potentially be used to gauge a person's likelihood of developing chronic pain after an experience with acute pain.
‘A major leap forward’
“This study represents a major leap forward in the field of pain science. A biomarker that can predict pain sensitivity with 88 per cent accuracy has the potential to transform the treatment and prevention of pain in future,” said Schabrun, who is also William and Lynne Gray Endowed Research Chair in Mobility and Activity at St. Joseph’s Health Care London.
Backed by the high rates of accuracy, reproducibility and reliability of their study, the researchers are now working to validate the biomarker in clinical populations to explore clinical translation, including predicting the transition from acute to chronic clinical pain.
“This would allow us to target treatments toward people with acute pain who are likely to transition to chronic pain,” said Schabrun. “If these brain biomarkers can predict that occurrence in future, we hope to be able to interfere with the transition to chronic pain to provide better patient outcomes.”
END
Researchers uncover new approach to predict pain sensitivity
Two biomarkers could transform the way chronic pain is understood and managed
2025-01-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
‘Embodied energy’ powers modular worm, jellyfish robots
2025-01-27
ITHACA, N.Y. – In the same way that terrestrial life evolved from ocean swimmers to land walkers, soft robots are progressing, too, thanks to recent Cornell University research in battery development and design.
A modular worm robot and jellyfish demonstrate the benefits of “embodied energy” – an approach that incorporates power sources into the body of a machine, to reduce its weight and cost.
The worm and jellyfish are direct descendants of an aqueous soft robot, inspired by a lionfish and unveiled in 2019, that could store energy and power its applications via a circulating hydraulic fluid – i.e., “robot blood.” Similar blood sustains ...
Hebrew SeniorLife’s Deanna and Sidney Wolk Center for Memory Health recognized as an age-friendly health system
2025-01-27
Hebrew SeniorLife, New England’s largest nonprofit provider of senior health care and living communities and the only senior care organization affiliated with Harvard Medical School, announces that its Deanna and Sidney Wolk Center for Memory Health has been recognized by the Institute of Healthcare Improvement (IHI) as an Age-Friendly Health System, level 2, Committed to Care Excellence.
To qualify as an Age-Friendly Health System, level 2, the Wolk Center, which provides comprehensive outpatient care related to brain health, cognitive and behavioral problems, and memory loss, whether due to Alzheimer’s disease, other dementias, or other neurological or psychiatric ...
Scientists develop ultra-thin absorbers with record-breaking bandwidth
2025-01-27
Absorbing layers have been fundamental to advancements in technologies like energy harvesting, stealth systems, and communication networks. These absorbers efficiently capture electromagnetic waves across broad frequency ranges, enabling the development of sustainable, self-powered devices such as remote sensors and internet of things (IoT) systems. In addition to energy applications, these layers are pivotal in stealth technology, where they minimize radar visibility and enhance the performance of aircraft and naval systems. They also play a crucial role in improving communication networks by reducing ...
Floating solar increases greenhouse gas emissions on small ponds
2025-01-27
ITHACA, N.Y. – While floating solar – the emerging practice of putting solar panels on bodies of water – is promising in its efficiency and its potential to spare agricultural and conservation lands, a new experiment finds environmental trade-offs.
In the first manipulative field study examining the environmental impacts of floating solar, published in Environmental Science and Technology, researchers found that floating solar panels increased greenhouse gas emissions on small ponds by nearly 27%.
“There ...
Cancer risk established before birth
2025-01-27
GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (Jan. 27, 2025) — A person’s lifetime risk for cancer may begin before they are even born, reports a paradigm-shifting study by Van Andel Institute scientists.
The findings, published in Nature Cancer, identified two distinct epigenetic states that arise during development and are linked to cancer risk. One of these states is associated with a lower lifetime risk while the other is associated with a higher lifetime risk.
If cancer does develop in the lower risk state, it ...
Sinking truths: University of Houston confirms Miami’s coastal subsidence challenges
2025-01-27
On the barrier islands of Miami, 35 skyscrapers – including Trump Tower III - have sunk as much as eight centimeters, or three inches, into the ground since 2016, and researchers from the University of Houston have played a pivotal role in uncovering the reason why – urban development.
The findings, published in Earth and Space Science, reveal alarming rates of subsidence – or land sinking – in coastal structures between 2016 and 2023.
According to the report, "About half of the subsiding structures are younger than 2014 and at the majority of them subsidence decays with ...
Sun receives funding for CyberCorps scholarship for service
2025-01-27
Kun Sun, Professor, Information Sciences and Technology, Center for Secure Information Systems, College of Engineering and Computing (CEC), received funding for: “CyberCorps Scholarship for Service: EAGLE: Empowering American Government Leadership in Cybersecurity through Education.”
Due to the proliferation of cyber-attacks, the ...
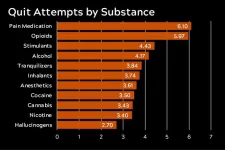
If at first you don’t succeed: Virginia Tech researchers ask how many attempts it takes to quit substance abuse
2025-01-27
Relapse is common when someone is trying to quit, regardless of whether they’re giving up opioids or alcohol or cigarettes.
To better inform treatment, researchers with the Fralin Biomedical Research Institute at VTC’s Addiction Recovery Research Center wanted to better understand how the experience of quitting differed across substances.
“When we talk about intervention for addiction, we know that we are far from the ideal model of treatment,” said Rafaela Fontes, a research scientist at the Fralin Biomedical Research Institute and first author on the study, “Beyond ...
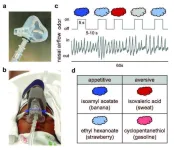
Characterizing olfactory brain responses in young infants
2025-01-27
The sense of smell promotes adaptive behaviors such as feeding and soothing, but how early humans begin to process odors represents a gap in knowledge for researchers. In a new study in JNeurosci, Thorsten Kahnt from the National Institute on Drug Abuse and colleagues explored olfaction development in humans and reveal how early humans begin to smell. The researchers used fMRI to image the brains of sleeping infants as they inhaled appetitive (pleasant) and aversive (unpleasant) odors. As early as one month of age, odors triggered activity in brain regions strongly associated ...
Underwater mud volcanos are a haven for marine organisms
2025-01-27
The underwater volcano Borealis Mud Volcano is located in the Barents Sea and was first discovered by researchers at UiT The Arctic University of Norway in 2023. The discovery received a lot of attention, and images of the volcano circulated around the world. Now researchers from UiT, in collaboration with REV Ocean, have finally published the results from an interdisciplinary investigation showing that Borealis mud volcano has a unique ecological role as a natural sanctuary for several marine species in the Barents Sea.
While some parts of the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
[Press-News.org] Researchers uncover new approach to predict pain sensitivityTwo biomarkers could transform the way chronic pain is understood and managed