(Press-News.org) Background and Goal: Despite the removal of the X-waiver requirement, which once restricted clinicians from prescribing buprenorphine for opioid use disorder (OUD), only a small percentage of primary care clinicians currently prescribe medication for OUD (MOUD). This study evaluated a structured support program to help small, rural primary care clinics improve their capacity to provide this treatment.
Study Approach: Researchers worked with 15 primary care practices in Colorado over a 12-month period from January 2022 through January 2023. The program provided clinics with monthly educational sessions, direct access to an addiction medicine specialist, and support from practice facilitators to achieve specific milestones in MOUD implementation.. The researchers measured changes in buprenorphine prescribing and milestone completion rates at baseline and at 12 months.
Main Results:
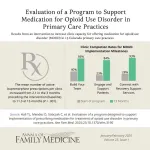
The average number of active buprenorphine prescriptions per clinic increased significantly from 2.1 in the three months preceding the intervention (baseline) to 11.3 at 13 months.
Clinic completion rates for MOUD implementation milestones also showed significant improvements:
Core Aim 1 ("Build Your Team"): Increased from 40% at the start of the program to 93% at 12 months
Core Aim 2 ("Engage and Support Patients"): Increased from 23% to 84%
Core Aim 3 ("Connect with Recovery Support Services"): Increased from 28% to 93%
Why It Matters: The findings from this study highlight a potentially scalable and effective model to expand access to MOUD in rural communities, where treatment options for opioid use disorder are often limited.
Evaluation of a Program Designed to Support Implementation of Prescribing Medication for Treatment of Opioid Use Disorder in Primary Care Practices
Tristen L. Hall, PhD, MPH, et al
University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Aurora, Colorado
PERMANENT LINK
END
Support program for small, rural primary care clinics increases their ability to prescribe buprenorphine for opioid use disorder fivefold
Evaluation of a program designed to support implementation of prescribing medication for treatment of opioid use disorder in primary care practices
2025-01-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Peer health navigators improve health equity and patient well-being for transgender and gender-diverse patients
2025-01-27
Background and Goal: Transgender and gender-diverse individuals often experience additional difficulties navigating health care. This study examined the effectiveness of a peer health navigator pilot program in Saskatchewan, Canada that aimed to improve access to affirming health care for transgender and gender-diverse individuals.
Study Approach: Two peer health navigators were recruited to pilot the program. The navigators were required to be transgender or gender diverse and have experience in health care or community-based organizations. Navigators supported clients by providing information on gender transition and ...
Flexible practice-centric approach improves behavioral health integration in primary care practices
2025-01-27
ackground and Goal: Integrated behavioral health (IBH), which combines behavioral health and primary care, improves patient outcomes and experience. This study evaluated whether a tailored, toolkit-based intervention could improve IBH and patient outcomes in primary care practices serving patients with multiple chronic medical and behavioral health conditions.
Study Approach: The study used a cluster randomized controlled trial design. Practices were randomized into two groups. The intervention arm received ...
Study highlights general practitioner strategies to ease type 2 diabetes management burden
2025-01-27
Background and Goal: Managing type 2 diabetes involves complex treatment, workload, and costs that impose a significant burden on individuals, impacting their physical and mental health. This study examines how general practitioners (GPs) in China identify and respond to these burdens during patient consultations.
Study Approach: The study examined video recordings of 29 GP-patient consultations recorded between 2018 and 2019 in a primary care clinic in China. Researchers reviewed these consultations for discussions related to treatment burdens in managing type 2 diabetes and analyzed the interviews to identify specific burdens and the strategies GPs employed to address them.
Main ...
Special report proposes strategies for preserving diversity in medicine after reshaped affirmative action policies
2025-01-27
Background and Goal: In 2023, the Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) struck down race-conscious admissions in higher education, reshaping affirmative action policies. This special report examines the ruling’s wide-reaching effects, particularly on underrepresented minority (URM) students, and proposes strategies for preserving diversity in higher education and professional fields, including medicine.
Key Insights: Institutions such as MIT and Amherst College have reported significant declines in Black and Latino student enrollment. In medical school admissions, the lack of standardized guidelines ...
Annals of Family January/February 2025 Tip Sheet
2025-01-27
Editorial
Family Medicine Journal Editors Suggest Guiding Principles for AI Use in Publishing
Background: This editorial by editors of family medicine journals provides a unified stance on the use of artificial intelligence (AI) in family medicine research and publishing.
Editorial Stance: Family medicine journals must address the implications of AI, including ethical considerations, accuracy, and potential for bias. The authors recommend guiding principles for AI use in family medicine publishing, emphasizing:
Full disclosure of AI tool use in research and manuscript preparation
Accountability ...
International disease classification codes ambiguities create challenges in comparing respiratory infection diagnosis
2025-01-27
Background and Goal: The International Classification of Diseases (ICD) system standardizes diagnostic codes globally, enabling accurate comparisons of health data. This study investigated regional differences in respiratory infection diagnoses in Poland to identify potential ambiguities in ICD coding and their implications for data comparability.
Study Approach: Researchers analyzed over 292 million primary care visits for acute respiratory infections in Poland between 2010 and 2019, using ICD-10 codes (J00–J22). Diagnosis data were ...
Family medicine department chairs face high patient care demands and barriers to scholarly activity
2025-01-27
Background and Goal: Research in family medicine is vital for improving patient care, health care systems, and population health. However, family medicine faces barriers to producing scholarly work, including high patient care demands and limited funding. This study examined whether financial incentives and department size influence the amount and type of scholarly activity produced by family medicine departments.
Study Approach: Researchers surveyed family medicine department chairs across the U.S. and Canada using a Council of Academic Family Medicine Educational Research Alliance (CERA) questionnaire. The survey gathered data ...
AI in primary care should address time spent on electronic health records and other real-world needs
2025-01-27
Background and Goal: Primary care clinicians face significant burnout, driven by excessive administrative tasks and time spent on electronic health records (EHRs). This report emphasizes that generative AI tools must focus on addressing specific, impactful problems.
Key Insights: The Segway, once expected to revolutionize transportation, failed because it did not solve a real need. Conversely, rentable scooters succeeded by addressing a narrow, specific problem: the “last-mile” challenge in urban commutes. Similarly, AI in primary care must tackle clinicians' “last-mile” issue—time. With over half of ...
Motivational interviewing techniques and reframing universal screening for patients with alcohol abuse or risk reduces stigma
2025-01-27
The AHRQ EvidenceNOW initiative, launched in 2019, implemented a comprehensive approach to help primary care practices reduce stigma and better serve patients who exhibit risky or harmful alcohol use.
The program engaged practice facilitators (PFs) to support primary care practices in integrating universal screening, brief interventions, and medication-assisted therapy/medication for alcohol use disorders. PFs trained clinicians to use person-centered communication, and modeled empathetic and nonjudgmental interactions, to normalize unhealthy alcohol use screenings. PFs also taught clinicians ...
former NIJ director proposes new framework to enhance rigor, impact of criminal justice intervention evaluations
2025-01-27
Experimental research is fundamental to criminology, but reaching consensus on rigorous evidence and using that evidence to determine what works remains an ongoing challenge to the field. In a new article, the former director of the National Institute of Justice (NIJ) within the U.S. Department of Justice’s Office of Justice programs, proposes a framework to situate both the role of rigorous evaluation and its results in a more robust understanding of the effectiveness of social programs. According to her new framework, the more deliberate the implementation of a social program, the more likely it will yield its intended impact.
“Deliberate implementation can ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
[Press-News.org] Support program for small, rural primary care clinics increases their ability to prescribe buprenorphine for opioid use disorder fivefoldEvaluation of a program designed to support implementation of prescribing medication for treatment of opioid use disorder in primary care practices