(Press-News.org) The microbial ecosystems within our mouths may affect our cognitive function as we age, according to a study. Interventions such as prebiotics, including dietary nitrate, have potential for delaying cognitive decline.
About 15% of older adults have mild cognitive impairment, which is the largest risk factor for the development of dementia or Alzheimer’s disease. There is a known association between periodontitis—gum disease—and worsened cognitive function. Researchers have identified two possible links between the mouth and the mind: pathogenic oral bacteria could enter the bloodstream and move to the brain, or pathogenic oral bacteria could displace nitrate-reducing bacteria, which help create nitric oxide the brain needs for synaptic plasticity and long-term potentiation. Anni Vanhatalo and colleagues characterized the oral microbiome of 115 participants, 55 of whom had mild cognitive impairment. Some participants had the apolipoprotein E4 (APOE4) allele, which increases risk for cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease. A high relative abundance of bacteria in the genus Neisseria was associated with better executive function and visual attention within the mild cognitive impairment group. Among healthy participants, Neisseria correlated with working memory. High prevalence of bacteria in the genus Porphyromonas predicted mild cognitive impairment status, while Prevotella intermedia predicted APOE4-carrier status. According to the authors, diet can affect the oral microbiome, and a nitrate-rich diet (such as the Mediterranean and ‘Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension’ diets), favors bacteria associated with good cognitive outcomes.
END
The oral microbiome and dementia
2025-01-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Paywalls shape newspaper coverage
2025-01-28
Adopting paywalls subtly shapes newspaper coverage, according to a study. Online journalism is increasingly found behind paywalls, as outlets pivot from funding their operations by selling ads to relying on subscriptions for revenue. This shift has raised questions about how newspapers might adjust their coverage to cater to paid subscribers' desires for popular news and soft news—entertainment, lifestyle, sports, and human-interest stories—at the expense of providing local news and maintaining democratic accountability. Paramveer S. Dhillon ...
Escaping the endosome: Bend lipids improve LNP mRNA delivery and gene editing
2025-01-28
Every time a shuttle docks with the International Space Station (ISS), a delicate dance unfolds between the shuttle's docking system and its counterpart on the station. Thanks to international standards, these mechanisms are universally compatible, ensuring astronauts and cargo can safely and seamlessly enter the station.
A similar challenge arises at the microscopic level when lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) — the revolutionary drug delivery vehicles behind the COVID-19 vaccines — attempt to deliver mRNA to cells. Optimizing the design and delivery of LNPs can greatly enhance their ability to deliver mRNA successfully, ...
Could fecal microbiota transplantation help patients heal after stem cell transplantation?
2025-01-28
SEATTLE — Jan. 28, 2025 — A new study shows that oral fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) is a feasible and safe addition to preventing graft-versus-host disease in patients undergoing stem cell transplantation for blood cancers.
The study, published Jan. 25 in Nature Communications, is part of a phase 2 clinical trial led by clinicians at Fred Hutch Cancer Center. The study builds on earlier research of the role of the gut microbiome in helping patients recover after stem cell transplantation.
“The gut microbiome is an organ in itself, and it is connected to the immune system,” said lead author Armin ...
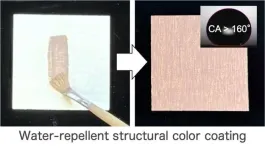
Structural color shields: water repellent coatings
2025-01-28
Ever wondered about the brilliant blue hues of peacock feathers or the shimmering metallic chitin on beetles? These natural wonders are examples of structural colors—a phenomenon in which microscopic structures create vibrant, lasting hues. Inspired by these marvels, a research team from Japan has been exploring structural colors. Their earlier work realized that the preparation of structural color materials from melanin particles mimics the coloration mechanism of peacock feathers. Building on this foundation, the team set out to develop a coating material that captures ...
Researchers enhance wildlife studies with novel prey measurement technique using animal-borne cameras
2025-01-28
A team of international scientists, led by researchers from the University of Otago, has introduced a groundbreaking method to improve the accuracy of prey size estimation using footage captured by animal-borne cameras. This innovative approach, published in PeerJ Life and Environment, enhances our understanding of predator-prey interactions in natural habitats by refining a critical tool for ecological research.
Animal-borne cameras, such as the "PenguCams" used in this study, allow ...
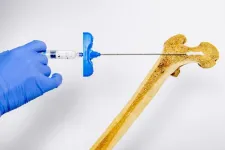
An injectable hydrogel for local bone densification
2025-01-28
Osteoporosis is a disease in which bone resorbs faster than it is formed, gradually weakening its structure over time and leading to fractures. Although the condition is well recognized, Dominique Pioletti, head of the Laboratory of Biomechanical Orthopedics in EPFL’s School of Engineering, emphasizes that the economic and societal impacts of osteoporosis fractures are often underestimated.
“In the absence of effective preventive measures, around 40% of women aged 50 will suffer at least one major osteoporotic fracture; in ...
Forgery and fiscal fraud: a new papyrus from Israel reveals a spectacular criminal case from the Roman empire
2025-01-28
Scholars from the Austrian Academy of Sciences, the University of Vienna and the Hebrew University of Jerusalem unveil a unique papyrus from the collections held by the Israel Antiquities Authority, offering rare insights into Roman legal proceedings and life in the Roman Near East. In a new publication in the international scholarly journal Tyche, the research team reveals how the Roman imperial state dealt with financial crimes – specifically, tax fraud involving slaves – in the Roman provinces of Iudaea and Arabia. The new papyrus furnishes a strikingly direct view of Roman jurisdiction and legal practice, as well as important new information ...
A super-Earth laboratory for searching life elsewhere in the Universe
2025-01-28
Thirty years after the discovery of the first exoplanet, we detected more than 7000 of them in our Galaxy. But there are still billions
more to be discovered! At the same time, exoplanetologists have begun to take an interest in their characteristics, with the aim of finding life elsewhere in the Universe. This is the background to the discovery of super-Earth HD 20794 d by an international team including the University of Geneva (UNIGE) and the NCCR PlanetS. The new planet lies in an eccentric orbit, so that it oscillates in and out of its ...
Testing the effect of thousands of compounds on cellular metabolism
2025-01-28
Researchers at the University of Basel are able to test in parallel the effects of over 1500 active substances on cell metabolism. Their analysis also led to the discovery of previously unknown mechanisms for known medications. This approach might help scientists to better predict side effects and find additional uses for commercially available pharmaceuticals.
How do active substances alter metabolic processes in cells? Answering that question would provide valuable clues for the development of new medications. ...
Follow the water: Searching for a lunar oasis
2025-01-28
As humankind imagines living off-planet — on the moon, Mars and beyond — the question of how to sustain life revolves around the physical necessities of oxygen, food and water. We know there is water on the moon, but how do we find it? Is it in the craters? The shadowed regions? The poles? Knowing where to look gives astronauts the best chance at successfully living on the moon, something that has, heretofore, remained the stuff of science fiction.
Researchers from the University of California ...