(Press-News.org) PULLMAN, Wash. — An environmentally-friendly preparation of plant material from pine could serve as a substitute for petroleum-based chemicals in polyurethane foams.
The innovation could lead to more environmentally friendly versions of foams used ubiquitously in products such as kitchen sponges, foam cushions, coatings, adhesives, packaging and insulation. The global market for polyurethane totaled more than $75 billion in 2022.
A Washington State University-led research team used an environmentally-friendly preparation of lignin as a substitute for 20% of the fossil fuel-based chemicals in the foam. The bio-based foam was as strong and flexible as typical polyurethane foam. They report on their work in the journal, ACS Sustainable Chemistry and Engineering.
“It’s quite novel in terms of the material we generate and the process we have,” said Xiao Zhang, corresponding author on the paper and professor in the Gene and Linda Voiland School of Chemical Engineering and Bioengineering. “Our extracted lignin offers a new class of renewable building blocks for the development of bio-based value-added products.”
Petroleum-based plastic materials are an increasing waste problem. They take centuries to break down, but they are expensive and difficult to recycle, most often producing an inferior second-generation product. Because it costs more to recycle than to generate new plastic, the plastics recycling rate has consistently stayed below 20%, said Zhang.
“It’s basically a no-win situation if you’re using petroleum-based plastics,” he said. “The ultimate solution is to replace them with naturally derived materials.”
Lignin is the second most abundant renewable carbon source, making up about 30% of the non-fossil fuel-based carbon on Earth. It is also notoriously difficult to extract from plants. The material is usually separated during papermaking and biorefining, but these processes often contaminate and significantly alter its chemical and physical properties, decreasing its value. So most lignin is either burned to produce fuel and electricity or used in low-value products, such as for cement additives or as a binder in animal feed.
In their work, the researchers used a mild, environmentally friendly solvent to separate a high-quality lignin from pine. Compared to other lignin formulations, their formulation was homogenous with good thermal stability — similar to native lignin. The structural homogeneity is important in being able to produce high-value products.
When they tested their formulation, their product was stable and performed as well mechanically as the conventional foams.
“This work demonstrates that our prepared lignin formulation has a great potential for generating flexible, bio-based polyurethane foams,” said Zhang.
The interest in developing lignin-based polyurethane (PU) flexible foam work was also validated by industrial partners. Zhang’s team will now work with the industrial partners to optimize and scale up lignin PU foam production.
The work was funded by the National Science Foundation’s Industry-University Cooperative Research Center for Bioplastics and Biocomposites (CB2), the USDA National Institute of Food and Agriculture programs, and WSU’s Office of Commercialization.
END
Plant-based substitute for fossil fuels developed for plastic foams
2025-01-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Q&A: How rate of CO2 rise can affect a global ocean current
2025-01-28
As we burn fossil fuels, the amount of carbon dioxide in Earth’s atmosphere is gradually rising, and with it, the planet’s average temperature. How fast the level of atmospheric carbon dioxide — and with it, the temperature — goes up matters for the ability of humans and ecosystems to adjust. A slower increase gives humans time to move away from low-lying coasts and animals time to move to new habitats.
It turns out the rate of that increase matters for non-living systems, too. A recent University of Washington study looked at how a major current in the Atlantic Ocean that includes the Gulf Stream will respond ...
The oral microbiome and dementia
2025-01-28
The microbial ecosystems within our mouths may affect our cognitive function as we age, according to a study. Interventions such as prebiotics, including dietary nitrate, have potential for delaying cognitive decline.
About 15% of older adults have mild cognitive impairment, which is the largest risk factor for the development of dementia or Alzheimer’s disease. There is a known association between periodontitis—gum disease—and worsened cognitive function. Researchers have identified two possible links between the mouth and the mind: pathogenic ...
Paywalls shape newspaper coverage
2025-01-28
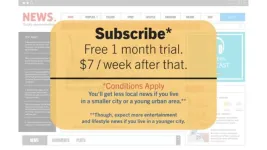
Adopting paywalls subtly shapes newspaper coverage, according to a study. Online journalism is increasingly found behind paywalls, as outlets pivot from funding their operations by selling ads to relying on subscriptions for revenue. This shift has raised questions about how newspapers might adjust their coverage to cater to paid subscribers' desires for popular news and soft news—entertainment, lifestyle, sports, and human-interest stories—at the expense of providing local news and maintaining democratic accountability. Paramveer S. Dhillon ...
Escaping the endosome: Bend lipids improve LNP mRNA delivery and gene editing
2025-01-28
Every time a shuttle docks with the International Space Station (ISS), a delicate dance unfolds between the shuttle's docking system and its counterpart on the station. Thanks to international standards, these mechanisms are universally compatible, ensuring astronauts and cargo can safely and seamlessly enter the station.
A similar challenge arises at the microscopic level when lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) — the revolutionary drug delivery vehicles behind the COVID-19 vaccines — attempt to deliver mRNA to cells. Optimizing the design and delivery of LNPs can greatly enhance their ability to deliver mRNA successfully, ...
Could fecal microbiota transplantation help patients heal after stem cell transplantation?
2025-01-28
SEATTLE — Jan. 28, 2025 — A new study shows that oral fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) is a feasible and safe addition to preventing graft-versus-host disease in patients undergoing stem cell transplantation for blood cancers.
The study, published Jan. 25 in Nature Communications, is part of a phase 2 clinical trial led by clinicians at Fred Hutch Cancer Center. The study builds on earlier research of the role of the gut microbiome in helping patients recover after stem cell transplantation.
“The gut microbiome is an organ in itself, and it is connected to the immune system,” said lead author Armin ...
Structural color shields: water repellent coatings
2025-01-28
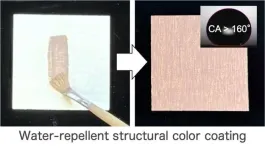
Ever wondered about the brilliant blue hues of peacock feathers or the shimmering metallic chitin on beetles? These natural wonders are examples of structural colors—a phenomenon in which microscopic structures create vibrant, lasting hues. Inspired by these marvels, a research team from Japan has been exploring structural colors. Their earlier work realized that the preparation of structural color materials from melanin particles mimics the coloration mechanism of peacock feathers. Building on this foundation, the team set out to develop a coating material that captures ...
Researchers enhance wildlife studies with novel prey measurement technique using animal-borne cameras
2025-01-28
A team of international scientists, led by researchers from the University of Otago, has introduced a groundbreaking method to improve the accuracy of prey size estimation using footage captured by animal-borne cameras. This innovative approach, published in PeerJ Life and Environment, enhances our understanding of predator-prey interactions in natural habitats by refining a critical tool for ecological research.
Animal-borne cameras, such as the "PenguCams" used in this study, allow ...
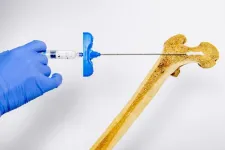
An injectable hydrogel for local bone densification
2025-01-28
Osteoporosis is a disease in which bone resorbs faster than it is formed, gradually weakening its structure over time and leading to fractures. Although the condition is well recognized, Dominique Pioletti, head of the Laboratory of Biomechanical Orthopedics in EPFL’s School of Engineering, emphasizes that the economic and societal impacts of osteoporosis fractures are often underestimated.
“In the absence of effective preventive measures, around 40% of women aged 50 will suffer at least one major osteoporotic fracture; in ...
Forgery and fiscal fraud: a new papyrus from Israel reveals a spectacular criminal case from the Roman empire
2025-01-28
Scholars from the Austrian Academy of Sciences, the University of Vienna and the Hebrew University of Jerusalem unveil a unique papyrus from the collections held by the Israel Antiquities Authority, offering rare insights into Roman legal proceedings and life in the Roman Near East. In a new publication in the international scholarly journal Tyche, the research team reveals how the Roman imperial state dealt with financial crimes – specifically, tax fraud involving slaves – in the Roman provinces of Iudaea and Arabia. The new papyrus furnishes a strikingly direct view of Roman jurisdiction and legal practice, as well as important new information ...
A super-Earth laboratory for searching life elsewhere in the Universe
2025-01-28
Thirty years after the discovery of the first exoplanet, we detected more than 7000 of them in our Galaxy. But there are still billions
more to be discovered! At the same time, exoplanetologists have begun to take an interest in their characteristics, with the aim of finding life elsewhere in the Universe. This is the background to the discovery of super-Earth HD 20794 d by an international team including the University of Geneva (UNIGE) and the NCCR PlanetS. The new planet lies in an eccentric orbit, so that it oscillates in and out of its ...