(Press-News.org) A new study published today in JAMA Network Open explores the effects of both recent and lifetime cannabis use on brain function during cognitive tasks.
The study, the largest of its kind ever to be completed, examined the effects of cannabis use on over 1,000 young adults aged 22 to 36 using brain imaging technology. The researchers found that 63% of heavy lifetime cannabis users exhibited reduced brain activity during a working memory task, while 68% of recent users also demonstrated a similar impact.
This decline in brain activity was associated with worse performance on working memory - the ability to retain and use information to perform tasks. For example, working memory allows a person to follow instructions they’ve just been given or to mentally visualize and manipulate information, like solving a math problem.
“As cannabis use continues to grow globally, studying its effects on human health has become increasingly important. By doing so, we can provide a well-rounded understanding of both the benefits and risks of cannabis use, empowering people to make informed decisions and fully comprehend the potential consequences," said the study’s first author Joshua Gowin, PhD, assistant professor of radiology at the University of Colorado School of Medicine on the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus.
In the study, heavy users are considered young adults who’ve used cannabis more than 1000 times over their lifetime. Whereas, using 10 to 999 times was considered a moderate user and less than 10 times was considered a nonuser.
The researchers studied the neural response of participants during a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) session and gave them seven cognitive tasks to complete. The tasks tested working memory, reward, emotion, language, motor skills – such as tapping a finger to map brain control, relational assessment and theory of mind.
The researchers found that cannabis had a statistically significant effect on brain function during working memory tasks, meaning the observed impact is very unlikely to be due to random chance. This effect was seen in both recent and lifetime cannabis users. The impact was less significant for the other tasks.
"We applied the highest standards to our research, setting rigorous thresholds for statistical significance across all seven cognitive function tests. To minimize the risk of false positives, we employed false discovery rate (FDR) correction. While some of the other tasks indicated potential cognitive impairment, only the working memory task showed a statistically significant impact,” adds Gowin.
During working memory tasks, the researchers found heavy cannabis use appeared to reduce brain activity in certain areas of the brain (dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, dorsomedial prefrontal cortex and anterior insula). These regions of the brain are involved in important cognitive functions such as decision-making, memory, attention and emotional processing.
However, Gowin mentions their research also suggests that abstaining from using cannabis before doing a cognitive task could help to improve performance. “People need to be aware of their relationship with cannabis since abstaining cold turkey could disrupt their cognition as well. For example, heavy users may need to be more cautious,” Gowin says.
He adds, “There are a lot of questions we still need answers to regarding how cannabis impacts the brain. Large, long-term studies are needed next to understand whether cannabis use directly changes brain function, how long these effects last and the impact on different age groups.”
About the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus
The University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus is a world-class medical destination at the forefront of transformative science, medicine, education and patient care. The campus encompasses the University of Colorado health professional schools, more than 60 centers and institutes and two nationally ranked independent hospitals - UCHealth University of Colorado Hospital and Children's Hospital Colorado – which see more than two adult and pediatric patient visits yearly. Innovative, interconnected and highly collaborative, the CU Anschutz Medical Campus delivers life-changing treatments, patient care and professional training and conducts world-renowned research fueled by $910 million in annual research funding, including $757 million in sponsored awards and $153 million in philanthropic gifts.
END
Largest study ever done on cannabis and brain function finds impact on working memory
The study looked at the effect of cannabis use on young adults who are recent or heavy users
2025-01-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Brain function outcomes of recent and lifetime cannabis use
2025-01-28
About The Study: Lifetime history of heavy cannabis use was associated with lower brain activation during a working memory task in this study of young adults. These findings identify negative outcomes associated with heavy lifetime cannabis use and working memory in healthy young adults that may be long lasting.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Joshua L. Gowin, PhD, email joshua.gowin@cuanschutz.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.57069)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including ...
Nourishing T cells to fight cancer
2025-01-28
Researchers from the University of Pittsburgh have developed a new way to grow T cells in the lab that enables them to live longer and better destroy cancer cells in a mouse model of melanoma compared to those grown in traditional growth media.
The findings, published recently in Cell Metabolism, have the potential to greatly improve the effectiveness of cancer immunotherapies that involve taking T cells from a patient and growing them to enormous numbers in the lab before reinfusing them back into the body.
“The way we traditionally grow T cells ...
Temperature exposure and psychiatric symptoms in adolescents from 2 European birth cohorts
2025-01-28
About The Study: In this cohort study, exposure to cold in the Netherlands and heat in Spain were associated with more psychiatric symptoms, highlighting distinct temperature exposure and mental health associations among adolescents. Future studies should explore this across diverse climates to further quantify the intricate and multifactorial association of climate change with mental health.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Monica Guxens, MD, email monica.guxens@isglobal.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.56898)
Editor’s ...
Severe maternal morbidity associated with chronic hypertension, preeclampsia, and gestational hypertension
2025-01-28
About The Study: In pregnant patients with uncomplicated chronic hypertension, prevention of preeclampsia may potentially reduce severe maternal morbidity risk comparable to normotensive patients.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Erica P. Gunderson, PhD, MPH, email erica.gunderson@kp.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.51406)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding ...
Standardizing provider assessments reveals important information about gun and opioid access for veterans at risk of suicide
2025-01-28
PHILADELPHIA—Standardizing an assessment process currently used by doctors during care discussions with veterans at risk for suicide in other context could shed more light on the risks related to firearms and opioids.
The findings from researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania were reported today in JAMA Network Open. They found that fewer veterans reported having access to firearms than expected—either because some didn't mention it to their doctor, it wasn't ...
The environmental and economic impact of COVID-19 on Japan’s tourism industry
2025-01-28
Fukuoka, Japan—It goes without saying that the tourism industry in Japan is booming. Walk around any major city and you’ll see people from all around the world enjoying the country’s food, culture, and hospitality. Naturally, the revenue generated by the industry has had a positive economic impact throughout Japan. However, between 2020 and 2022, the tourism industry was hit particularly hard due to the COVID-19 pandemic and subsequent travel restrictions. While the government implemented policies ...
Study reveals gaps in healthcare quality assessments across Israel, the US, and the UK
2025-01-28
A new study has taken a closer look at how healthcare quality is measured in three major countries—Israel, the United States, and the United Kingdom—uncovering striking similarities and critical gaps. The research delved into Israel’s Quality Indicators in Community Healthcare (QICH), the US’s Healthcare Effectiveness Data and Information Set (HEDIS), and the UK’s Quality and Outcomes Framework (QOF). While all three systems prioritize family medicine and process-focused metrics, the study highlights a lack of attention to structural and outcome-based ...
Mapping Antarctica’s hidden ice-free lands: a blueprint for conservation
2025-01-28
Antarctica, often regarded as the planet’s last true wilderness, harbours unique ecosystems that support extraordinary biodiversity and contribute to global diversity and environmental stability. These ecosystems, which occupy permanently ice-free land covering less than 0.5% of the continent, are now under growing threat from human activity and climate change.
Now, a team led by researchers at UNSW Sydney’s Centre for Ecosystem Science has developed a high-resolution map and hierarchical classification system of Antarctica’s ice-free lands, which can be seen in full in Scientific Data.
This new inventory categorizes Antarctica’s ecosystems ...
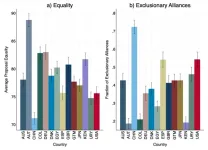
National and gender differences in exclusionary behavior
2025-01-28
When given the power to distribute resources, a person’s nationality, gender, and ideology can help predict how likely that person is to exclude others to maximize their own profit, according to a study. The results suggest that the identities and cultural backgrounds of decision-makers affect how equitably resources are divided.
Andrzej Baranski and Nicholas Haas placed study participants into groups of three to play a negotiation game. All interactions were via computer and no information about the other ...
The journal Genes & Development has new editorial leadership and an expanded scope
2025-01-28
Cold Spring Harbor, NY – Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press (CSHL Press) has announced the appointment of new editorial leadership at its renowned journal, Genes & Development. Professor Andrew Dillin has been named Editor-in-Chief, and Dr. Eric Sawey becomes Executive Editor.
These changes are associated with an intentional expansion of the journal’s scope into new and exciting aspects of life science research. While the journal remains committed to its traditional areas of coverage, it will also actively foster additional dynamic fields including physiology, metabolism, aging, gene and environmental interactions, and molecular neuroscience. Genes & ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
[Press-News.org] Largest study ever done on cannabis and brain function finds impact on working memoryThe study looked at the effect of cannabis use on young adults who are recent or heavy users