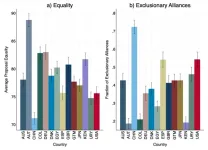
(Press-News.org) When given the power to distribute resources, a person’s nationality, gender, and ideology can help predict how likely that person is to exclude others to maximize their own profit, according to a study. The results suggest that the identities and cultural backgrounds of decision-makers affect how equitably resources are divided.
Andrzej Baranski and Nicholas Haas placed study participants into groups of three to play a negotiation game. All interactions were via computer and no information about the other participants, such as names, ages, or genders was shared. A randomly chosen player was asked to propose a division for a fixed amount of money. As long as one other player approved of the division, the payout would proceed along the proposed lines. Players could propose a three-way split, or something like a 60%/40%/0% split, which might be acceptable to the player receiving 40% and net the proposer almost twice as much. The experiment was repeated in Australia, Austria, China, Colombia, Denmark, Egypt, Germany, Guatemala, Japan, Kenya, Spain, United Kingdom, United States, and Uruguay. In total, there were 1,485 participants, all university students. The most egalitarian nation was Austria, where just under 20% of negotiations ended in exclusionary alliances. In China, 70% of negotiations resulted in exclusionary alliances. In the United States, around 54% of negotiations resulted in exclusionary alliances. The best predictor for a high rate of exclusionary alliances was a high national score on the Hierarchy Tolerance Index, which attempts to quantify cultural acceptance of power inequalities. Men and ideologically right-wing participants were more likely to propose unequal splits than women and ideologically left-wing participants. All-male groups were 45% more likely to form an exclusionary alliance compared to all-female groups. According to the authors, ensuring gender equity in decision-making bodies may increase equality and inclusion in the distribution of resources.
END
National and gender differences in exclusionary behavior
2025-01-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The journal Genes & Development has new editorial leadership and an expanded scope
2025-01-28
Cold Spring Harbor, NY – Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press (CSHL Press) has announced the appointment of new editorial leadership at its renowned journal, Genes & Development. Professor Andrew Dillin has been named Editor-in-Chief, and Dr. Eric Sawey becomes Executive Editor.
These changes are associated with an intentional expansion of the journal’s scope into new and exciting aspects of life science research. While the journal remains committed to its traditional areas of coverage, it will also actively foster additional dynamic fields including physiology, metabolism, aging, gene and environmental interactions, and molecular neuroscience. Genes & ...
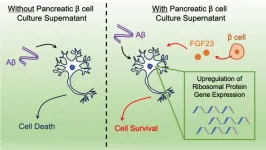
Pancreas cells secrete neuroprotective factor
2025-01-28
Pancreas cells may produce a protein that can protect the brain from Alzheimer's disease. In individuals with Alzheimer's disease, a peptide known as amyloid-β accumulates and forms tangled plaques. People with diabetes have a higher probability of developing Alzheimer's disease, raising the possibility of a link between the cells that are disordered in diabetes—pancreatic β cells—and the onset of Alzheimer's disease. However, insulin supplementation may not halt the development of Alzheimer's disease. Toru Hosoi and colleagues ...
Plant-based substitute for fossil fuels developed for plastic foams
2025-01-28
PULLMAN, Wash. — An environmentally-friendly preparation of plant material from pine could serve as a substitute for petroleum-based chemicals in polyurethane foams.
The innovation could lead to more environmentally friendly versions of foams used ubiquitously in products such as kitchen sponges, foam cushions, coatings, adhesives, packaging and insulation. The global market for polyurethane totaled more than $75 billion in 2022.
A Washington State University-led research team used an environmentally-friendly preparation of lignin as a substitute for 20% of the fossil fuel-based chemicals in the foam. The bio-based foam ...
Q&A: How rate of CO2 rise can affect a global ocean current
2025-01-28
As we burn fossil fuels, the amount of carbon dioxide in Earth’s atmosphere is gradually rising, and with it, the planet’s average temperature. How fast the level of atmospheric carbon dioxide — and with it, the temperature — goes up matters for the ability of humans and ecosystems to adjust. A slower increase gives humans time to move away from low-lying coasts and animals time to move to new habitats.
It turns out the rate of that increase matters for non-living systems, too. A recent University of Washington study looked at how a major current in the Atlantic Ocean that includes the Gulf Stream will respond ...
The oral microbiome and dementia
2025-01-28
The microbial ecosystems within our mouths may affect our cognitive function as we age, according to a study. Interventions such as prebiotics, including dietary nitrate, have potential for delaying cognitive decline.
About 15% of older adults have mild cognitive impairment, which is the largest risk factor for the development of dementia or Alzheimer’s disease. There is a known association between periodontitis—gum disease—and worsened cognitive function. Researchers have identified two possible links between the mouth and the mind: pathogenic ...
Paywalls shape newspaper coverage
2025-01-28
Adopting paywalls subtly shapes newspaper coverage, according to a study. Online journalism is increasingly found behind paywalls, as outlets pivot from funding their operations by selling ads to relying on subscriptions for revenue. This shift has raised questions about how newspapers might adjust their coverage to cater to paid subscribers' desires for popular news and soft news—entertainment, lifestyle, sports, and human-interest stories—at the expense of providing local news and maintaining democratic accountability. Paramveer S. Dhillon ...
Escaping the endosome: Bend lipids improve LNP mRNA delivery and gene editing
2025-01-28
Every time a shuttle docks with the International Space Station (ISS), a delicate dance unfolds between the shuttle's docking system and its counterpart on the station. Thanks to international standards, these mechanisms are universally compatible, ensuring astronauts and cargo can safely and seamlessly enter the station.
A similar challenge arises at the microscopic level when lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) — the revolutionary drug delivery vehicles behind the COVID-19 vaccines — attempt to deliver mRNA to cells. Optimizing the design and delivery of LNPs can greatly enhance their ability to deliver mRNA successfully, ...
Could fecal microbiota transplantation help patients heal after stem cell transplantation?
2025-01-28
SEATTLE — Jan. 28, 2025 — A new study shows that oral fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) is a feasible and safe addition to preventing graft-versus-host disease in patients undergoing stem cell transplantation for blood cancers.
The study, published Jan. 25 in Nature Communications, is part of a phase 2 clinical trial led by clinicians at Fred Hutch Cancer Center. The study builds on earlier research of the role of the gut microbiome in helping patients recover after stem cell transplantation.
“The gut microbiome is an organ in itself, and it is connected to the immune system,” said lead author Armin ...
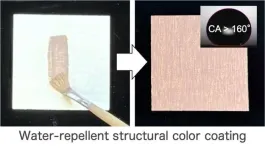
Structural color shields: water repellent coatings
2025-01-28
Ever wondered about the brilliant blue hues of peacock feathers or the shimmering metallic chitin on beetles? These natural wonders are examples of structural colors—a phenomenon in which microscopic structures create vibrant, lasting hues. Inspired by these marvels, a research team from Japan has been exploring structural colors. Their earlier work realized that the preparation of structural color materials from melanin particles mimics the coloration mechanism of peacock feathers. Building on this foundation, the team set out to develop a coating material that captures ...
Researchers enhance wildlife studies with novel prey measurement technique using animal-borne cameras
2025-01-28
A team of international scientists, led by researchers from the University of Otago, has introduced a groundbreaking method to improve the accuracy of prey size estimation using footage captured by animal-borne cameras. This innovative approach, published in PeerJ Life and Environment, enhances our understanding of predator-prey interactions in natural habitats by refining a critical tool for ecological research.
Animal-borne cameras, such as the "PenguCams" used in this study, allow ...