(Press-News.org) The American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS), the nonprofit publisher of the Science family of journals, is conducting a pilot with ProRata as part of its commitment to communicate trusted scientific findings broadly. ProRata is an AI company guided by the belief that content creators should receive attribution for their work. Partnering with AAAS will strengthen ProRata’s new AI-driven search engine, Gist.ai, while showing how content that powers AI-driven searches can be sustainably attributed.
The pilot – ProRata’s first with a scientific publisher – will initially include peer-reviewed articles from AAAS’s open-access journal Science Advances, as well as stories from Science Magazine’s award-winning news team. Combined, these research and news pieces cover a broad range of scientific developments, and their inclusion in results generated by Gist.ai will help more people – researchers, educators, science enthusiasts, and beyond – find relevant and accurate insights.
Today, partnerships between AI companies and publishers are becoming more common. However, not all partnerships have explicitly prioritized attribution to original creators nor focused on the reliability of AI outputs. For ProRata AI, however, attribution and reliability – as challenging as they are to achieve from a technical perspective – are guiding values. AAAS shares in these values.
“We are delighted to partner with ProRata AI,” said Bill Moran, Publisher of the Science family of journals. “This partnership is a significant step forward in ensuring that the critical work of global scientists and science journalists is recognized and distributed with the utmost care in this new AI age.”
AAAS is not licensing all historical journal content to ProRata for training large language models, as some deals do. Instead, the partnership is focused on licensing select high-quality content to the company, for a period, to help ensure people searching the internet on key topics can access today’s most relevant and up-to-date scientific information. ProRata’s Gist.ai, a beta version of which was unveiled in December 2024, will use this content – along with its proprietary model to credit creators – to deliver accurate AI-powered search results.
Search results from Gist.ai appear with labels that indicate what proportion of any result is from a listed source. The partnership will thus foster a more informed relationship between readers, AI tools, and the original sources of these studies and news stories.
"ProRata's technology helps ensure fairness and fact in the world of generative AI," said Bill Gross, CEO of ProRata. "Accurate search results are imperative when searching scientific information, and we are excited to collaborate with AAAS to provide such a depth of valuable information to Gist.ai."
About AAAS
The American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) is the world’s largest general scientific society and publisher of the journal Science, as well as Science Translational Medicine; Science Signaling; a digital, open-access journal, Science Advances; Science Immunology; and Science Robotics. AAAS was founded in 1848 and includes more than 250 affiliated societies and academies of science, serving 10 million individuals. The nonprofit AAAS is open to all and fulfills its mission to “advance science and serve society” through initiatives in science policy, international programs, science education, public engagement, and more. For additional information about AAAS, visit www.aaas.org.
About ProRata.ai
Founded in 2024 by Bill Gross at Idealab Studio, ProRata’s mission is to ensure that generative AI platforms compensate and credit content owners for the use of their material. ProRata builds technology that enables generative AI platforms to attribute contributing content sources and share revenues on a per-use basis, protecting and rewarding creators while helping to prevent unreliable content from compromising AI results. For more information, please visit prorata.ai.
END
AAAS enters pilot with ProRata to bolster standards for transparency and reliability in AI searches
The pilot – ProRata’s first with a scientific publisher – will initially include peer-reviewed articles from AAAS’s open-access journal Science Advances, as well as stories from Science Magazine’s award-winning news team.
2025-01-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Improving the way flash memory is made
2025-01-29
To store ever more data in electronic devices of the same size, the manufacturing processes for these devices need to be studied in greater detail. By investigating new approaches to making digital memory at the atomic scale, researchers engaged in a public-private partnership are aiming to address the endless demand for denser data storage.
One such effort has focused on developing the ideal manufacturing process for a type of digital memory known as 3D NAND flash memory, which stacks data vertically to increase storage density. The narrow, deep holes required for this type of memory can be etched ...
NFL PLAY 60 Fitness Break broadcast delivers movement minutes in advance of Super Bowl LIX
2025-01-29
DALLAS, Jan. 29, 2025 — The American Heart Association, a global force changing the future of health for all, and the National Football League (NFL), in collaboration with its 32 NFL clubs, are challenging kids to get moving and PLAY 60 in advance of Super Bowl LIX with the latest installment of the NFL PLAY 60 Fitness Break school broadcast series. On Thursday, Feb. 5 at 1 p.m. ET/ 12 p.m. CT/ 10 a.m. PT the Association and the NFL will deliver an action-packed, 15-minute synchronous streaming broadcast to help elementary school students ...
Blood-powered toes give salamanders an arboreal edge
2025-01-29
PULLMAN, Wash. — Wandering salamanders are known for gliding high through the canopies of coastal redwood forests, but how the small amphibians stick their landing and take-off with ease remains something of a mystery.
A new study in the Journal of Morphology reveals the answer may have a lot to do with a surprising mechanism: blood-powered toes. The Washington State University-led research team discovered that wandering salamanders (Aneides vagrans) can rapidly fill, trap, and drain the blood in their toe tips to optimize attachment, detachment and general locomotion through their arboreal environment.
The research not only uncovers a previously ...
Better nurse staffing linked to fewer C-sections
2025-01-29
Labor and delivery units that are adequately staffed by nurses have lower cesarean birth rates, according to new research published in the journal Nursing Outlook.
“Our findings highlight how crucial nurse staffing is for optimal maternal outcomes,” said Audrey Lyndon, the Vernice D. Ferguson Professor in Health Equity and executive vice dean at NYU Rory Meyers College of Nursing.
C-sections account for nearly a third of births in the US and are the most common surgery performed in hospitals. While C-sections can be lifesaving and some are necessary for the health of the mother and child, the surgery carries more risks and a longer recovery ...
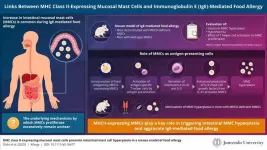
Role of specialized mucosal mast cells in IgE-mediated food allergy
2025-01-29
Food allergy, or the aggressive immune system reaction following the consumption of a certain food or food ingredient, typically involves immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies and can be potentially life-threatening. Often, the immune response to a food protein can be rapid and severe, requiring emergency care. In recent years, scientific studies have revealed that mucosal mast cells (MMCs), which are immune cells that arise from bone marrow, are excessively produced and play a key role in the severity and sudden onset ...
Study reveals how microbes help detoxify our atmosphere
2025-01-29
Melbourne researchers have discovered crucial new information about how microbes consume huge amounts of carbon monoxide (CO) and help reduce levels of this deadly gas.
Over two billion tonnes of carbon monoxide are released into the atmosphere globally each year. Microbes consume about 250 million tonnes of this, reducing CO to safer levels.
The Monash University-led Study, published in Nature Chemical Biology, reveals at an atomic level how microbes consume CO present in the atmosphere. They use a special enzyme, called the CO dehydrogenase, ...
White blood cell count could predict severity of COVID-19 symptoms
2025-01-29
CLEVELAND, Ohio (Jan 29, 2025)—Thanks to advances in treatment options, a COVID-19 diagnosis is no longer as scary as it once was, at least for most people. A new study, however, suggests that it may now be easier to predict who is most likely to suffer with more serious disease symptoms based on leukocyte (white blood cell) count. Results of the study are published online today in Menopause, the journal of The Menopause Society.
Millions of people worldwide suffer from the ongoing effects of COVID-19—which is caused by the SARs-CoV-2 ...
Moderate exercise keeps appetite at bay
2025-01-29
A recent study involving researchers at Murdoch University’s Health Futures Institute has revealed that moderate-intensity exercise can significantly influence appetite-related hormones and perceptions in males with obesity.
The study, titled “Acute effect of exercise on appetite-related factors in males with obesity,” provides new insights into how exercise can aid appetite control and weight management.
One of the study authors, Associate Professor Timothy Fairchild from Murdoch’s School ...
Cancer drugs linked to severe chronic peripheral nerve pain for 4 in every 10 patients
2025-01-29
Worldwide, cancer chemotherapy is linked to persistent severe peripheral nerve pain (neuropathy) for around 4 in every 10 patients treated with these drugs, suggests a pooled data analysis of the available evidence, published in the open access journal Regional Anesthesia & Pain Medicine.
Notwithstanding wide regional variations, platinum based drugs, taxanes, and lung cancer seem to be associated with the highest rates of persistent painful neuropathy, lasting at least 3 months, the findings suggest, prompting the researchers to call for tailored approaches to pain ...
Lack of essential vitamins and minerals common in people with type 2 diabetes
2025-01-29
Micronutrient deficiency, whereby levels of vitamins and minerals essential for healthy bodily function are far too low, is common in people with type 2 diabetes, finds a pooled data analysis of the available evidence, published in the open access journal BMJ Nutrition Prevention & Health.
A lack of vitamin D is the most common ‘missing’ micronutrient, overall, the findings indicate, with women at greater risk than men of these deficiencies, dubbed 'hidden hunger.'
Genetic predisposition, various environmental factors, sedentary ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Enzymes work as Maxwell's demon by using memory stored as motion
Methane’s missing emissions: The underestimated impact of small sources
Beating cancer by eating cancer
How sleep disruption impairs social memory: Oxytocin circuits reveal mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities
Natural compound from pomegranate leaves disrupts disease-causing amyloid
A depression treatment that once took eight weeks may work just as well in one
New study calls for personalized, tiered approach to postpartum care
The hidden breath of cities: Why we need to look closer at public fountains
Rewetting peatlands could unlock more effective carbon removal using biochar
Microplastics discovered in prostate tumors
ACES marks 150 years of the Morrow Plots, our nation's oldest research field
Physicists open door to future, hyper-efficient ‘orbitronic’ devices
$80 million supports research into exceptional longevity
Why the planet doesn’t dry out together: scientists solve a global climate puzzle
Global greening: The Earth’s green wave is shifting
You don't need to be very altruistic to stop an epidemic
Signs on Stone Age objects: Precursor to written language dates back 40,000 years
MIT study reveals climatic fingerprints of wildfires and volcanic eruptions
A shift from the sandlot to the travel team for youth sports
Hair-width LEDs could replace lasers
The hidden infections that refuse to go away: how household practices can stop deadly diseases
Ochsner MD Anderson uses groundbreaking TIL therapy to treat advanced melanoma in adults
A heatshield for ‘never-wet’ surfaces: Rice engineering team repels even near-boiling water with low-cost, scalable coating
Skills from being a birder may change—and benefit—your brain
Waterloo researchers turning plastic waste into vinegar
Measuring the expansion of the universe with cosmic fireworks
How horses whinny: Whistling while singing
US newborn hepatitis B virus vaccination rates
When influencers raise a glass, young viewers want to join them
Exposure to alcohol-related social media content and desire to drink among young adults
[Press-News.org] AAAS enters pilot with ProRata to bolster standards for transparency and reliability in AI searchesThe pilot – ProRata’s first with a scientific publisher – will initially include peer-reviewed articles from AAAS’s open-access journal Science Advances, as well as stories from Science Magazine’s award-winning news team.