(Press-News.org) Systemic lupus erythematosus, more commonly known as lupus, has a variety of symptoms and room for improvement when it comes to treatment.
Cutaneous lupus erythematosus is a common manifestation of systemic lupus erythematosus.
The condition is characterized by rashes on various parts of the body including the face and scalp, hair loss and scarring of the skin.
The rashes are caused by inflammation from the immune system fighting the body.
The standard treatment for cutaneous lupus erythematosus is using immunosuppressants and biologic drugs to reduce inflammation.
While the medications can be helpful, many patients with systemic lupus erythematosus already take a high number of drugs and are looking for other treatment methods other than pills.
J. Michelle Kahlenberg, M.D., Ph.D., a professor of internal medicine in the Division of Rheumatology at University of Michigan Health led a team of researchers looking at one of these alternatives, a topical treatment called mupirocin.
This trial was based on Kahlenberg’s previous discovery that cutaneous lupus rashes are often colonized with a common skin bacteria, Staphyloccous areus, also known as staph, and contributes to inflammation in the rashes.
Mupirocin kills this type of bacteria.
Lupus: A frustrating diagnosis journey you don’t need to embark alone
The study randomly selected systemic lupus erythematosus patients currently experiencing cutaneous lupus erythematosus flares to treat their skin lesions with mupirocin or with an inactive control, petrolatum jelly.
Samples from the nose and lesional skin were used to determine baseline and post treatment Staphylococcus abundance and microbial community profiles.
Paired samples collected prior to treatment with the topical solution and seven days after treatment showed decreases in lesional staphylococcus aureus in the mupirocin treated samples.
Importantly, the reduction in staph also was accompanied by a reduction in inflammatory signals, including interferon-driven gene expression, in the lesions.
“In addition to decreasing the inflammation by decreasing lesional staphylococcus aureus, the mupirocin treatment also lowered skin monocyte levels, which are important in driving cutaneous lupus,” said Kahlenberg.
Mupirocin is a prescription treatment, and while this early study showed signs of decreasing inflammation, the study wasn’t designed to see if it can decrease the rash of cutaneous lupus erythematosus.
Fixing racial inequities in lupus care
“Additional larger studies are needed to determine whether topical antibiotics will be helpful to make rashes go away,” Kahlenberg said.
“However, this is an exciting first step to show that there may be additional treatments that can improve inflammation beyond our usual immunosuppressant and biologic drugs.”
Additional authors: Lisa Abernathy-Close, Ph.D., Sirisha Sirobhushanam, Ph.D., Annie Lu, Joseph Mears, B.S.Allison C. Billi, M.D., Ph.D.
Funding/disclosures: This study was funded by the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation and NIAMS. Michelle Kahlenberg: Aditum Bio; Anaptys Bio; AstraZeneca, PLC; Biogen; EMD Serono; Exo Therapeutics; Gilead Science, Inc.; GSK; Lilly, Eli, and Company; Lupus Research Alliance; Related Science, LLC; Rome Therapeutics; Synthekine; Ventus Therapeutics.
Paper cited: “Topical mupirocin treatment reduces interferon and myeloid signatures in cutaneous lupus erythematous lesions through targeting of Staphylococcus species,” Arthritis & Rheumatology. DOI: 10.1002.art.43079
Sign up for Health Lab newsletters today. Get medical tips from top experts and learn about new scientific discoveries every week.
Sign up for the Health Lab Podcast. Add us wherever you listen to your favorite shows.
END
Topical mupirocin lowers lupus inflammation
2025-01-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New atom-based thermometer measures temperature more accurately
2025-01-29
Scientists at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have created a new thermometer using atoms boosted to such high energy levels that they are a thousand times larger than normal. By monitoring how these giant “Rydberg” atoms interact with heat in their environment, researchers can measure temperature with remarkable accuracy. The thermometer’s sensitivity could improve temperature measurements in fields ranging from quantum research to industrial manufacturing.
Unlike traditional thermometers, a Rydberg thermometer doesn’t need to be first adjusted or calibrated at the ...
COVID lockdowns disrupted a crucial social skill among preschoolers, trailblazing study finds
2025-01-29
Lockdowns. Social distancing. Shuttered schools and businesses. The COVID-19 pandemic and its sweeping disruptions set off a stampede of “what it’s doing to us” research, focused largely on schoolchildren. How were students’ academics affected? Their mental health? Their social development?
Left unexamined was whether the pandemic impacted the social cognition of preschool children — kids younger than 6 — whose social norms were upended by day care closures and families sheltered at home.
That changed when a UC Merced ...
Otago scientists discover Antarctic fast ice secrets
2025-01-29
University of Otago – Ōtākou Whakaihu Waka scientists have successfully analysed more than 30 years of vital data on the thickness of landfast sea ice in Antarctica’s McMurdo Sound, which will prove useful to measure future impacts of climate change.
The study, published in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, set out to discover what key influences determine the thickness of landfast sea-ice, known as fast ice, using data from 1986 to 2022.
Fast ice is frozen ocean water that is attached to shorelines and persists for at least 15 days. It provides vital habitats for penguins and seals, as well as fish, krill and algae underneath the ice.
Scientists ...
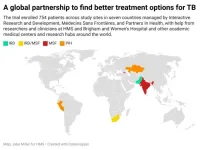
Study finds three new safe, effective ways to treat drug-resistant tuberculosis
2025-01-29
Tuberculosis remains one of the top infectious disease killers worldwide, a challenge amplified by drug-resistant forms of the disease. Now, in a major step forward, an international clinical trial has found three new safe and effective drug regimens for tuberculosis that is resistant to rifampin, the most effective of the first-line antibiotics used to treat TB.
The research, published Jan. 30 in the New England Journal of Medicine, was led by researchers at Harvard Medical School and other members of the endTB project, ...
A weekly injection could replace painful daily treatment for rare fat disorder
2025-01-29
Rutgers Health researchers have found that a weekly injection of diabetes medication could replace painful daily hormone shots for people with a rare genetic form of lipodystrophy that leaves patients with almost zero fat tissue, according to a study in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Congenital generalized lipodystrophy (CGL), which affects only a few thousand people worldwide, results in severe metabolic disease, diabetes, insulin resistance and reduced life expectancy. With no fat tissue for proper storage, fat accumulates in organs ...
More Americans than ever are confident about providing lifesaving CPR, new survey suggests
2025-01-29
DALLAS, January 29, 2025 — When someone’s heart stops pumping, early CPR can save their life.[1] New survey research from the American Heart Association reveals more Americans are prepared to provide that lifesaving rhythm for their friends, family and community.
The newly released data, conducted by Decision Analyst on behalf of the American Heart Association, indicates more U.S. adults now say they feel ready to handle and respond to a cardiac arrest[2]. When Damar Hamlin collapsed on the field during Monday Night Football in January ...
Uber, Lyft or transit? The answer appears to align with how people value their time
2025-01-29
Research led by the University of Michigan arrived at a surprisingly unsurprising result while assessing the sustainability gap between public transit and services like Uber and Lyft, formally known as transport network companies or TNCs.
With data collected by the city of Chicago, the researchers studied people's use of TNCs over transit, allowing the team to put a value on the time riders saved with their choices. The median value of that number, about $34 per hour, was virtually identical to the Chicago region’s median hourly wage.
"I was a bit surprised that our median ...
Researchers uncover key insights into how the body protects against neuron damage
2025-01-29
Neurons may get all the glory, but they would be nothing without glial cells. While brain cells do the heavy lifting in the nervous system, it’s the glia that provide nutrients, clean up waste, and protect neurons from harm.
Now, scientists have discovered a new mechanism by which these crucial supporting players detect and respond to neuron damage. Published in Nature Communications, the study describes how two key proteins allow glial cells to actively monitor the hair-like cilia that extend out of nematode dendrites, so that the glial cells can respond ...
Diagnostic stewardship optimizes detection of appendicitis
2025-01-29
Abdominal pain is among the most common reasons children are taken to the emergency department.
A small proportion of them usually have appendicitis, and timely detection is essential.
To do so, clinicians often rely on imaging, such as ultrasound or CT scans.
Although delayed diagnosis of appendicitis in children can be life threatening, overtesting is wasteful and can even cause harm.
Now in a study, published in Academic Emergency Medicine, University of Michigan researchers found that emergency departments vary widely in how they balance the ...
Optical fiber sensor provides simple and sensitive detection of arsenic in drinking water
2025-01-29
WASHINGTON — Researchers have developed a new optical sensor that provides a simple way to achieve real-time detection of extremely low levels of arsenic in water. The technology could enable household testing for arsenic, empowering individuals to monitor their own water quality.
Arsenic contamination is a serious environmental and public health challenge affecting millions of people around the world. This contamination occurs when natural geological processes release arsenic from rocks and soil into groundwater ...