(Press-News.org) What began as a demonstration of the complexity of fluid systems became an art piece in the American Physical Society’s Gallery of Fluid Motion, and ultimately its own puzzle that the researchers just solved. Their new study is published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
“We came up with this experiment because we were having a hard time convincing people of certain effects happening for the problem of drag reduction,” said assistant
professor Paolo Luzzatto-Fegiz, an assistant professor of mechanical engineering, whose research specialties include modeling flow and investigating drag — as in, the resistive forces that act on solid objects traveling through fluids.
“We had a hypothesis for how this worked,” Luzzatto-Fegiz said. “And this paper actually works out a mathematical model of that phenomenon.”
Of particular interest to the research group, which included UCSB engineering professor Frederic Gibou and collaborators at Princeton University, University of Manchester in the UK, and the Université de Rennes in France, was the ink’s rather uncanny ability to “choose” and move in the correct direction, when intuition would perhaps suggest that the ink would diffuse in a more general manner.
Surface tension — the cohesion that causes molecules on the surface of a fluid to pull together and act like a membrane, resisting exterior forces — plays a large role in this ink-on-milk experiment. The soap — a surfactant, or a substance that reduces surface tension — reduces local tension around the ink, creating motion. However, according to the researchers’ calculations, it’s the presence of surfactants already in the milk that help the ink/soap mixture solve the maze.
“The added surfactant and the preexisting one end up working together,” Luzzatto-Fegiz said. The endogenous surfactant already in the milk creates a landscape of varying resistances that push back on the ink and soap as the mixture moves through the maze, he explained. Dead ends and small spaces push back more strongly, according to the researchers, while the route with the greatest surface area, which also happens to be the one with the exit, offers the path of least resistance.
“That means the added surfactant instantly knows the layout of the maze,” Luzzatto- Fegiz said.
This work complements earlier studies of the forces that drive the movement of the ink/soap. Called the Marangoni effect, it’s what happens when there is a gradient of
surface tension, such as that introduced by the added surfactant, which results in the liquid being pulled from regions of lower surface tension to areas of higher surface
tension. This effect is a “new consequence” that hasn’t been studied yet, and can be relevant in applications and processes that involve “surfactant-driven transport in
complex networks, such as lung airways,” according to the study, and “can inspire improved strategies for drug delivery or fluid transport in complex systems.”
END
Researchers solve a fluid mechanics mystery
What began as a demonstration of the complexity of fluid systems became an art piece in the American Physical Society’s Gallery of Fluid Motion, and ultimately its own puzzle that the researchers just solved
2025-02-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New grant funds first-of-its-kind gene therapy to treat aggressive brain cancer
2025-02-03
The California Institute for Regenerative Medicine has awarded a $6 million grant to USC investigators pioneering a new first-of-its-kind genetic therapy for glioblastoma, a severe form of brain cancer. The treatment would be the first gene therapy for glioblastoma to use a novel, more precise delivery system that is less likely to harm non-cancerous cells.
Glioblastoma is an aggressive and fast-growing cancer originating in the brain that occurs primarily in adults and has no known cure. Patients diagnosed with this type of tumor have a five-year survival rate of just 5 percent. The cancer’s location—in the sensitive brain—combined ...
HHS external communications pause prevents critical updates on current public health threats
2025-02-03
The Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA) is concerned that two weeks have passed since the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) announced a pause on mass communications and public appearances that are not directly related to emergencies or critical to preserving health. With the order remaining in effect until a new HHS secretary is confirmed, this unpredictable timeline prolongs uncertainty for both healthcare professionals and the public, and endangers the nation by hindering our ability to detect and respond to public health threats, such as avian influenza (H5N1). Public ...
New ACP guideline on migraine prevention shows no clinically important advantages for newer, expensive medications
2025-02-03
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 3 February 2025
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
New ...
Revolutionary lubricant prevents friction at high temperatures
2025-02-03
Through a multi-university collaboration, researchers at Virginia Tech have discovered a new, solid lubricating mechanism that can reduce friction in machinery at extremely high temperatures. It works well beyond the breakdown temperature of traditional solid lubricants such as graphite, and the findings were published in Nature Communications.
“This breakthrough solid-state lubricant could change how we design materials for high-tech engines, making them last longer and work better under extreme conditions,” said Rebecca Cai, associate professor in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and one of the ...
Do women talk more than men? It might depend on their age
2025-02-03
The stereotype that women are much more talkative than men is pervasive across many cultures, but a widely reported study by University of Arizona researchers in 2007 refuted the claim, finding that men and women speak roughly the same number of words per day – around 16,000.
A new, larger follow-up to that study paints a more nuanced picture, suggesting that women may be the chattier gender, but only during a certain period of life.
"There is a strong cross-cultural assumption that women talk a lot more than men," said ...
The right kind of fusion neutrons
2025-02-03
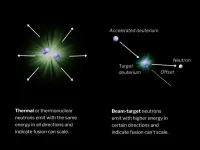
In physics, the term “isotropy” means a system where the properties are the same in all directions. For fusion, neutron energy isotropy is an important measurement that analyzes the streams of neutrons coming from the device and how uniform they are. This is critical because so-called isotropic fusion plasmas suggest a stable, thermal plasma that can be scaled to higher fusion energy gains, whereas anisotropic plasmas, those emitting irregular neutron energies, can lead to a dead end.
A new Zap research paper, published last week ...
The cost of preventing extinction of Australia’s priority species
2025-02-03
A new study has estimated it would cost $15.6 billion per year for 30 years to prevent extinction for 99 of Australia’s priority species.
The research, led by Griffith University’s Centre for Planetary Health and Food Security with WWF-Australia and the University of Queensland, highlights the urgent need for increased funding to combat threats such as habitat destruction, invasive species and climate change.
Australia has already lost more than 100 endemic species in the past three centuries, placing it at the forefront of the global extinction crisis.
The ...
JMIR Publications announces new CEO
2025-02-03
(Toronto, February 3, 2025) JMIR Publications, the leading open access publisher in digital health and open science, announced today that Sean Jeong has been appointed as its new chief executive officer (CEO), effective January 23, 2025. Dr Gunther Eysenbach, founder of JMIR Publications, will be stepping down as CEO after over two decades of transformative leadership to focus on new opportunities for innovation in academic publishing, including artificial intelligence (AI)–driven solutions and the advancement of Plan P. He will continue to serve as the editor in chief of the Journal of Medical ...
NCSA awards 17 students Fiddler Innovation Fellowships
2025-02-03
The National Center for Supercomputing Applications awarded Fiddler Innovation Fellowships to 17 University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and NCSA graduate students in a ceremony January 28 honoring the outstanding achievements and interdisciplinary contributions to NCSA programs Students Pushing Innovation (SPIN) and Design for America during the 2023-24 academic year.
The awards are part of a $2 million endowment from Jerry Fiddler and Melissa Alden to Illinois in support of student ...
How prenatal alcohol exposure affects behavior into adulthood
2025-02-03
Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASD), characterized by symptoms of cognitive decline, such as worsened memory and impaired decision-making, are alarmingly prevalent globally. In a new study in JNeurosci led by Amy Griffin at the University of Delaware, researchers used rats to find brain circuits that may contribute to the cognitive issues that FASD patients experience, with the end goal of informing treatment strategies. Brain regions linked with working memory and decision-making were damaged in baby rats following exposure to alcohol during the age equivalent of the third trimester ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Chimps’ love for crystals could help us understand our own ancestors’ fascination with these stones
Vaginal estrogen therapy not linked to cancer recurrence in survivors of endometrial cancer
How estrogen helps protect women from high blood pressure
Breaking the efficiency barrier: Researchers propose multi-stage solar system to harness the full spectrum
A new name, a new beginning: Building a green energy future together
From algorithms to atoms: How artificial intelligence is accelerating the discovery of next-generation energy materials
Loneliness linked to fear of embarrassment: teen research
New MOH–NUS Fellowship launched to strengthen everyday ethics in Singapore’s healthcare sector
Sungkyunkwan University researchers develop next-generation transparent electrode without rare metal indium
What's going on inside quantum computers?: New method simplifies process tomography
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
Jackdaw chicks listen to adults to learn about predators
Toxic algal bloom has taken a heavy toll on mental health
Beyond silicon: SKKU team presents Indium Selenide roadmap for ultra-low-power AI and quantum computing
Sugar comforts newborn babies during painful procedures
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
From herbal waste to high performance clean water material: Turning traditional medicine residues into powerful biochar
New sulfur-iron biochar shows powerful ability to lock up arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils
AI-driven chart review accurately identifies potential rare disease trial participants in new study
Paleontologist Stephen Chester and colleagues reveal new clues about early primate evolution
UF research finds a gentler way to treat aggressive gum disease
Strong alcohol policy could reduce cancer in Canada
[Press-News.org] Researchers solve a fluid mechanics mysteryWhat began as a demonstration of the complexity of fluid systems became an art piece in the American Physical Society’s Gallery of Fluid Motion, and ultimately its own puzzle that the researchers just solved