(Press-News.org) Ever notice that batteries in electronics don't last as long as they did when they were brand new?
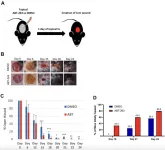
An international research team led by The University of Texas at Austin took on this well-known battery challenge, called degradation, with a twist. They're focusing their work on real-world technology that many of us use daily: wireless earbuds. They deployed x-ray, infrared, and other imaging technologies to understand the complexities of all the technology packed in these tiny devices and learn why their battery lives erode over time.
"This started with my personal headphones; I only wear the right one, and I found that after two years, the left earbud had a much longer battery life," said Yijin Liu, an associate professor in the Cockrell School of Engineering's Walker Department of Mechanical Engineering, who led the new research published in Advanced Materials. "So, we decided to look into it and see what we could find."
They found that other critical components in the compact device, like the Bluetooth antenna, microphones and circuits, clashed with the battery, creating a challenging microenvironment. This dynamic led to a temperature gradient—different temperatures at the top and bottom portions of the battery—that damaged the battery.
Exposure to the real world, with many different temperatures, degrees of air quality and other wildcard factors, also plays a role. Batteries are often designed to withstand harsh environments, but frequent environmental changes are challenging in their own way.
These findings, the researchers say, illustrate the need to think more about how batteries fit into real-world devices like phones, laptops and vehicles. How can they be packaged to mitigate interactions with potentially damaging components, and how can they be adjusted for different user behaviors?
"Using devices differently changes how the battery behaves and performs," said Guannan Qian, the first author of this paper and a postdoctoral researcher in Liu’s lab. "They could be exposed to different temperatures; one person has different charging habits than another; and every electric vehicle owner has their own driving style. This all matters."
To conduct experiments, Liu and his team worked closely with UT's Fire Research Group, led by mechanical engineer Ofodike Ezekoye. They used Ezekoye's infrared imaging technology to complement their laboratory x-ray technology at UT Austin and Sigray Inc. But to get the full picture, Liu and his team turned to some of the most powerful x-ray facilities on the planet.
They collaborated with teams from SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory’s Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource, Brookhaven National Laboratory's National Synchrotron Light Source II, Argonne National Laboratory's Advanced Photon Source, and the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF) in France. These national and international institutions grant researchers access to world-class synchrotron facilities, enabling them to uncover the hidden dynamics of batteries under real-life conditions.
"Most of the time, in the lab, we're looking at either pristine and stable conditions or extremes," said Xiaojing Huang, a physicist at Brookhaven National Laboratory. "As we discover and develop new types of batteries, we must understand the differences between lab conditions and the unpredictability of the real world and react accordingly. X-ray imaging can offer valuable insights for this."
Liu says his team will continue to investigate battery performance in real-world conditions. That work could extend to larger cells, like the batteries that power our phones, laptops and electric vehicles.
The full team includes: Tianxiao Sun and Ayrton M. Yanyachi of the Walker Department of Mechanical Engineering; Guibin Zan, Jizhou Li, Dechao Meng, Vivek Thampy, Sang-Jun Lee, Jun-Sik Lee and Piero Pianetta of SLAC; Sheraz Gul and Wenbing Yun of Sigray; Xiaojing Huang, Hanfei Yan and Yong S. Chu of Brookhaven National Laboratory; Juanjuan Huang and Shelly D. Kelly of Argonne National Laboratory; Peter Cloetens of ESRF; and Kejie Zhao of Purdue University.
END
Why your headphone battery doesn't last
Texas Engineers took on the well-known battery challenge of degradation in a real-world technology that many of us use daily: wireless earbuds.
2025-02-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study probes how to predict complications from preeclampsia
2025-02-04
The existing prediction models for severe complications of preeclampsia are most accurate only in the two days after hospital admission, with deteriorating performance over time, according to a new study published February 4th in the open-access journal PLOS Medicine by Henk Groen of University of Groningen, the Netherlands, and colleagues.
Preeclampsia is a potentially life-threatening condition that can occur during pregnancy; of women diagnosed with preeclampsia, 5-20% will develop severe complications. Two existing PIERS (Pre-eclampsia Integrated ...
CNIC scientists design an effective treatment strategy to prevent heart injury caused by a class of anticancer drugs
2025-02-04
A team of scientists at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC), working in collaboration with international partners, has designed a strategy for preventing the cardiotoxic effects of anthracyclines, a widely used class of anticancer drugs. Cardiotoxicity is a frequent adverse secondary effect of cancer therapy with these drugs. The study, published in JACC: CardioOncology, demonstrates that treatment with the SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin can mitigate the cardiac injury associated with anthracycline therapy.
Anthracyclines are first-line medications in the treatment of cancer, but in 5% of patients their use is associated ...
NYU’s Yann LeCun a winner of the 2025 Queen Elizabeth Prize for Engineering
2025-02-04
New York University’s Yann LeCun has been selected as a winner of the 2025 Queen Elizabeth Prize for Engineering—one of seven recognized for contributions to the advancement of Modern Machine Learning, which has fueled advances in artificial intelligence.
“This year, we celebrate the remarkable achievements that these seven engineers have contributed to Modern Machine Learning, a field that has revolutionized artificial intelligence by uniting algorithms, hardware, and data,” said Lord Vallance, chair of the Queen Elizabeth Prize for Engineering Foundation. “The impact of this innovation is felt across industries, economies, and the planet, ...
New study assesses impact of agricultural research investments on biodiversity, land use
2025-02-04
New study assesses impact of agricultural research investments on biodiversity and land use
Data analysis spans 1960s Green Revolution to 2015
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. — New, groundbreaking research shows how, at a local scale, agricultural research and development led to improved crop varieties that resulted in global benefits to the environment and food system sustainability. The Purdue University study appears in the latest issue of Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“At the global level, we see a reduction in cropland use from these technology ...
High-precision NEID spectrograph helps confirm first Gaia astrometric planet discovery
2025-02-04
NEID (rhymes with fluid) is a high-precision radial-velocity spectrograph that is designed to measure the extremely minute wobble of nearby stars using the radial velocity effect. This effect results from the mutual gravitational force between a planet and its host star which causes the star’s position to shift very slightly as the planet travels around it. With this powerful capability, one of NEID’s main science goals is to confirm exoplanet candidates found by other exoplanet missions.
NEID is funded by the NASA/NSF Exoplanet Exploration Program (NN-EXPLORE) and is mounted on the WIYN 3.5-meter Telescope at ...
ABT-263 treatment rejuvenates aged skin and enhances wound healing
2025-02-04
“[…] topical ABT-263 effectively reduced several senescence markers in aged skin, thereby priming the skin for improved subsequent wound healing.”
BUFFALO, NY—February 4, 2025 — A new research paper was published by Aging (Aging-US) on December 3, 2024, in Volume 17, Issue 1, titled “Topical ABT-263 treatment reduces aged skin senescence and improves subsequent wound healing.”
Researchers Maria Shvedova, Rex Jeya Rajkumar Samdavid Thanapaul, Joy Ha, Jannat ...
The challenge of pursuit – how saccades enable mammals to simultaneously chase prey and navigate through complex environments
2025-02-04
How do predators use their vision to both navigate through the terrain whilst tracking prey running for its life? Pursuing prey through a complex environment is a major challenge for the visual system as not only do the prey constantly change direction, sometimes in the opposite direction to the pursuer, but running after something evokes self-induced motion-blur which degrades vision. In a study, published in Current Biology, researchers reconstructed the visual fields of freely moving ferrets as they chased a fleeing target. They discovered that the eye saccades, like those that normally track objects when sitting still, aligned the motion of the environment, ...
Music can touch the heart, even inside the womb
2025-02-04
WASHINGTON, Feb. 4, 2025 – Playing music has long been a way for expectant parents to connect with their children in the womb, but a group of researchers has found evidence it can calm fetal heart rates, potentially providing developmental benefits.
In Chaos, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the Autonomous University of the State of Mexico, the Metropolitan Autonomous University, the General Hospital Nicolás San Juan, and the National Institute of Cardiology Ignacio Chávez studied the effect of classical music on a fetal heartbeat. The team used mathematical analysis tools to identify patterns in heart rate variability.
Typical measures ...
Contribution of cannabis use disorder to new cases of schizophrenia has almost tripled over the past 17 years
2025-02-04
Ottawa, ON, February 4, 2025 – The proportion of new cases of schizophrenia associated with a cannabis use disorder has risen from 4% pre-legalization to 10% after cannabis legalization in Ontario, according to new research.
A new study from researchers at ICES, The Ottawa Hospital, University of Ottawa’s Department of Family Medicine, and Bruyère Health Research Institute and published in the journal JAMA Network Open used data capturing the healthcare visits of everyone living in Ontario, Canada to track whether the liberalization of medical cannabis in 2015 and legalization of non-medical ...
Listening for multiple mental health disorders
2025-02-04
WASHINGTON, Feb. 4, 2025 – It’s no secret that there is a mental health crisis in the United States. As of 2021, 8.3% adults had major depressive disorder (MDD) and 19.1% had anxiety disorders (AD), and the COVID-19 pandemic exacerbated these statistics. Despite the high prevalence of AD/MDD, diagnosis and treatment rates remain low – 36.9% for AD and 61.0% for MDD – due to a variety of social, perceptual, and structural barriers. Automated screening tools can help.
In JASA Express Letters, published on behalf of the Acoustical Society ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Ten-point plan to deliver climate education unveiled by experts
Team led by UC San Diego researchers selected for prestigious global cancer prize
Study: Reported crop yield gains from breeding may be overstated
Stem cells from human baby teeth show promise for treating cerebral palsy
Chimps’ love for crystals could help us understand our own ancestors’ fascination with these stones
Vaginal estrogen therapy not linked to cancer recurrence in survivors of endometrial cancer
How estrogen helps protect women from high blood pressure
Breaking the efficiency barrier: Researchers propose multi-stage solar system to harness the full spectrum
A new name, a new beginning: Building a green energy future together
From algorithms to atoms: How artificial intelligence is accelerating the discovery of next-generation energy materials
Loneliness linked to fear of embarrassment: teen research
New MOH–NUS Fellowship launched to strengthen everyday ethics in Singapore’s healthcare sector
Sungkyunkwan University researchers develop next-generation transparent electrode without rare metal indium
What's going on inside quantum computers?: New method simplifies process tomography
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
Jackdaw chicks listen to adults to learn about predators
Toxic algal bloom has taken a heavy toll on mental health
Beyond silicon: SKKU team presents Indium Selenide roadmap for ultra-low-power AI and quantum computing
Sugar comforts newborn babies during painful procedures
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
From herbal waste to high performance clean water material: Turning traditional medicine residues into powerful biochar
New sulfur-iron biochar shows powerful ability to lock up arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils
[Press-News.org] Why your headphone battery doesn't lastTexas Engineers took on the well-known battery challenge of degradation in a real-world technology that many of us use daily: wireless earbuds.