(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, Feb. 4, 2025 – Playing music has long been a way for expectant parents to connect with their children in the womb, but a group of researchers has found evidence it can calm fetal heart rates, potentially providing developmental benefits.
In Chaos, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the Autonomous University of the State of Mexico, the Metropolitan Autonomous University, the General Hospital Nicolás San Juan, and the National Institute of Cardiology Ignacio Chávez studied the effect of classical music on a fetal heartbeat. The team used mathematical analysis tools to identify patterns in heart rate variability.
Typical measures of heart rate are an average of several beats across multiple seconds. In contrast, heart rate variability measures the time between individual beats. This measure can provide insight into the maturation of the fetal autonomic nervous system, with greater variability often indicating healthy development.
To test the effects music can have on fetal heart rate, the group of researchers recruited 36 pregnant women and played a pair of classical pieces for their fetuses. For the experiment, they chose “The Swan,” by French composer Camille Saint-Saëns, and “Arpa de Oro,” by Mexican composer Abundio Martínez.
By attaching external heart rate monitors, the researchers could measure the fetal heart rate response to both songs. And by employing nonlinear recurrence quantification analysis, they could identify changes in heart rate variability during and after the music was played.
“Overall, we discovered that exposure to music resulted in more stable and predictable fetal heart rate patterns,” said author Claudia Lerma. “We speculate that this momentary effect could stimulate the development of the fetal autonomic nervous system.”
In addition to the overall effects of playing music, the researchers looked at the differences between the two classical pieces. While both were effective, they found that the Mexican guitar melody had a stronger effect.
“When contrasting ‘The Swan’ with ‘Arpa de Oro,’ we did notice some significant differences,” said author Eric Alonso Abarca-Castro. “In particular, the second piece appeared to have a stronger impact on some measures, indicating that it produced heart rate patterns that were more predictable and regular. Factors like rhythmic characteristics, melodic structure, or cultural familiarity may be linked to this differentiation.”
For expectant parents at home, the researchers suggest that classical music could help promote fetal development.
“Our results suggest that these changes in fetal heart rate dynamics occur instantly in short-term fluctuations, so parents might want to consider exposing their fetuses to quiet music,” said Abarca-Castro. “Parents who play soothing music may stimulate and benefit the fetal autonomic system.”
The authors plan to continue to explore this effect, looking at different genres and types of music to further their understanding.
“To ascertain whether rhythmic or cultural variations elicit distinct fetal cardiac responses, we intend to increase the size of our sample and expand our investigation to include a variety of musical styles beyond classical pieces,” said author José Javier Reyes-Lagos.
###
The article “Response to music on the nonlinear dynamics of human fetal heart rate fluctuations: A recurrence plot analysis” is authored by José Javier Reyes-Lagos, Hugo Mendieta-Zerón, Migdania Martínez-Madrigal, Juan Carlos Santiago-Nuñez, Luis Emilio Reyes-Mendoza, Ximena Gonzalez-Reyes, Juan Carlos Echeverria, Eric Alonso Abarca-Castro, Ana Karen Talavera-Peña, Sara Avilés-Hernández, and Claudia Lerma. It will appear in Chaos on Feb. 4, 2025 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0236416). After that date, it can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0236416.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Chaos is devoted to increasing the understanding of nonlinear phenomena in all areas of science and engineering and describing their manifestations in a manner comprehensible to researchers from a broad spectrum of disciplines. See https://pubs.aip.org/aip/cha.
###
END
Music can touch the heart, even inside the womb
Playing classical music can smooth variations in fetal heart rates.
2025-02-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Contribution of cannabis use disorder to new cases of schizophrenia has almost tripled over the past 17 years
2025-02-04
Ottawa, ON, February 4, 2025 – The proportion of new cases of schizophrenia associated with a cannabis use disorder has risen from 4% pre-legalization to 10% after cannabis legalization in Ontario, according to new research.
A new study from researchers at ICES, The Ottawa Hospital, University of Ottawa’s Department of Family Medicine, and Bruyère Health Research Institute and published in the journal JAMA Network Open used data capturing the healthcare visits of everyone living in Ontario, Canada to track whether the liberalization of medical cannabis in 2015 and legalization of non-medical ...
Listening for multiple mental health disorders
2025-02-04
WASHINGTON, Feb. 4, 2025 – It’s no secret that there is a mental health crisis in the United States. As of 2021, 8.3% adults had major depressive disorder (MDD) and 19.1% had anxiety disorders (AD), and the COVID-19 pandemic exacerbated these statistics. Despite the high prevalence of AD/MDD, diagnosis and treatment rates remain low – 36.9% for AD and 61.0% for MDD – due to a variety of social, perceptual, and structural barriers. Automated screening tools can help.
In JASA Express Letters, published on behalf of the Acoustical Society ...
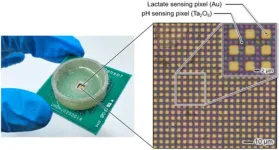
Visualization of chemical phenomena in the microscopic world using semiconductor image sensor
2025-02-04
<Overview>
A research team led by Professor Kazuaki Sawada and Project Assistant Professor Hideo Doi of the Department of Electrical and Electronic Information Engineering, Toyohashi University of Technology has developed a semiconductor sensor enabling the real-time observation of two types of biomolecule dynamics in solutions. By using semiconductor technology to pattern a thin metal film functioning as a neurotransmitter-sensitive membrane on sensor pixels arranged two-dimensionally in a 2 µm pitch, the sensor captures the movement of hydrogen ions and lactate ...
Virus that causes COVID-19 increases risk of cardiac events
2025-02-04
OAK BROOK, Ill. – A new study found severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection was associated with the rapid growth of plaque in the coronary arteries and an increased risk of cardiovascular events. The results were published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
“COVID-19, caused by SARS-CoV-2, is initially characterized by acute lung injury and respiratory failure,” said the study’s senior author, Junbo Ge, M.D., professor and director of the Cardiology Department at Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University in Shanghai, ...
Half a degree rise in global warming will triple area of Earth too hot for humans
2025-02-04
New assessment warns area the size of the USA will become too hot during extreme heat events for even healthy young humans to maintain a safe body temperature if we hit 2°C above preindustrial levels.
For those aged over 60, the same 2°C rise would see more than a third of the planet’s land mass cross this critical ‘overheating’ threshold
An international group of scientists, led by King’s College London, has revealed how continued global warming will lead to more parts of the planet becoming too ...
Identifying ED patients likely to have health-related social needs
2025-02-04
INDIANAPOLIS -- Addressing patients’ health-related social needs such as housing instability, food insecurity, transportation barriers and financial strain is important to improving health outcomes yet can be challenging. A new study from Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University Indianapolis Richard M. Fairbanks School of Public Health investigates the best approach to predicting likely need for one or more health-related social need services.
To identify emergency department (E.D.) patients needing these services, researchers ...
Yo-yo dieting may significantly increase kidney disease risk in people with type 1 diabetes
2025-02-04
WASHINGTON—Body-weight cycling (also known as yo-yo dieting) has been shown to significantly increase the risk of kidney disease in people with type 1 diabetes, regardless of body mass index (BMI) and other traditional risk factors, according to a new study published in the Endocrine Society’s Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Yo-yo dieting is defined as repeatedly losing and gaining weight multiple times over the years. Its prevalence is reported to be as high as 35% in men and 55% in women.
This patten of dieting has been shown to increase risks of cardiovascular events ...
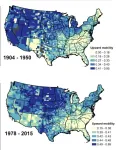
Big cities fuel inequality
2025-02-04
A study combining remote sensing and administrative data finds that since the mid-20th century, large, growing cities have ceased to be centers of upward social and economic mobility.
Cities have been celebrated as places of innovation and social mobility but also as hotspots of inequality and poverty. Dylan Shane Connor and colleagues measured how the size, density, and connectedness of urban areas in an American’s birth county predicted their social mobility across the 20th century. The results tell a tale of a waning relationship between ...
Financial comfort and prosociality
2025-02-04
People who feel financially comfortable are more likely to report prosocial actions like donating money and prosocial attitudes than people in a tough financial situation, according to a study. Prosociality—preferences and behaviors that benefit others—is essential to human society. In practice, it is determined by both the desire and the ability to help. Paul Vanags and colleagues analyzed data from the Global Preferences Survey and the Gallup World Poll, including 80,337 people in 76 countries with incomes ranging from about $200 a year to about $380,000 per year, adjusted to be equivalent across the different countries ...
Painted lady butterflies migrations and genetics
2025-02-04
A broadly distributed migratory butterfly travels varying distances, influenced by environmental conditions rather than following genetically coded instructions, according to a study. The Afro-Palearctic population of the painted lady butterfly, Vanessa cardui, is a single freely interbreeding, or ‘panmictic’ population.
Vanessa cardui is a renowned world traveler, undertaking multigenerational migrations throughout Africa, Asia, Europe, and North America. The winter breeding range of painted ladies in the Afro-Palearctic includes areas north and south of the Sahara ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Music can touch the heart, even inside the wombPlaying classical music can smooth variations in fetal heart rates.