(Press-News.org) People who feel financially comfortable are more likely to report prosocial actions like donating money and prosocial attitudes than people in a tough financial situation, according to a study. Prosociality—preferences and behaviors that benefit others—is essential to human society. In practice, it is determined by both the desire and the ability to help. Paul Vanags and colleagues analyzed data from the Global Preferences Survey and the Gallup World Poll, including 80,337 people in 76 countries with incomes ranging from about $200 a year to about $380,000 per year, adjusted to be equivalent across the different countries measured. The authors gathered responses to questions assessing participants’ levels of prosociality and wealth, in terms of both self-reported household income and subjective financial well-being. Subjective financial wellbeing was quantified based on whether participants reported they were “living comfortably” or merely “getting by” or worse, whether they were satisfied or dissatisfied with their standard of living, whether their standard of living was improving or deteriorating, and whether their city or area’s standard of living was improving or deteriorating. Around the world, people with higher incomes were more likely to report that they gave money to good causes, volunteered, or helped strangers within the past month than people with lower incomes. People with higher incomes were also more willing than people with lower incomes to return a prosocial act (e.g., the authors considered the amount of money that respondents would give a stranger who gave them directions), give to good causes without expecting anything in return, and punish unfair behavior towards themselves or others. However, those with higher incomes reported lower trust in others than those with lower incomes. People with higher subjective financial wellbeing scored higher on every prosocial measure than people with lower subjective financial wellbeing—including trust. According to the authors, the findings have implications for social policy.
END
Financial comfort and prosociality
2025-02-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Painted lady butterflies migrations and genetics
2025-02-04
A broadly distributed migratory butterfly travels varying distances, influenced by environmental conditions rather than following genetically coded instructions, according to a study. The Afro-Palearctic population of the painted lady butterfly, Vanessa cardui, is a single freely interbreeding, or ‘panmictic’ population.
Vanessa cardui is a renowned world traveler, undertaking multigenerational migrations throughout Africa, Asia, Europe, and North America. The winter breeding range of painted ladies in the Afro-Palearctic includes areas north and south of the Sahara ...
Globetrotting not in the genes
2025-02-04
Painted lady butterflies are world travelers. The ones we encounter in Europe fly from Africa to Sweden, ultimately returning to areas north and south of the Sahara. But what determines whether some butterflies travel long distances while others travel short distances? A group of scientists, including from the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA), shows that the different migration strategies are shaped by environmental conditions rather than being encoded in the butterfly’s DNA.
It is a warm summer day in June. A group of scientists with sunhats and nets is hiking along a trail in the Catalan mountains. They meticulously search for painted ladies—vibrant orange ...
Patient advocates from NCCN guidelines panels share their ‘united by unique’ stories for world cancer day
2025-02-04
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [February 4, 2025] — The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®) is joining people and organizations across the globe to commemorate World Cancer Day today. World Cancer Day is a global initiative to improve awareness and knowledge of cancer risks and actions for better prevention, detection, and treatment. It is led and organized by the Union of International Cancer Control (UICC) every February 4.
World Cancer Day 2025 marks the start of the ‘United by Unique’ campaign to highlight how every experience with cancer is unique, even as people touched by cancer ...
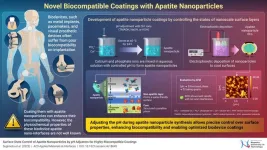
Innovative apatite nanoparticles for advancing the biocompatibility of implanted biodevices
2025-02-04
Medical implants have transformed healthcare, offering innovative solutions with advanced materials and technologies. However, many biomedical devices face challenges like insufficient cell adhesion, leading to inflammatory responses after their implantation in the body. Apatite coatings, particularly hydroxyapatite (HA)—a naturally occurring form of apatite found in bones, have been shown to promote better integration with surrounding tissues. However, the biocompatibility of artificially synthesized apatite nanoparticles often falls short of expectations, primarily due to the nanoparticles’ limited ability to bind effectively with biological tissues.
To overcome ...
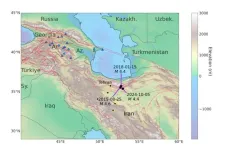
Study debunks nuclear test misinformation following 2024 Iran earthquake
2025-02-04
A new study debunks claims that a magnitude 4.5 earthquake in Iran was a covert nuclear weapons test, as widely alleged on social media and some mainstream news outlets in October 2024, a period of heightened geopolitical tensions in the Middle East.
Led by Johns Hopkins University scientists, the study warns about the potential consequences of mishandling and misinterpreting scientific information, particularly during periods of international conflict. The findings appear in the journal Seismica.
“There was a concerted misinformation and disinformation campaign around this event that promoted the idea this was a nuclear test, ...
Quantum machine offers peek into “dance” of cosmic bubbles
2025-02-04
Physicists have performed a groundbreaking simulation they say sheds new light on an elusive phenomenon that could determine the ultimate fate of the Universe.
Pioneering research in quantum field theory around 50 years ago proposed that the universe may be trapped in a false vacuum – meaning it appears stable but in fact could be on the verge of transitioning to an even more stable, true vacuum state. While this process could trigger a catastrophic change in the Universe's structure, experts agree that predicting the timeline ...
How hungry fat cells could someday starve cancer to death
2025-02-04
How Hungry Fat Cells Could Someday Starve Cancer to Death
Scientists transformed energy-storing white fat cells into calorie-burning ‘beige’ fat. Once implanted, they outcompeted tumors for resources, beating back five different types of cancer in lab experiments.
Liposuction and plastic surgery aren’t often mentioned in the same breath as cancer.
But they are the inspiration for a new approach to treating cancer that uses engineered fat cells to deprive tumors of nutrition.
Researchers at UC San Francisco used the gene editing technology CRISPR to turn ordinary white fat cells into “beige” fat cells, which voraciously consume calories to make ...
Breakthrough in childhood brain cancer research could heal treatment-resistant tumors, keep them in remission
2025-02-04
Brain cancer is the second-leading cause of death in children in the developed world. For the children who survive, standard treatments have long-term impacts on their development and quality of life, particularly in small children and infants.
Research out of Emory University and QIMR Berghofer Medical Research Institute in Queensland, Australia, has shown that a potential new targeted therapy for childhood brain cancer is effective in infiltrating and killing tumor cells in preclinical models tested in mice.
In ...
Research discovery halts childhood brain tumor before it forms
2025-02-04
Scientists at The Hospital for Sick Children (SickKids) have discovered a way to stop tumour growth before it starts for a subtype of medulloblastoma, the most common childhood malignant brain cancer.
Brain cancer presents a unique set of challenges for researchers – by the time a person experiences symptoms, the tumours are often so complex that the fundamental mechanisms driving the tumour growth are no longer easy to identify. A research team led by Dr. Peter Dirks is working to combat ...
Scientists want to throw a wrench in the gears of cancer’s growth
2025-02-04
Preventing the cell’s protein factories from making the notorious cancer-causing protein MYC could stop out-of-control tumors.
For decades, scientists have tried to stop cancer by disabling the mutated proteins that are found in tumors. But many cancers manage to overcome this and continue growing.
Now, UCSF scientists think they can throw a wrench into the fabrication of a key growth-related protein, MYC, that escalates wildly in 70% of all cancers. Unlike some other targets of cancer therapies, MYC can be dangerous simply due to its abundance.
In a paper that appears Feb. 4 in Nature Cell Biology, researchers at UC San Francisco ...