(Press-News.org) OAK BROOK, Ill. – A new study found severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection was associated with the rapid growth of plaque in the coronary arteries and an increased risk of cardiovascular events. The results were published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
“COVID-19, caused by SARS-CoV-2, is initially characterized by acute lung injury and respiratory failure,” said the study’s senior author, Junbo Ge, M.D., professor and director of the Cardiology Department at Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University in Shanghai, China. “However, emerging evidence indicates COVID-19 also involves an extreme inflammatory response that can affect the cardiovascular system.”
According to Dr. Ge, this systemic inflammation produces consequences for the heart beyond the first month of infection, leading to high mortality and unfavorable outcomes.
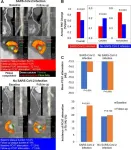
The researchers investigated the impact of SARS-CoV-2 infection using coronary CT angiography (CCTA) to assess coronary inflammation, determined by analyzing changes in tissue surrounding the coronary arteries, as well as plaque burden and type.
The retrospective study included patients who underwent CCTA between September 2018 and October 2023. The final study group of 803 patients (mean age, 63.9 years, 543 men) included 329 patients (41%) imaged before the COVID-19 pandemic and 474 patients imaged during the pandemic. Of those, 25 patients were infected with SARS-CoV-2 before imaging.
The research team analyzed a total of 2,588 coronary artery lesions, including 2,108 lesions among SARS-CoV-2 patients and 480 lesions among uninfected patients.
For all patients, researchers compared baseline and follow-up measurements of plaque volume changes, the presence of high-risk plaque and inflammation. They also analyzed the relationship between SARS-CoV-2 and cardiovascular events, such as a heart attack or revascularization procedure.
At baseline, the mean stenosis, or narrowing of the artery, per lesion was 31.3%. Only 8.1% of lesions had diameter stenosis of 50% or more.
Compared to the uninfected patients, the plaque volumes grew faster in SARS-CoV-2 patients. Lesions in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection had a higher incidence of developing into high-risk plaques (20.1% versus 15.8%) and coronary inflammation (27% versus 19.9%). Patients with COVID-19 also had a higher risk of target lesion failure (10.4% versus 3.1%), an indicator of increased heart attack or stroke risk.
“Inflammation following COVID-19 can lead to ongoing plaque growth, particularly in high-risk, noncalcified plaques.” Dr. Ge said. “Patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection are at increased risk for myocardial infarction, acute coronary syndrome and stroke for up to a year.”
He added that these effects persist during the aftermath of COVID-19, regardless of comorbidities such as age, hypertension, and diabetes.
“Effective management strategies for these patients are imperative,” Dr. Ge said.
The findings suggest that SARS-CoV-2 infection may exacerbate cardiovascular risk by accelerating the progression of susceptible plaques and coronary inflammation. However, a more comprehensive understanding of the biological mechanisms is required to formulate preventative and therapeutic approaches.
“It’s crucial to anticipate a heavier cardiovascular patient burden in the future as most infected individuals recover from acute SARS-CoV-2 infection,” Dr. Ge said.
###
“SARS-CoV-2 Infection Association with Atherosclerotic Plaque Progression at Coronary CT Angiography and Adverse Cardiovascular Events.” Collaborating with Dr. Ge were Neng Dai, M.D., Xianglin Tang, M.D., Yiqing Hu, M.D., Hao Lu, M.D., Zhangwei Chen, M.D., Shaofeng Duan, Ph.D., Weifeng Guo, M.D., Pranav Prakash Edavi, M.D., Yongfu Yu, Ph.D., Dong Huang, M.D., and Juying Qian, M.D.
Radiology is edited by Linda Moy, M.D., New York University, New York, N.Y., and owned and published by the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. (https://pubs.rsna.org/journal/radiology)
RSNA is an association of radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists and related scientists promoting excellence in patient care and health care delivery through education, research and technologic innovation. The Society is based in Oak Brook, Illinois. (RSNA.org)
For patient-friendly information on CT angiography, visit RadiologyInfo.org.
END
New assessment warns area the size of the USA will become too hot during extreme heat events for even healthy young humans to maintain a safe body temperature if we hit 2°C above preindustrial levels.
For those aged over 60, the same 2°C rise would see more than a third of the planet’s land mass cross this critical ‘overheating’ threshold
An international group of scientists, led by King’s College London, has revealed how continued global warming will lead to more parts of the planet becoming too ...
INDIANAPOLIS -- Addressing patients’ health-related social needs such as housing instability, food insecurity, transportation barriers and financial strain is important to improving health outcomes yet can be challenging. A new study from Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University Indianapolis Richard M. Fairbanks School of Public Health investigates the best approach to predicting likely need for one or more health-related social need services.
To identify emergency department (E.D.) patients needing these services, researchers ...
WASHINGTON—Body-weight cycling (also known as yo-yo dieting) has been shown to significantly increase the risk of kidney disease in people with type 1 diabetes, regardless of body mass index (BMI) and other traditional risk factors, according to a new study published in the Endocrine Society’s Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Yo-yo dieting is defined as repeatedly losing and gaining weight multiple times over the years. Its prevalence is reported to be as high as 35% in men and 55% in women.
This patten of dieting has been shown to increase risks of cardiovascular events ...
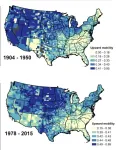
A study combining remote sensing and administrative data finds that since the mid-20th century, large, growing cities have ceased to be centers of upward social and economic mobility.
Cities have been celebrated as places of innovation and social mobility but also as hotspots of inequality and poverty. Dylan Shane Connor and colleagues measured how the size, density, and connectedness of urban areas in an American’s birth county predicted their social mobility across the 20th century. The results tell a tale of a waning relationship between ...
People who feel financially comfortable are more likely to report prosocial actions like donating money and prosocial attitudes than people in a tough financial situation, according to a study. Prosociality—preferences and behaviors that benefit others—is essential to human society. In practice, it is determined by both the desire and the ability to help. Paul Vanags and colleagues analyzed data from the Global Preferences Survey and the Gallup World Poll, including 80,337 people in 76 countries with incomes ranging from about $200 a year to about $380,000 per year, adjusted to be equivalent across the different countries ...
A broadly distributed migratory butterfly travels varying distances, influenced by environmental conditions rather than following genetically coded instructions, according to a study. The Afro-Palearctic population of the painted lady butterfly, Vanessa cardui, is a single freely interbreeding, or ‘panmictic’ population.
Vanessa cardui is a renowned world traveler, undertaking multigenerational migrations throughout Africa, Asia, Europe, and North America. The winter breeding range of painted ladies in the Afro-Palearctic includes areas north and south of the Sahara ...
Painted lady butterflies are world travelers. The ones we encounter in Europe fly from Africa to Sweden, ultimately returning to areas north and south of the Sahara. But what determines whether some butterflies travel long distances while others travel short distances? A group of scientists, including from the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA), shows that the different migration strategies are shaped by environmental conditions rather than being encoded in the butterfly’s DNA.
It is a warm summer day in June. A group of scientists with sunhats and nets is hiking along a trail in the Catalan mountains. They meticulously search for painted ladies—vibrant orange ...
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [February 4, 2025] — The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®) is joining people and organizations across the globe to commemorate World Cancer Day today. World Cancer Day is a global initiative to improve awareness and knowledge of cancer risks and actions for better prevention, detection, and treatment. It is led and organized by the Union of International Cancer Control (UICC) every February 4.
World Cancer Day 2025 marks the start of the ‘United by Unique’ campaign to highlight how every experience with cancer is unique, even as people touched by cancer ...
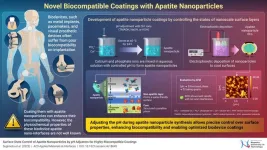
Medical implants have transformed healthcare, offering innovative solutions with advanced materials and technologies. However, many biomedical devices face challenges like insufficient cell adhesion, leading to inflammatory responses after their implantation in the body. Apatite coatings, particularly hydroxyapatite (HA)—a naturally occurring form of apatite found in bones, have been shown to promote better integration with surrounding tissues. However, the biocompatibility of artificially synthesized apatite nanoparticles often falls short of expectations, primarily due to the nanoparticles’ limited ability to bind effectively with biological tissues.
To overcome ...
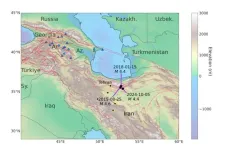
A new study debunks claims that a magnitude 4.5 earthquake in Iran was a covert nuclear weapons test, as widely alleged on social media and some mainstream news outlets in October 2024, a period of heightened geopolitical tensions in the Middle East.
Led by Johns Hopkins University scientists, the study warns about the potential consequences of mishandling and misinterpreting scientific information, particularly during periods of international conflict. The findings appear in the journal Seismica.
“There was a concerted misinformation and disinformation campaign around this event that promoted the idea this was a nuclear test, ...