Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a common digestive disorder that affects the intestine, causing symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, gas, and changes in bowel habits, including diarrhea, constipation, or both. Although this condition affects about a tenth of the global population, the underlying causes and mechanisms of IBS remain unclear. Consequently, treatments for IBS primarily focus on managing symptoms rather than addressing the root cause of the disorder.
At Tokyo University of Science (TUS), Japan, Professor Akiyoshi Saitoh and his research group have spent the past decade exploring this topic. This study published online in the British Journal of Pharmacology on December 25, 2024, discovered that a class of drugs called opioid delta-receptor (DOP) agonists may help alleviate IBS symptoms by targeting the central nervous system rather than acting directly on the intestine. This study was co-authored by Toshinori Yoshioka, a third-year PhD student at TUS.
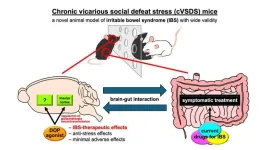
One of the main motivations for this study was the growing evidence linking IBS closely to psychological stress. Saitoh’s group aimed to address this potential root cause by focusing on finding a novel animal model for this condition. In a study published in 2022, they developed a mice model repeatedly exposed to psychological stress—using a method called chronic vicarious social defeat stress (cVSDS)—which developed symptoms similar to a type of IBS called IBS-D. These symptoms included overly active intestines and heightened sensitivity to abdominal pain, even though their organs showed no physical damage. The cVSDS animal model involved having the subject mouse repeatedly witness a territorial, aggressive mouse defeating a cage mate, inducing indirect chronic stress.
Using the cVSDS model, the researchers sought to determine whether DOP in the brain, which is closely linked to pain and mood regulation, could serve as promising drug targets for treating stress-induced IBS. To achieve this, they performed a series of detailed experiments to observe the effects of DOP agonists on IBS symptoms and chemical signaling in the brain. Some experiments involved measuring the speed of a charcoal meal through the intestine to assess gastrointestinal motility and evaluate the impact of stress or treatments on bowel movement speed, along with directly measuring neurotransmitter concentrations using in vivo brain microdialysis. This revealed that re-exposure to VSDS increased glutamate levels in the insular cortex, but these elevated levels were normalized with DOP agonists.
According to the results, the administration of DOP agonists helped relieve abdominal pain and regulated bowel movements in cVSDS mice. Interestingly, applying the DOP agonists directly to a specific brain region called the insular cortex had similar effects on IBS symptoms as systemic treatment. “Our findings demonstrated that DOP agonists acted directly on the central nervous system to improve diarrhea-predominant IBS symptoms in mice, and suggest that the mechanism of action involves the regulation of glutamate neurotransmission in the insular cortex,” highlights Saitoh.
Taken together, the continued research by Saitoh’s group on this topic could pave the way for effective treatments for IBS. “DOP agonists could represent a groundbreaking new IBS treatment that not only improves IBS-like symptoms but also provides anti-stress and emotional regulation effects. In the future, we would like to conduct clinical developments with the goal of expanding the indication of DOP agonists for IBS, in addition to depression,” remarks Saitoh.
Compared to currently available IBS treatments, such as laxatives, antidiarrheals, analgesics, and antispasmodics, targeting the underlying stress with DOP agonists may offer a more definitive solution with minimal adverse effects. Further clarification of the roles of stress and brain chemistry in the development of IBS will be essential in achieving this much-needed medical breakthrough. With promising prospects, future studies will translate Saitoh’s group’s findings to humans, bringing great relief to those affected by IBS.
***
Reference
Title of original paper: Agonists of the opioid δ-receptor improve irritable bowel syndrome-like symptoms via the central nervous system
Journal: British Journal of Pharmacology
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.17428
About The Tokyo University of Science
Tokyo University of Science (TUS) is a well-known and respected university, and the largest science-specialized private research university in Japan, with four campuses in central Tokyo and its suburbs and in Hokkaido. Established in 1881, the university has continually contributed to Japan's development in science through inculcating the love for science in researchers, technicians, and educators.
With a mission of “Creating science and technology for the harmonious development of nature, human beings, and society," TUS has undertaken a wide range of research from basic to applied science. TUS has embraced a multidisciplinary approach to research and undertaken intensive study in some of today's most vital fields. TUS is a meritocracy where the best in science is recognized and nurtured. It is the only private university in Japan that has produced a Nobel Prize winner and the only private university in Asia to produce Nobel Prize winners within the natural sciences field.
Website: https://www.tus.ac.jp/en/mediarelations/
About Professor Akiyoshi Saitoh from Tokyo University of Science
Professor Akiyoshi Saitoh, a distinguished researcher and professor at Tokyo University of Science's Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, is renowned for his expertise in medical and behavioral pharmacology, neuroscience, and anti-anxiety drug development. Holding a Ph.D. from Hoshi University, he has authored over 130 impactful publications in areas such as pharmacology, psychopharmacology, and neuropharmacology. With multiple patents to his name, Prof. Saitoh's innovative contributions have left a lasting mark. His influential work, reflected in numerous citations, has established him as a key figure in advancing the pharmaceutical and neuroscience disciplines.
Funding information
This work was supported by the Core Research for Evolutional Science and Technology as part of the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED, grant number JP24gm1510008).
END