Drying and rewetting cycles substantially increased soil CO2 release
2025-02-06
(Press-News.org)
Niigata, Japan - The amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) released by microbial decomposition of soil organic carbon on a global scale is approximately five times greater than the amount of anthropogenic CO2 emissions. Thus, it is essential to clarify the impact of climate change on soil CO2 release dynamics.
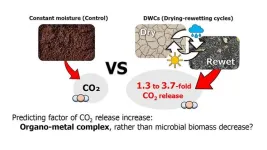
A collaborative research group consisting of Dr. Hirohiko Nagano and Ms. Yuri Suzuki of Niigata University with researchers of Kyushu University and the Japan Atomic Energy Agency conducted incubation experiments on forest and pastureland soils at 10 locations across Japan. The research group revealed that the amount of CO2 released from soil increases significantly due to repeated drying and rewetting cycles (DWCs) expected to be caused by changes in precipitation patterns due to global warming. Here, the CO2 release under DWCs were 1.3- to 3.7-fold greater than under continuous constant moisture conditions. They also observed a significant decrease in microbial biomass under DWCs, suggesting that the newly supplied organic carbon resulting from the destruction of microbial cells by repeated DWCs contributed to the increase in CO2 release. In addition, it was found that the increased rate of CO2 release due to repeated DWCs was greater in soils with a higher abundance of reactive metal-organic matter complex. This suggests that the reactive metal-organic matter complex, considered important as a stable accumulation mechanism for soil organic carbon, may become more readily available to microorganisms through repeated DWCs. Thus, organic carbon that has previously avoided decomposition may become a new source of CO2 release under DWCs.
Dr. Nagano pointed out that extreme weather phenomena are becoming more evident due to global warming. Furthermore, he says that the results of this research will lead to a detailed elucidation of the impact of extreme weather phenomena on soil CO2 emissions, contributing to improving the accuracy of prediction models for the future of the global environment. In the future, they plan to conduct impact assessments and mechanism verification in outdoor environments in addition to further detailed research of mechanisms for the DWCs-induced increase in CO2 releases among various soils all over the world.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-02-05
URBANA, Ill. – Globally, women’s workforce participation is about 25% lower than men’s, often due to barriers such as domestic responsibilities and cultural norms. Vocational training can increase employment opportunities, but women may not be able to attend training programs that require them to be away from home. A new study from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, in collaboration with an international research team, explored whether hybrid distance learning can improve accessibility to ...
2025-02-05
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — People’s bodies can be old or young for their chronological age, depending, in part, on the amount and types of stressors they have experienced. Scientists can estimate people’s biological age, but whether they use oral tissue or blood to make the measurement matters, according to a new study led by researchers in the Penn State Department of Biobehavioral Health.
Biological age — a measure of how well one’s body is functioning — differs from chronological age — the amount of time since someone was born. While chronological age can be correlated to disease risk, researchers and medical ...
2025-02-05
After combing through 4,000 existing medications, an artificial intelligence tool helped uncover one that saved the life of a patient with idiopathic multicentric Castleman’s disease (iMCD). This rare disease has an especially poor survival rate and few treatment options. The patient could be the first of many to have their lives saved by an AI prediction system, which could potentially apply to other rare conditions.
Detailed in a new paper published in NEJM, a group led by researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania used an AI technique called machine learning to determine that adalimumab—a ...
2025-02-05
How do bacteria — harmless ones living in our bodies, or those that cause disease — organize their activities? A new study, combining powerful genomic-scale microscopy with a technical innovation, captured which genes bacteria turn on in different situations and in different spatial environments. The technology, described January 23 in Science, promises to take the study of bacteria to the next level.
Jeffrey Moffitt, PhD, and colleagues in the Program in Cellular and Molecular Medicine (PCMM) at Boston Children’s Hospital applied MERFISH, a molecular ...
2025-02-05
February 5, 2025, Mountain View, CA -- The SETI Institute announced the Davie Postdoctoral Fellowship in Artificial Intelligence for Astronomy, inviting researchers to refine and expand ML-driven pipelines for exoplanet discovery. The successful candidate will join the SETI Institute researcher Dr. Vishal Gajjar and his team and collaborators at the SETI Institute and IIT Tirupati in India. This project will focus on enhancing supervised CNN architectures and integrating anomaly-detection techniques to uncover subtle or unconventional signals hidden within massive datasets. The application deadline is March 15, 2025. Information about how to apply is here.
“Machine ...
2025-02-05
University of Delaware Associate Professor Teomara Rutherford, along with UD co-authors Hye Rin Lee, Austin Cory Bart and Andrew Rodrigues and Megan Englert of the University of Colorado Boulder, investigated changes in student motivation in first-year university CS courses. Although students’ perception of the value of CS declined over the semester, their sense of belonging and beliefs in their ability to succeed increased. Rutherford and her co-authors also found that students’ beliefs in their ability to succeed, their view of the course’s importance and their perception of its emotional cost ...
2025-02-05
Research Highlights:
Mechanically retrieving a blood clot blocking a medium- or small-sized brain artery was no better at reducing disability 90 days after a stroke than standard care alone (including clot-busting medication if indicated).
While researchers say using thrombectomy devices to remove blood clots is increasingly performed, this research suggests that it may not be needed in all cases.
However, because endovascular therapy seemed to be safe, it might still be used on select patients.
Note: The study featured in this news release is a research abstract. Abstracts ...
2025-02-05
CHICAGO, IL USA – 5 February, 2025 – Following a five-year hiatus, the world’s only registry of patients with durable mechanical circulatory support (MCS) devices is re-launching and will begin collecting data from institutions around the globe in early 2025.
The International Registry for Mechanically Assisted Circulatory Support (IMACS) registry is operated by the International Society for Health and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT), a global multidisciplinary professional organization ...
2025-02-05
The study is an international collaboration based on previous research that has suggested a possible connection between trauma and endometriosis.
Endometriosis is tissue resembling the uterine lining that grows outside the uterus. The condition is very common among women and can cause significant pain and fertility problems for many.
– The motivation for the study was to better understand this potential link between traumatic experiences and the development of endometriosis. Specifically, we wanted to explore whether certain types of trauma were more strongly associated with endometriosis than others, and whether this potential interaction is independent ...
2025-02-05
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, FEBRUARY 5, 2025
MINNEAPOLIS – Children and young people who are Black or Hispanic are less likely to be diagnosed with migraine than those who are white when being seen for headache in a pediatric emergency department, according to a study published in the February 5, 2025, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study also found they received fewer tests and less intensive treatment.
“Migraine is disabling and can significantly impact ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Drying and rewetting cycles substantially increased soil CO2 release



