New genetic mutation linked to drug resistance in non-small cell lung cancer patient
“Here we present a case of a patient with stage IV CD-74-ROS1 fusion NSCLC discovered initially with RNA next generation sequencing (NGS) who acquired resistance to lorlatinib after 6 months on therapy through a novel RUFY1-RET fusion, detected..."
2025-02-06
(Press-News.org)
“Here we present a case of a patient with stage IV CD-74-ROS1 fusion NSCLC discovered initially with RNA next generation sequencing (NGS) who acquired resistance to lorlatinib after 6 months on therapy through a novel RUFY1-RET fusion, detected only through RNA NGS.”
BUFFALO, NY - February 6, 2025 – A new case report was published in Volume 16 of Oncotarget on February 5, 2025, titled “Acquired RUFY1-RET rearrangement as a mechanism of resistance to lorlatinib in a patient with CD74-ROS1 rearranged non-small cell lung cancer: A case report."
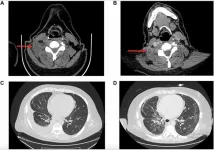
In this case report, Jenny L. Wu from Vanderbilt University School of Medicine and Wade T. Iams from Vanderbilt-Ingram Cancer Center describe a rare case of drug resistance in a patient with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The patient, a 42-year-old man who had never smoked, initially responded well to lorlatinib, a targeted therapy designed to treat cancer driven by specific genetic alterations. However, after six months, his cancer began to grow again. Clinicians discovered that this was due to a new genetic change, known as the RUFY1-RET fusion. This finding highlights how cancers can adapt to treatment and the importance of ongoing genetic testing to guide therapy decisions.
NSCLC is the most common type of lung cancer, and in some cases, it is driven by genetic changes that can be targeted with specific drugs. The patient’s cancer originally had a ROS1 gene rearrangement, which made it responsive to lorlatinib. But as time went on, the cancer started to grow again, and tests revealed a new genetic alteration called RUFY1-RET fusion, which likely caused resistance to lorlatinib.
This new genetic change was identified using RNA next-generation sequencing (RNA NGS), an advanced test that can find mutations that standard genetic tests might miss. After discovering the RUFY1-RET gene fusion, the patient was treated with a combination of lorlatinib and pralsetinib, a drug that specifically targets RET gene alterations. While this combination helped control the cancer for about four months, the patient’s condition unfortunately worsened after four months.
“This is the first reported case of a RET fusion as a potential mechanism of resistance to lorlatinib, it identifies a novel RET fusion partner, and it emphasizes the importance of testing for acquired resistance mutations with both DNA and RNA at the time of progression in patients with targetable oncogenic drivers.”
Understanding cases like this can help clinicians and researchers develop more effective treatment strategies, including combination therapies that target multiple genetic changes to combat drug resistance. While the combined therapy in this case provided only temporary benefits, it offers important insights for future research and patient care, particularly for cancers that no longer respond to standard treatments.
Continue reading: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.28682
Correspondence to: Wade T. Iams - wade.t.iams@vumc.org
Keywords: cancer, ROS1 rearrangement, RET rearrangement, non-small cell lung cancer, targeted therapy, case report
Click here to sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article.
About Oncotarget:
Oncotarget (a primarily oncology-focused, peer-reviewed, open access journal) aims to maximize research impact through insightful peer-review; eliminate borders between specialties by linking different fields of oncology, cancer research and biomedical sciences; and foster application of basic and clinical science.
Oncotarget is indexed and archived by PubMed/Medline, PubMed Central, Scopus, EMBASE, META (Chan Zuckerberg Initiative) (2018-2022), and Dimensions (Digital Science).
To learn more about Oncotarget, visit Oncotarget.com and connect with us on social media:
X
Facebook
YouTube
Instagram
LinkedIn
Pinterest
Spotify, and available wherever you listen to podcasts
Click here to subscribe to Oncotarget publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Oncotarget Journal Office
6666 East Quaker St., Suite 1
Orchard Park, NY 14127
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-02-06
WASHINGTON — Researchers have designed a single-photon time-of-flight LiDAR system that can acquire a high-resolution 3D image of an object or scene up to 1 kilometer away. The new system could help enhance security, monitoring, and remote sensing by enabling detailed imaging even in challenging environmental conditions or when objects are obscured by foliage or camouflage netting.
“Our system uses a single-photon detector approximately twice as efficient as detectors deployed in similar LiDAR systems ...
2025-02-06
INDIANAPOLIS – Breast cancer is the world’s most prevalent cancer. Although earlier detection and targeted treatment have resulted in high survival rates, many breast cancer survivors experience fear of cancer recurrence. For some survivors this fear is occasional, for others it is persistent and often debilitating.
A new study of breast cancer survivors has found this psychosocial challenge impacts almost every important domain of their lives – the emotional, behavioral, cognitive, relational and professional. A larger number of domains was affected, ...
2025-02-06
Korea University Researchers Analysis of Income-Related Disparities in Mortality Among Young Adults with Diabetes
Type 2 diabetics (T2D) under 40 years of age with low income have a threefold higher risk of mortality
Young people with T2D are more affected by income than elderly people with T2D
The research team of Professor Sin Gon Kim and Professor Nam Hoon Kim of department of internal medicine (Endocrinology and Metabolism) of Korea University Anam Hospital, and Professor Ji Yoon Kim of Samsung Medical Center confirmed that young adults with T2D with low income have 3 times higher mortality ...
2025-02-06
New research forthcoming in Social Psychological and Personality Science shows that when people understand how income inequality creates disparities in healthcare and education access, they become more likely to support policies addressing economic inequality.
Across four studies, the research shows that highlighting connections between income gaps and inequalities in health and education access decreases acceptance of economic disparities and increase support for redistributive actions.
"Research has shown that people often tolerate income inequality. However, our study shows that when people perceive ...
2025-02-06
SCOTTSDALE, Ariz. — Feb. 6, 2025 — Michael S. Gordon, M.D., Chief Medical Officer of HonorHealth Research Institute, today was named a Fellow of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (FASCO), the world’s leading professional organization for physicians and oncology professionals caring for people with cancer.
“The title of FASCO is a recognition bestowed upon ASCO members who have shown extraordinary dedication for their voluntary efforts that benefit the Society, the specialty of oncology, and most importantly, the patients whom we serve,” according to a letter ...
2025-02-06
AMES, Iowa – A farmer notices an unfamiliar insect on a leaf.
Is this a pollinator? Or a pest? Good news at harvest time? Or bad? Need to be controlled? Or not?
That farmer can snap a picture, use a smartphone or computer to feed the photo into a web-based application called InsectNet and, with the help of machine learning technology, get back real-time information.
“The app identifies the insect and returns a prediction of its taxonomic classification and role in the ecosystem as a pest, predator, pollinator, parasitoid, decomposer, herbivore, indicator ...
2025-02-06
Restoring Predators, Restoring Ecosystems: Yellowstone Wolves and other Carnivores Drive Strong Trophic Cascade
Corvallis, OR — February 6, 2025 — A new study reveals the profound ecological effects of wolves and other large carnivores in Yellowstone National Park, showcasing the cascading effects predators can have on ecosystems. In Yellowstone, this involves wolves and other large carnivores, elk, and willows. The research, which utilized previously published data from 25 riparian (streamside) ...
2025-02-06
The domestication of maize is one of the greatest examples of humankind’s impact on evolution. Early farmers’ pre-industrial plant breeding choices turned corn from a nearly inedible crop into the major global food source it is today.
Now, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Professors Rob Martienssen and Thomas Gingeras are uncovering the genetics behind choices farmers made 9,000 years ago. They aim to better understand how evolution works and to help today’s farmers update corn so it can grow in harsh conditions. To ...
2025-02-06
Boston, MA – Today, the Kraft Center for Community Health at Mass General Brigham announced the launch of the inaugural Kraft Prize for Excellence and Innovation in Community Health. This national prize seeks to honor a transformative organization, program or innovation that is making a measurable impact on health outcomes and has the potential to become a scalable model for addressing community health.
“We established The Kraft Center for Community Health with a mission to expand access to high-quality, cost-effective healthcare for medically underserved patients, families, and communities,” ...
2025-02-06
The blue whale is the largest animal on the planet. It consumes enormous quantities of tiny, shrimp-like animals known as krill to support a body of up to 100 feet (30 meters) long. Blue whales and other baleen whales, which filter seawater through their mouths to feed on small marine life, once teemed in Earth’s oceans. Then over the past century they were hunted almost to extinction for their energy-dense blubber.
As whales were decimated, some thought the krill would proliferate in predator-free waters. But that’s not what happened. Krill populations dropped, too, and neither population has ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New genetic mutation linked to drug resistance in non-small cell lung cancer patient
“Here we present a case of a patient with stage IV CD-74-ROS1 fusion NSCLC discovered initially with RNA next generation sequencing (NGS) who acquired resistance to lorlatinib after 6 months on therapy through a novel RUFY1-RET fusion, detected..."