(Press-News.org) The domestication of maize is one of the greatest examples of humankind’s impact on evolution. Early farmers’ pre-industrial plant breeding choices turned corn from a nearly inedible crop into the major global food source it is today.
Now, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Professors Rob Martienssen and Thomas Gingeras are uncovering the genetics behind choices farmers made 9,000 years ago. They aim to better understand how evolution works and to help today’s farmers update corn so it can grow in harsh conditions. To get there, they’ve launched a new genomic encyclopedia called MaizeCODE. The research project is based on the Encyclopedia of DNA Elements (ENCODE). ENCODE aimed to identify functional elements in the human genome. Gingeras was one of its principal investigators. He explains:
“The original purpose—and it’s copied in the MaizeCODE effort—is to find all the domains of the genome that encode operational and coding information that the cell uses to reproduce and carry out the functions the cell serves.”
In a new study, the Gingeras and Martienssen labs analyzed regulatory sequences across five different tissue types from three strains of maize and its ancestor teosinte. They found hundreds of thousands of regulatory regions, called enhancers, that help turn genes on and off in plants.
They also saw that maize has a few thousand “super enhancers.” Each controls several genes at once. Incredibly, these super enhancers were very strongly selected when maize was domesticated 9,000 years ago. Martienssen explains:
“We can now say that maize domestication was really focused—unwittingly perhaps —by selection on this rather narrow set of super enhancers in maize ears.”
In addition to expanding our understanding of evolution, these findings could help point the way to new strains of maize. Martienssen and Gingeras have received a grant from the National Science Foundation to work on creating crops that can grow in soil with high levels of aluminum. Such conditions are common in South America. The scientists will use MaizeCODE “to find all the regulatory regions that are responsible for endowing both maize and sorghum with aluminum resistance,” Martienssen says.
But that’s not MaizeCODE’s only use. The genome database may one day help farmers further improve their maize crops. Imagine plants that are more resistant to disease or tolerant to droughts. Better still, imagine crops with higher yields that can feed more people. MaizeCODE may help make all of this possible. And because the data is publicly available, it can be accessed by plant biologists and breeders across the globe. “We’re only touching the tip of the iceberg,” Martienssen says.
END
Corn’s ancient ancestors are calling
2025-02-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mass General Brigham’s Kraft Center Announces the 2025 Kraft Prize for Excellence and Innovation in Community Health
2025-02-06
Boston, MA – Today, the Kraft Center for Community Health at Mass General Brigham announced the launch of the inaugural Kraft Prize for Excellence and Innovation in Community Health. This national prize seeks to honor a transformative organization, program or innovation that is making a measurable impact on health outcomes and has the potential to become a scalable model for addressing community health.
“We established The Kraft Center for Community Health with a mission to expand access to high-quality, cost-effective healthcare for medically underserved patients, families, and communities,” ...
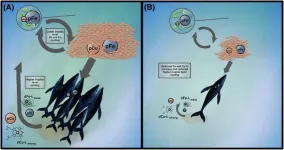
Whale poop contains iron that may have helped fertilize past oceans
2025-02-06
The blue whale is the largest animal on the planet. It consumes enormous quantities of tiny, shrimp-like animals known as krill to support a body of up to 100 feet (30 meters) long. Blue whales and other baleen whales, which filter seawater through their mouths to feed on small marine life, once teemed in Earth’s oceans. Then over the past century they were hunted almost to extinction for their energy-dense blubber.
As whales were decimated, some thought the krill would proliferate in predator-free waters. But that’s not what happened. Krill populations dropped, too, and neither population has ...
Mercury content in tuna can be reduced with new packaging solution
2025-02-06
Fish is a high-quality source of protein, containing omega-3 fatty acids and many other beneficial nutrients. However, the accumulation of toxic mercury also makes fish consumption a concern, of which tuna is particularly susceptible. Researchers from Chalmers University of Technology in Sweden have come up with a novel approach to packaging canned tuna infused in the water-based solution of amino acid cysteine. It was shown to remove up to 35 percent of the accumulated mercury in canned tuna, significantly reducing human exposure to mercury via food.
Fish and other seafood, provide people with a broad variety of essential nutrients in their diet However, the consumption ...
Recycling the unrecyclable
2025-02-06
Epoxy resins are coatings and adhesives used in a broad range of familiar applications, such as construction, engineering and manufacturing. However, they often present a challenge to recycle or dispose of responsibly. For the first time, a team of researchers, including those from the University of Tokyo, developed a method to efficiently reclaim materials from a range of epoxy products for reuse by using a novel solid catalyst.
There’s a high chance you are surrounded by epoxy compounds as you read this. They are used in electronic devices due to their insulating ...
Alien ocean could hide signs of life from spacecraft
2025-02-06
Searching for life in alien oceans may be more difficult than scientists previously thought, even when we can sample these extraterrestrial waters directly.
A new study focusing on Enceladus, a moon of Saturn that sprays its ocean water into space through cracks in its icy surface, shows that the physics of alien oceans could prevent evidence of deep-sea life from reaching places where we can detect it.
Published today (Thursday, 6 February 2025) in Communications Earth and Environment, the study shows how Enceladus's ocean forms distinct layers that dramatically slow the movement of material ...
Research unveils new strategies to tackle atrial fibrillation, a condition linked to stroke and dementia risks
2025-02-06
A recent Brazilian study published in Nature Cardiovascular Research has highlighted promising pathways for preventing and treating atrial fibrillation, a condition that significantly raises the risks of stroke and dementia. The research was led by the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro (UFRJ) in partnership with the D’Or Institute for Research and Education (IDOR).
What Is Atrial Fibrillation?
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common cardiac arrhythmia worldwide. It disrupts the normal rhythm of the heart, causing irregular and often rapid heartbeats. This condition is associated with increased risks of stroke, dementia, and heart failure. It is also linked to other health ...
Research spotlight: Researchers identify potential drug targets for future heart failure therapeutics
2025-02-06
How would you summarize your study for a lay audience?
Heart failure remains a substantial burden for patients due to its high prevalence and limited therapeutic options. Heart failure is classified into two major clinical subtypes— heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) and heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). While there have been significant therapeutic advances in HFrEF, the rate of complications and death from HFrEF remains high. Additionally, most drugs that have shown benefits for patients with HFrEF have not demonstrated a comparable benefit in patients with HFpEF, highlighting a critical need for the development of targeted therapies ...
Air pollution clouds the mind and makes everyday tasks challenging
2025-02-06
People’s ability to interpret emotions or focus on performing a task is reduced by short-term exposure to particulate matter (PM) air pollution, potentially making everyday activities, such as the weekly supermarket shop, more challenging, a new study reveals.
Scientists discovered that even brief exposure to high concentrations of PM may impair a person’s ability to focus on tasks, avoid distractions, and behave in a socially acceptable manner.
Researchers exposed study participants to either high levels of air pollution - using candle smoke - or clean air, testing cognitive abilities ...
Uncovering how developmental genes are held in a poised state
2025-02-06
Key points:
Researchers from the Voigt lab have extended our understanding of how developmental genes are held in a poised state to allow timely expression once they receive the correct ‘go’ signals.
The next layer of regulation has been uncovered by the identification of proteins that interact with the epigenetic marks that poise developmental genes ready for expression.
The research provides insight into the mechanisms through which the phenomenon of bivalency – where both activating and repressive marks are laid down at the same site on the genome – acts to ready developmental ...
Multimillion-pound research project aims to advance production of next-generation sustainable packaging
2025-02-06
A multimillion-pound research project, called SustaPack, aims to overcome manufacturing challenges for the next generation of sustainable, paper-based packaging for liquids. Backed by a £1 million grant from the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) as part of UKRI’s co-investing programme, packaging technology company Pulpex Ltd has joined forces with the University of Surrey to refine its manufacturing processes to provide a viable solution to plastic pollution.
Contributing matching support towards the project, Pulpex has already made significant strides in the development of its patented technology, ...