(Press-News.org) Collagen, the body’s most abundant protein, has long been viewed as a predictable structural component of tissues. However, a new study led by Rice University’s Jeffrey Hartgerink and Tracy Yu, in collaboration with Mark Kreutzberger and Edward Egelman at the University of Virginia (UVA), challenges that notion, revealing an unexpected confirmation in collagen structure that could reshape biomedical research.
The researchers used advanced cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) to determine the atomic structure of a packed collagen assembly that deviates from the traditionally accepted right-handed superhelical twist. Published Feb. 3 in ACS Central Science, the study suggests collagen’s structural diversity may be greater than previously believed.
“This work fundamentally changes how we think about collagen,” said Hartgerink, professor of chemistry and bioengineering. “For decades, we have assumed that collagen triple helices always follow a strict structural paradigm. Our findings show that collagen assemblies can adopt a wider range of conformations than previously thought.”
Unveiling a new collagen conformation
To explore collagen assembly at an atomic level, the research team designed a system of self-assembling peptides based on the collagen-like region of C1q, a key immune protein. They then used cryo-EM, a technology that allows scientists to visualize biomolecules in unprecedented detail, to analyze the structure of the assembled peptides. The resulting model revealed a deviation from the canonical right-handed superhelical twist.
This unexpected conformation enables unique molecular interactions, including hydroxyproline stacking between adjacent helices and forming a symmetrical hydrophobic cavity. Such features suggest that collagenous assemblies may be far more structurally diverse than previously believed.
“The absence of the superhelical twist allows for molecular interactions not seen before in collagen,” said Yu, a former graduate student of Hartgerink who is now a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Washington.
Kreutzberger, the first author of this study, said that this discovery indeed questions previous beliefs. “It challenges the long-held dogma about collagen structure and opens the door to re-examining its biological roles,” Kreutzberger said.
Significance for medicine and biomaterials
The implications of this discovery could extend beyond fundamental biology. Collagen is not just a structural protein — it plays essential roles in cell signaling, immune function and tissue repair.
By gaining a deeper understanding of collagen’s structural variability, researchers may unlock new insights into diseases where collagen assembly is compromised, including Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, fibrosis and certain cancers.
Additionally, this work lays the foundation for innovations in biomaterials and regenerative medicine. By harnessing the unique structural properties of this newly identified collagen conformation, scientists could design novel materials for wound healing, tissue engineering and drug delivery.
Cryo-EM’s breakthrough in structural biology
Despite collagen’s ubiquity in human biology, studying its higher-order structures at high resolution has been a challenge. Traditional techniques such as X-ray crystallography and fiber diffraction have provided valuable insights but could not capture collagen packing in complex assemblies. Cryo-EM, however, has overcome these limitations, allowing the research team to visualize collagen’s intricate architecture in new detail.
“Our research refines our understanding of collagen and highlights the importance of re-examining other biological structures previously thought to be well understood,” said Egelman, study co-corresponding author.
Additional co-authors of the study include Michael Purdy of UVA; Thi Bui and Maria Hancu of the Department of Chemistry at Rice; Tomasz Osinski of the University of Southern California; and Peter Kasson of the Georgia Institute of Technology.
The U.S. National Science Foundation Division of Chemistry, The Robert A. Welch Foundation and the National Institute of General Medical Sciences supported this work.
END
Discovery of unexpected collagen structure could ‘reshape biomedical research’
2025-02-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Changes in US primary care access and capabilities during the COVID-19 pandemic
2025-02-07
About The Study: In this cohort study, over the time period including the COVID-19 pandemic, primary care practices reported a decline in access to care, while average practice capabilities improved. Integrated practice ownership and accountable care organization participation were both associated with better access and capability scores, suggesting that value-based payment and integrated care delivery support the development of higher-quality primary care. Variations across practices point to large opportunities for improvement overall and underscore the importance of incentives and structures as levers to improve primary care delivery.
Corresponding Author: To contact the ...
Cardiometabolic trajectories preceding dementia in community-dwelling older individuals
2025-02-07
About The Study: In this study of older individuals, decline in body mass index, waist circumference, and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) occurred up to a decade before dementia diagnosis. These findings provide insights into cardiometabolic changes preceding dementia and the potential for early monitoring and intervention.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Zimu Wu, PhD, email zimu.wu1@monash.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.58591)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, ...
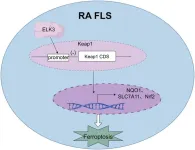
Role of ELK3 in ferroptosis of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes
2025-02-07
Background and objectives
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an inflammatory arthritis characterized by chronic joint inflammation, cartilage degradation, and bone erosion. ELK3 is a transcriptional repressor that can affect cell proliferation, migration, invasion, apoptosis, and other cellular processes. The study aimed to clarify the effect of ELK3 in the biological activity and ferroptosis phenotype of RA fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS), and to reveal its molecular mechanism in regulating ferroptosis in RA FLS.
Methods
We investigated the impact of ELK3 on the biological activity and ferroptosis phenotype of RA FLS using real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction, immunohistochemistry, ...
Team of Prof. Woo Young Jang Department of Orthopedic Surgery, KU Anam Hospital wins the Best Paper Award from the Korean Musculoskeletal Tumor Society
2025-02-07
Professor Woo Young Jang (Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Korea University Anam Hospital) recently won the best paper award at the 2024 fall academic conference of the Korean Musculoskeletal Tumor Society held in November 22th, 2024. This award recognizes the outstanding results and academic value of the research led by Professor Jang.
Professor Woo Young Jang, in collaboration with Professor Jun Seok Lee from the Department of Pharmacology and Dr. Jang Sun Hwang from the Department of Orthopedic Surgery at Korea University College of Medicine, conducted the research ‘Disaggregation-Activated ...
Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation announces recipients of inaugural Keith Terasaki Mid-Career Innovation Award
2025-02-07
Los Angeles, CA – February 7, 2025 - The Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Engineering (TIBI) is pleased to announce their selection of Dr. Liangfang Zhang - Irwin Jacobs Chancellor’s Endowed Chair Professor at the University of California San Diego, and Dr. Aydogan Ozcan – Chancellor’s Professor, UCLA & Professor, Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI), as the recipients of the inaugural Keith Terasaki Mid-Career Innovation Award. These awards will be presented at the 3rd Annual Terasaki Innovation Summit, to be held March ...
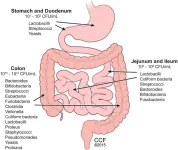
The impact of liver graft preservation method on longitudinal gut microbiome changes following liver transplant
2025-02-07
Background and Aims
End-stage liver disease is associated with disruptions in gut microbiota composition and function, which may facilitate gut-to-liver bacterial translocation, impacting liver graft integrity and clinical outcomes following liver transplantation. This study aimed to assess the impact of two liver graft preservation methods on fecal microbiota and changes in fecal and breath organic acids following liver transplantation.
Methods
This single-center, non-randomized prospective pilot study enrolled liver transplant patients whose grafts were preserved using either static cold storage or ex situ normothermic machine perfusion (NMP). Fresh stool ...
Cardiovascular health risks continue to grow within Black communities, action needed
2025-02-07
DALLAS, Feb. 7, 2025 — The American Heart Association’s 2025 Heart Disease and Stroke Statistical Update reports that while progress has been made in reducing cardiovascular and cerebral health disparities, Black communities in the United States still face disproportionately higher risk of heart disease, stroke and hypertension. These gaps subsequently contribute to equally disproportionate high death rates, underscoring the urgent need for lifesaving intervention. As part of its nationwide Heart Month and Black History Month activations, the ...
ALS survival may be cut short by living in disadvantaged communities
2025-02-07
Living in a disadvantaged community may decrease the length of time a person can survive with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, or ALS, by over 30%, a Michigan Medicine-led study suggests.
ALS is a progressive, incurable condition that causes muscle wasting and loss of muscle control.
While most people survive with ALS around two to four years, some people can live significantly longer.
In the study of more than 1,000 patients with ALS seen between 2012 and mid-2024, people from the most disadvantaged neighborhoods had up to a 37% ...
No quantum exorcism for Maxwell's demon (but it doesn't need one)
2025-02-07
In a groundbreaking discovery, researchers from Nagoya University in Japan and the Slovak Academy of Sciences have unveiled new insights into the interplay between quantum theory and thermodynamics. The team demonstrated that while quantum theory does not inherently forbid violations of the second law of thermodynamics, quantum processes may be implemented without actually breaching the law. This discovery, published in npj Quantum Information, highlights a harmonious coexistence between the two fields, ...
Balancing the pressure: How plant cells protect their vacuoles
2025-02-07
Plants droop and shed their leaves when parched, but with a splash of water, their stems regain strength and their leaves unfurl. This dramatic transformation is a clear signal for us to reach for the watering can – and it demonstrates a delicate balance at the cellular level, which lies at the heart of plant’s rigidity.
The structural support of a plant depends on the unique balance between two elements: The strong, flexible cell wall provides structural support, while the vacuole, a large cellular compartment filled with water, acts like a water balloon, pressing against the cell wall. The delicate pressure balance between the inside and the ...