(Press-News.org) Financial markets are reacting not just to Donald Trump's return to the White House but also to the unpredictability of this victory, according to a new study from the University of Surrey. Investors must diversify their portfolios to mitigate risks associated with political volatility and to remain vigilant about the potential for abrupt market corrections.
A new study, published in Economics Letters, indicates that while there was an immediate surge in stock prices following Trump's election, this was quickly tempered by investor concerns over potential trade wars and international instability.
A group of international researchers from the University of Surrey, Macquarie University, Australia, The Memorial University of Newfoundland, Canada and Paris School of Business, analysed the stock market response to Trump's decisive 2024 electoral win using a robust event study methodology. This involved examining the performance of over 1,500 publicly traded companies on the Standard & Poors' 1500 index, focusing on their stock price movements around the election date. The team observed significant abnormal returns, particularly among small-cap firms and specific sectors such as energy, which capitalised on anticipated regulatory changes.
Dr Shaker Ahmed, lead author of the study and Lecturer in Finance at the University of Surrey, said:
"Our findings highlight the complex landscape that investors navigate in the wake of major political events. While there is optimism surrounding pro-business policies, underlying fears of geopolitical conflicts can lead to volatility. Investors must prepare for a reality where gains can swiftly turn into losses."
The research reveals a clear contrast between the "Hope Hypothesis" — the belief that Trump's policies would foster a business-friendly environment — and the "Fear Hypothesis," which warns of potential trade disruptions and uncertainty. The data shows that small-cap firms, primarily domestic, benefited most from this political shift, suggesting that investors are weighing their options carefully in this divided market.
Dr Ahmed continued:
"Understanding the implications of political events on market dynamics is crucial for informed investment strategies."
[ENDS]
Notes to editors:
Dr Shaker Ahmed is available for interview, please contact mediarelations@surrey.ac.uk to arrange.
The full paper is available in in Economics Letters
END
Trump's 2024 election victory: A double-edged sword for the US stock market
2025-02-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
High-tech video optimization in our brain
2025-02-10
Why do our mental images stay sharp even when we are moving fast? A team of neuroscientists led by Professor Maximilian Jösch at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) has identified a mechanism that corrects visual distortions caused by movement in animals. The study, conducted in mice, identifies a core function that can be generalized across the vertebrate visual system, including primates such as humans. The findings are published in Nature Neuroscience.
Despite its rapid development in recent decades, the video camera industry is still catching up with the capabilities of the human eye. In particular, action cams are designed ...
Euclid discovers a stunning Einstein ring
2025-02-10
Euclid blasted off on its six-year mission to explore the dark Universe on 1 July 2023. Before the spacecraft could begin its survey, the team of scientists and engineers on Earth had to make sure everything was working properly. During this early testing phase, in September 2023, Euclid sent some images back to Earth. They were deliberately out of focus, but in one fuzzy image Euclid Archive Scientist Bruno Altieri saw a hint of a very special phenomenon and decided to take a closer look.
“I look at the data from Euclid as it comes in,” explains Bruno. “Even from that first observation, I could see it, but after Euclid made more observations of the area, ...
Biotech in Germany has significant potential, but lack of collaboration hampers growth
2025-02-10
The report “Assessing Deep-Tech Innovation Hubs in Germany: The Case of Biotechnology” evaluates Germany’s performance in deep-tech innovation within biotech using a comprehensive index and examines five key hubs: Berlin, Heidelberg, Munich, Nuremberg-Erlangen, and Stuttgart. These hubs were analyzed in terms of fundamental research, research and development in biotech, startup activity, public infrastructure, and business environment.
Berlin, Munich, and Heidelberg are the leading biotech hubs
Berlin leads the index due to its strong public infrastructure ...
Does pain affect cancer survivors’ use of non-opioid substances?
2025-02-10
Experiencing pain may increase the odds that cancer survivors will use cigarettes and cannabis, according to a recent study published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society. The study also found that cigarette smoking and pain are linked to more treatment-related side effects and worse health among cancer survivors.
Pain and use of cigarettes, e-cigarettes, alcohol, and cannabis commonly occur together in the general population. To characterize pain in relation to such non-opioid substance ...
Scientists find that a playful approach to life activates ‘lemonading’, which helps people cope with adversity
2025-02-10
Scientists have found that taking a playful approach to life doesn’t mean you don’t take your situation seriously, but it can mean you cope with it better. By surveying people about their experiences during a Covid-19 lockdown, they learned that more playful people were more positive about the future and coped more actively and creatively. Life gave them lemons, and they made lemonade.
“Our study revealed that playfulness and resilience are intimately connected through what we call ‘lemonading’ — the ability to imagine ...
Candidate genes in canine hepatocellular carcinoma for molecular targeted therapy
2025-02-10
Unresectable canine hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has limited nonsurgical treatment options. Sorafenib is a targeted therapy for unresectable canine HCC. However, there are limited reports on the expression of target genes. Therefore, the efficacy of the targeted therapies for canine HCC remains unclear.
In HCC, the prognosis is generally good when complete surgical resection is possible. Unresectable nodular and diffuse HCC have a poor prognosis and limited nonsurgical treatment options. In humans, systemic therapies including ...
Opioid prescriptions in the ED linked to small increases in future opioid use, hospitalizations
2025-02-10
Opioid prescriptions in the emergency department (ED) were associated with small increases in later opioid prescriptions and hospital admissions, found new research published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.241542.
To understand the relationship between opioid prescribing in the ED and subsequent harm, researchers looked at opioid prescribing at all Alberta EDs from 2010 to 2020. Of the more than 13 million visits, 689 074 patients (5.3%) filled an opioid prescription. The researchers found that opioid prescriptions did not increase the risk of ...
During pandemic, playful people were remarkably resilient, OSU research shows
2025-02-10
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Adults with high levels of playfulness showed strong resilience during the COVID-19 pandemic compared to less playful individuals, new research shows.
The study led by Xiangyou “Sharon” Shen of Oregon State University is important because playfulness is a vital but underappreciated resource for building resilience and maintaining well-being during difficult periods such as the pandemic, Shen said. And it’s a resource that individuals can cultivate.
“Understanding how playful people navigate adversity can inform interventions and strategies to help people cope with stress and uncertainty,” said Shen, an assistant professor ...
Tracing gas adsorption on “crowns” of platinum and gold connected by nanotunnels
2025-02-08
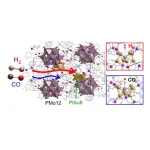
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have elucidated how hydrogen and carbon monoxide is adsorbed into solids containing a crown-motif structure of platinum and gold. Using quick-scan X-ray absorption measurements and theoretical calculations, they studied a solid of [PtAu8(PPh3)8]-H[PMo12O40] called PtAu8-PMo12 and found that gas adsorption is affected strongly by the dimension of nanoscale voids in the structure. This highlights the importance of engineering voids in materials for next generation sensors and gas separation.
Ligand-protected metal clusters have been a source of ...
Rare bird skull from the age of dinosaurs helps illuminate avian evolution
2025-02-08
A new study in Nature describing a fossil of a nearly complete and intact bird skull from Antarctica is shedding light on the early evolution of today’s birds and avian diversity at the end of the Age of Dinosaurs.
The skull is from Vegavis iaai, an extinct duck-like bird that lived during the Late Cretaceous, just before non-avian dinosaurs went extinct. It’s one of very few 3D bird skulls known to science from the Cretaceous — a 79-million-year geological period and the last era when ...