(Press-News.org) Doctors at Queen Mary University of London, Barts Health NHS Trust, and University College London have led the development of a simple, minimally invasive Targeted Thermal Therapy (Triple T) that has the potential to transform medical management of a common, but commonly overlooked, cause of high blood pressure.
This breakthrough, published today in The Lancet, could, after further testing, help millions of people worldwide who currently go undiagnosed and untreated.
In the UK, Triple T, known scientifically as endoscopic ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation, was rigorously tested, in collaboration with researchers from University College London, University College Hospital NHS Trust, Cambridge University NHS Trust, and the University of Cambridge.
A hidden cause of high blood pressure
High blood pressure affects one in three adults, of whom a hormonal condition called primary aldosteronism accounts for one in twenty cases. However, fewer than one percent of those affected are ever diagnosed.
The condition occurs when tiny benign nodules in one or both adrenal glands produce excess aldosterone, a hormone that raises blood pressure by increasing salt levels in the body. Patients with primary aldosteronism often do not respond well to standard blood pressure medications and face higher risks of heart attacks, strokes, and kidney failure.
A game-changing alternative to surgery
Until now, the only effective cure for primary aldosteronism has been surgical removal of the entire adrenal gland, requiring general anaesthesia, a two-to three-day hospital stay, and weeks of recovery. As a result, many patients go untreated.
Triple T offers a faster, safer alternative to surgery, by selectively destroying the small adrenal nodule without removing the gland. This is made possible by recent advances in diagnostic scans, using molecular dyes that accurately identify and locate even the smallest adrenal nodules. Those in the left adrenal gland are seen to be immediately adjacent to the stomach, from where they can be directly targeted.
The new treatment harnesses the energy of waves, adapting two well-established medical techniques: radiofrequency or microwaves generate heat in a small needle placed into the malfunctioning tissue, causing a controlled burn; ultrasound uses reflected sound waves to create a real-time video of the procedure.
In Triple T, as in routine endoscopy, a tiny internal camera—in this case using ultrasound as well as light—is passed by mouth into the stomach. The endoscopist visualises the
adrenal gland and guides a fine needle from the stomach precisely into the nodule. Short bursts of heat destroy the nodule but leave the surrounding healthy tissues unharmed. This minimally invasive approach takes only 20 minutes and eliminates the need for internal or external incisions.
Successful trial shows promise
The study is called FABULAS, the name being an acronym for Feasibility study of radiofrequency endoscopic ABlation, with ULtrasound guidance, as a non-surgical, Adrenal Sparing treatment for aldosterone-producing adenomas.
FABULAS tested Triple T in 28 patients with primary aldosteronism, whose molecular scan had pinpointed a hormone-producing nodule in the left adrenal gland. The new procedure was found to be safe and effective, with most patients having normal hormone levels six months later. Many participants were able to stop all blood pressure medications, with no recurrence of the condition.
Professor Morris Brown, co-senior author of the FABULAS study and Professor of Endocrine Hypertension at Queen Mary University of London, said: “It is 70 years since the discovery in London of the hormone aldosterone, and, a year later, of the first patient in USA with severe hypertension due to an aldosterone-producing tumour. This patient’s doctor, Jerome Conn, predicted, with perhaps only minor exaggeration, that 10-20% of all hypertensions might one day be traced to curable nodules in one or both glands. We are now able to realise this prospect, offering 21st-century breakthroughs in diagnosis and treatment.”
One of the trial participants, Michelina Alfieri, shared her experience:
“Before the study, I suffered from debilitating headaches for years despite multiple GP visits. As a full-time worker and single parent, my daily life was severely affected. This non-invasive treatment provided an immediate recovery—I was back to my normal routine straight away. I’m incredibly grateful to the team for giving me this choice.”
What’s next?
The success of FABULAS has led to a larger randomised trial called ‘WAVE’, which is comparing Triple T with traditional adrenal surgery. The results are expected in 2027.
Professor Stephen Pereira, Chief Investigator of FABULAS and Professor of Hepatology & Gastroenterology at UCL Institute for Liver and Digestive Health, added: “With appropriate training, this less invasive technique could be widely offered in endoscopy units across the UK and internationally.”
Clinical Endocrinology Lead at Addenbrooke’s Hospital and Professor of Clinical Endocrinology at the University of Cambridge, Professor Mark Gurnell, said: “This breakthrough was made possible thanks to the collaborative development of novel PET tracer molecules, which enable non-invasive diagnosis by allowing us to precisely locate and treat adrenal nodules for the first time.
“Thanks to this work, we may finally be able to diagnose and treat more people with primary aldosteronism, lowering their risk of developing cardiovascular diseases and other complications, and reducing the number of people dependent on long-term blood pressure medication,” he added.
A major step forward for hypertension treatment
For the millions of people suffering from undiagnosed primary aldosteronism, this research offers new hope. Safely targeted thermal therapy, delivered by mouth, could replace major surgery, allowing faster recovery and better outcomes.
With further studies underway, this breakthrough treatment could soon become a standard procedure worldwide, transforming care for patients with this curable form of hypertension.
The research was primarily supported by Barts Charity, National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) through the Barts and Cambridge Biomedical Research Centres (BRCs), and the British Heart Foundation.
It is being followed by a larger randomised trial, called ‘WAVE’, which will compare TTT to traditional surgery in 120 patients. The results are expected in 2027.
END
New treatment offers quick cure for common cause of high blood pressure
2025-02-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Satire more damaging to reputations than direct criticism
2025-02-10
WASHINGTON - In our digital times as we are inundated with YouTube videos, memes and social media, satire is everywhere, but it can be more damaging to people's reputations than direct criticism, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
Seemingly innocuous satire may be more harmful than direct criticism because it can dehumanize people and reduce them to caricatures, the study found. The research was published online in the Journal of Experimental Psychology: General.
“Most people think satire is just humorous and playful, but dehumanization exists on a spectrum and can include things like forgetting ...
E64FC26, a protein disulfide isomerase inhibitor, ameliorates articular cartilage damage and disease severity in a mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis
2025-02-10
Background and objectives
Protein disulfide isomerases (PDIs) are essential enzymes that facilitate the proper folding of proteins and maintain protein quality within the endoplasmic reticulum. Dysregulation of PDIs has been correlated with numerous disorders, including cancer and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). E64FC26 (EFC), a small molecule that inhibits a wide range of PDI family members, has shown promise as a therapeutic agent in oncology. However, its effects on RA have not yet been studied. This research investigates the efficacy of EFC as a potential treatment for RA.
Methods
To investigate EFC’s effects on RA fibroblast-like ...
KERI’s faster and higher-quality argyrodite structures for ASSBs!
2025-02-10
Dr. Ha Yoon-Cheol's team at KERI's Next Generation Battery Research Center has developed an 'enhanced coprecipitation method' that enables faster and higher-quality production of lithium superionic conductors for ASSBs.
ASSB replaces the ‘electrolyte’, which transfers ions between the anode and cathode, with a solid instead of a liquid, significantly reducing the risk of fire or explosion..
Solid electrolytes are difficult to manufacture and expensive. However, in 2021, Dr. Ha Yoon-Cheol's team garnered significant attention by proposing the 'coprecipitation method', ...
FAU Engineering designs new autonomous system to monitor Arctic’s melting ice
2025-02-10
The rapid melting and thinning of the Arctic ice have sparked serious concerns in the scientific community. In addition, sea ice thickness also has decreased, which makes ice cover more vulnerable to warming air and ocean temperature.
Understanding the ecological role of sea ice in the Arctic is crucial, particularly because the extent of sea ice in the region has been decreasing at an unprecedented rate. What would happen to the Arctic marine ecosystem if the sea ice melted even faster? To answer these questions, a long-term monitoring and data collection system is necessary in the harsh Arctic environment.
However, ...
The link between finances and loneliness in older adults
2025-02-10
Older adults who didn’t have enough savings to cover emergency expenses during the early months of the COVID-19 pandemic faced another surprising problem: higher levels of loneliness.
In a new study, researchers at The Ohio State University found that adults over the age of 65 faced increases in loneliness during the pandemic, regardless of income level or wealth.
But those who said they would have to use a credit card to pay off an emergency expense over time were more likely to report high levels of loneliness.
“Our ...
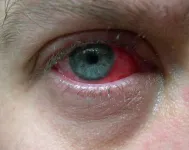
Stem cell shots: Unveiling a safer way to treat inflammatory eye diseases
2025-02-10
Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) is a common and severe complication that occurs after stem cell transplantation, where the donor’s immune cells attack the recipient’s tissues. Ocular manifestation of GVHD is among the most challenging to treat, often leading to chronic inflammation and corneal tissue damage, which can result in loss of vision. Conventional treatments, including corticosteroids, are frequently used to manage ocular inflammation associated with GVHD. However, these therapies come with significant side effects, including the risk of glaucoma and other ocular complications.
Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs), a heterogeneous population of cells present in various ...
Researchers from South Korea reveal how gender shapes perceptions of safety in urban parking spaces
2025-02-10
Multifamily residential buildings with multiple floors are common in South Korea. These buildings usually have pilotis—support structures like pillars that elevate the building, creating an open ground floor generally used for parking vehicles. These piloti parking spaces are often risky to navigate for pedestrians and residents due to limited visibility, unclear boundaries between adjacent areas, and poor management. For instance, these spaces have blind spots that criminals could exploit, which induces fear among people.
Though evidence-based architectural design strategies ...
Nanoscale tin catalyst discovery paves the way for sustainable CO2 conversion
2025-02-10
Researchers have developed a sustainable catalyst that increases its activity during use while converting carbon dioxide (CO2) into valuable products. This discovery offers a blueprint for designing next-generation electrocatalysts.
A collaborative team from the University of Nottingham's School of Chemistry and the University of Birmingham have developed a catalyst made of tin microparticles supported by a nanotextured carbon structure. The interactions between the tin particles and graphitised ...
Biomarker test can detect Alzheimer's pathology earlier, Pitt study shows
2025-02-10
Years before tau tangles show up in brain scans of patients with Alzheimer's disease, a biomarker test developed at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine can detect small amounts of the clumping-prone tau protein and its misfolded pathological forms that litter the brain, cerebrospinal fluid and potentially blood, new research published today in Nature Medicine suggests.
The cerebrospinal fluid biomarker test correlates with the severity of cognitive decline, independent of other factors, including brain amyloid deposition, thereby opening doors for early-stage disease diagnosis ...
Anomaly in the deep sea
2025-02-10
Beryllium-10, a rare radioactive isotope produced by cosmic rays in the atmosphere, provides valuable insights into the Earth's geological history. A research team from the Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR), in collaboration with the TUD Dresden University of Technology and the Australian National University (ANU), has discovered an unexpected accumulation of this isotope in samples taken from the Pacific seabed. Such an anomaly may be attributed to shifts in ocean currents or astrophysical events that occurred approximately 10 million years ago. The findings hold the potential to serve as a global time marker, representing a promising ...