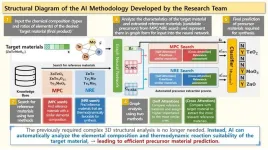
(Press-News.org) Researchers in Korea have developed a technology that automatically identifies the necessary precursor materials to synthesize specific target materials.
A joint research team led by Senior Researcher Gyoung S. Na from the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology (KRICT) and Professor Chanyoung Park from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) has developed an AI-based retrosynthesis methodology that predicts the required precursor materials solely based on the chemical formula of the target material without expensive material descriptors and chemical analysis.
Precursor materials refer to all essential materials required in the synthesis process of the desired target material.
In recent years, materials discovery has become a crucial task across various industries, including batteries and semiconductors. Traditionally, finding the right intermediate materials for synthesis has required costly and repetitive experiments. However, there is a growing demand for utilizing AI to identify these materials efficiently.
Existing AI-based technologies for predicting material synthesis processes have primarily focused on organic materials, such as drug compounds, whereas research on inorganic materials has been relatively insufficient. This is because inorganic compounds, such as metals, possess complex structures and diverse elemental compositions, making it challenging to determine synthesis pathways.
The research team developed an innovative AI technology that can learn the inverse process of predicting the necessary precursor materials of the target material using only its chemical formula.
Previously, KRICT developed and transferred the ‘ChemAI’ platform in 2022, which allows users to predict synthesis information without advanced programming skills and expensive hardware infrastructures.
This newly developed technology overcomes the challenges posed by the complex 3D structures of inorganic materials, such as atomic arrangements and bonding information. Instead, the AI analyzes the types and ratios of elements present in the target material and calculates the thermodynamic formation energy differences to identify precursors that facilitate easier synthesis reactions.
To improve the accuracy of precursor material predictions, the team employed a deep neural network specialized in chemical data. The AI model was trained on approximately 20,000 published research papers detailing material synthesis processes and precursor materials.
The AI model was tested on around 2,800 synthesis experiments that were not provided in the training dataset. The evaluation results showed that it successfully predicted the necessary precursor materials in over 80% of cases within just 0.01 seconds by utilizing GPU acceleration.
Looking ahead, the research team plans to expand the training dataset through research projects of KRICT to achieve 90% prediction accuracy. By 2026, they aim to establish a web-based public service for AI-based materials discovery. Future research will focus on fully-automated materials discovery that predicts both precursor materials and synthesis pathways based solely on the target material's chemical formula.
The research team emphasized the novelty of their approach, stating, “Unlike conventional precursor prediction AI models that are limited to specific material types, our AI can predict precursor materials universally, regardless of the applications of the target materials.”
KRICT President Young-Kuk Lee added, “This research is expected to enhance the efficiency of new material development across various industries.”
###
KRICT is a non-profit research institute funded by the Korean government. Since its foundation in 1976, KRICT has played a leading role in advancing national chemical technologies in the fields of chemistry, material science, environmental science, and chemical engineering. Now, KRICT is moving forward to become a globally leading research institute tackling the most challenging issues in the field of Chemistry and Engineering and will continue to fulfill its role in developing chemical technologies that benefit the entire world and contribute to maintaining a healthy planet. More detailed information on KRICT can be found at https://www.krict.re.kr/eng/
The study was presented at the 2024 Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), a top-tier conference in the AI field. The paper’s corresponding authors are Senior Researcher Kyungseok Na (KRICT) and Professor Chanyoung Park (KAIST), with first author Heewoong Noh (KAIST).
This research was supported by KRICT’s core projects, the Ministry of Science and ICT’s National Research Foundation of Korea (Grant No. RS-2024-00406985), and the Global Frontier Research Program.
END
AI predicts the precursor materials needed for material synthesis
AI trained on 20,000 research papers predicts precursor materials based solely on the chemical formula of the target material
2025-02-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
International Shark Attack File Report: Unprovoked shark bites plummeted in 2024
2025-02-11
2024 was an exceptionally calm year for shark bites. Worldwide, there were only 47 unprovoked attacks, down 22 from the previous year and well below the 10-year average of 70. Four of last year’s attacks resulted in fatalities, also a significant reduction from recent years.
The International Shark Attack File, maintained by the Florida Museum of Natural History, provides data on what are considered unprovoked bites, defined as incidents in which a person does not initiate contact with a shark. Instances in which a person intentionally or unintentionally initiates contact, including spearfishing and releasing sharks ...
Ketamine for mental health should only be provided by trained professionals
2025-02-11
CHICAGO – The anesthetic ketamine is being hailed as a breakthrough therapy for people with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), treatment-resistant depression and other mood disorders. But the drug does have side effects – some potentially life-threatening – and should only be prescribed and administered by trained health care professionals to ensure the patient’s safety, according to new guidance released by the American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA).
Long valued for its role in sedation and anesthesia during medical procedures, ...
Study takes a ‘bite’ out of shark depredation using citizen science
2025-02-11
Shark depredation is a hot-button issue in recreational fishing, as anglers face off against these stealthy ocean bandits. These underwater thieves snatch fish straight off the line, often leaving nothing but scraps – or a broken leader – as evidence of their heist.
The Southeast, a major hub for saltwater fishing, is a depredation “hot spot” due to high fishing activity. While fisheries managers in the United States monitor shark depredation in commercial fisheries, efforts to evaluate these interactions in recreational fishing have been limited.
With Florida’s recreational ...
A gender gap in using AI for research
2025-02-11
After the launch of ChatGPT male researchers’ productivity rate increased, pointing to a gender difference in how scientists use AI. Previous work has shown that men are more likely to use generative AI in their work than women. Shaobo Li and colleagues analyzed preprints uploaded to the Social Science Research Network (SSRN), one of the largest open-access repositories in the world, from May 2022 to June 2023. ChatGPT was released in late November 2022. After the release of ChatGPT, the productivity of male researchers significantly increased relative to that of female researchers, with the probability ...
Human-caused fires growing faster than lightning fires in the Western US
2025-02-11
A study shows that there are almost twice as many risky days for large human-caused fires in the American West as there are for lightning-caused fires, due to differences in the level of heat and aridity under which each type of fire is likely to occur. The discrepancy is not accounted for in most fire early warning systems. In addition, risky days for human-caused fires are growing faster than risky days for lighting-caused fires as the climate warms.
Fa Li and colleagues focused on Vapor Pressure Deficit (VPD), which captures both dryness ...
Barbeque and grandma’s cookies: New study looks at nostalgia, comfort in food preparation for older adults
2025-02-11
PULLMAN, Wash. — Foods that evoke a sense of nostalgia and comfort and have good texture variety are important considerations in prepared meals aimed at older adults, according to new Washington State University research.
“We want to help the prepared food industry produce appetizing, healthy meals for older adults,” said Carolyn Ross, professor in WSU’s School of Food Science. “Malnutrition is quite prevalent in people over 60 because food may be available, but they won’t eat it if they don’t like it. We want to walk a line where food is tasty, convenient, and full of nutrients.”
In a paper recently published ...
The political consequences of undocumented residents in the census
2025-02-11
In recent years, some public figures have argued that undocumented residents in the United States should not be included in census data used for congressional apportionment because their inclusion unfairly benefits Democratic-leaning states. John Robert Warren and Robert E. Warren analyzed data from every census from 1980 through 2020 and used high quality state-level estimates of the size of the undocumented resident population at each time point. The authors then calculated how many House seats and how many Electoral College votes would have changed had undocumented residents been excluded from the data after each census. Previous efforts to ...
Purity and environmental concern
2025-02-11
Attitudes about climate change and carbon footprints show strong regional patterning. Farzan Karimi-Malekabadi and colleagues investigated the role of moral values in these geographic patterns. The authors used Moral Foundations Theory, which posits that moral judgements emerge from deeply held intuitions about care, fairness, loyalty, authority, and purity. The authors used opinion surveys, comprising 12,061 respondents, conducted from 2008–2013 that measured beliefs regarding the reality, human causation, and negative impacts of climate change, as well as estimates of household carbon footprint provided by UC Berkeley CoolClimate Network. This data ...
Branch patterns in trees and art
2025-02-11
The math that describes the branching pattern of trees in nature also holds for trees depicted in art—and may even underlie our ability to recognize artworks as depictions of trees.
Trees are loosely fractal, branching forms that repeat the same patterns at smaller and smaller scales from trunk to branch tip. Jingyi Gao and Mitchell Newberry examine scaling of branch thickness in depictions of trees and derive mathematical rules for proportions among branch diameters and for the approximate number of branches of different diameters. The authors begin with ...
Researcher develops method to measure blood-brain barrier permeability accurately
2025-02-11
For decades, scientists across the globe have investigated methods to accurately measure drug permeability across the blood-brain barrier, a compact layer of cells that protect the brain from potentially dangerous substances and microbes. They struggled with a number of parameters, such as blood flow and binding to plasma proteins, which were shown to impact permeability in different ways.
In research published in the December 2024 issue of Fluids and Barriers of the CNS (“Brain endothelial permeability, transport and flow ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] AI predicts the precursor materials needed for material synthesisAI trained on 20,000 research papers predicts precursor materials based solely on the chemical formula of the target material