(Press-News.org) Boston, MA – The Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute is proud to announce the launch of the Center for Sepsis Epidemiology and Prevention Studies (SEPSIS). This pioneering center of excellence is dedicated to advancing understanding, prevention, and management of sepsis, a life-threatening condition caused by a dysregulated immune response to infection.
The SEPSIS Center will be led by Dr. Chanu Rhee and Dr. Michael Klompas, internationally recognized leaders in sepsis surveillance, prevention, treatment, and policy. Both serve as faculty at Harvard Medical School and the Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute and bring a wealth of expertise and a shared commitment to advancing sepsis research and care.
“Sepsis is a leading cause of death and disability worldwide, yet it remains under-recognized and challenging to address effectively,” said Dr. Rhee. “Our Center is uniquely positioned to generate insights to inform clinical care, quality improvement, public health practice, and health care policy.”
Each year in the United States, sepsis affects over 1.7 million adults and contributes to more than 350,000 deaths. Globally, the figures are even more alarming: 49 million cases and 11 million deaths annually, equating to one in five deaths worldwide. The economic and emotional toll is staggering, with survivors commonly facing long-term health challenges.
Despite its immense burden, progress in combating sepsis has been hindered by the challenge of accurate diagnosis, gaps in epidemiologic surveillance, uncertainties about optimal prevention and treatment, and limited public understanding. The launch of the SEPSIS Center represents an important step forward towards addressing these challenges and accelerating solutions.
The SEPSIS Center will collaborate with partners across Harvard and around the world to address critical challenges in sepsis care and prevention. Key focus areas include:
Sepsis Surveillance and Epidemiology: Conducting comprehensive studies to characterize sepsis incidence, outcomes, antibiotic use, and antibiotic resistance patterns.
Quality Measures and Policy Impact: Evaluating current sepsis policies and quality measures, developing evidence to support new policies and quality measures.
Innovative Research Collaborations: Partnering with leading health care systems and public health agencies to design and implement evidence-based strategies to enhance sepsis prevention, recognition, and treatment.
“We have both the responsibility and the opportunity to drive meaningful change in the fight against sepsis,” added Dr. Klompas. “We aim to reduce sepsis incidence, inform more targeted and effective treatments, refine sepsis policies, and ultimately help drive better patient outcomes.”
The Center’s mission aligns with the Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute’s commitment to improving health care delivery and population health through research and innovation.
“The SEPSIS Center embodies our dedication to tackling the most pressing challenges in health care,” said Emily Oken, president of the Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute and Harvard Medical School Professor and chair of the Department of Population Medicine. “We are thrilled to support this initiative and its potential to make a lasting impact on sepsis care and prevention.”
About the Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute’s Department of Population Medicine
The Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute's Department of Population Medicine is a unique collaboration between Harvard Pilgrim Health Care and Harvard Medical School. Created in 1992, it is the first appointing medical school department in the United States based in a health plan. The Institute focuses on improving health care delivery and population health through innovative research and education, in partnership with health plans, delivery systems, and public health agencies. Follow us on Bluesky, X, and LinkedIn.
END
Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute announces launch of Center for Sepsis Epidemiology and Prevention Studies (SEPSIS)
New Center to enhance sepsis care and prevention through innovative research
2025-02-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New perspectives for personalized therapy of brain tumors
2025-02-11
Scientists from the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) and ShanghaiTech University have developed an innovative method for growing brain tumors of individual patients in the laboratory that mimic the original structure and the molecular property of the parental tumor as closely as possible. Drug tests in this model were found to correlate very well with actual patient responses, making it a valuable method for investigating therapies.
Tumor organoids, i.e. mini-tumors grown from surgical material in the culture dish, ...
IEEE researchers provide mathematical solutions to study 2D light interaction in photonic crystal lasers
2025-02-11
Laser diodes are semiconductors that generate light and amplify it using repeated reflection or ‘optical feedback’. Once the light has achieved desirable optical gain, laser diodes release it as powerful laser beams. Photonic crystal surface-emitting lasers (PCSELs) are advanced laser diodes where the optical gain is typically distributed laterally to the propagating light within a photonic crystal (PC) structure. They differ from traditional lasers by separating gain, feedback, and emission functions, offering scalable single-mode power and innovative ...
New joint project to investigate quantum repeaters designed to provide for secure quantum communication networks of the future
2025-02-11
There are reports of IT sabotage, cyber espionage, and other acts of hybrid warfare almost every day. Communication networks based on quantum physics could help eliminate threats of this kind. Researchers throughout Germany have already been working on developing those networks based on quantum repeaters for several years. In January 2025, the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) started funding a new research project, entitled Quantenrepeater.Net (QR.N), which aims to demonstrate the viability of quantum repeaters over test networks outside the protected lab environment. The BMBF will be providing a total of EUR 20 million over three years. ...
PhRMA Foundation welcomes two board members
2025-02-11
The PhRMA Foundation announced the appointment to its Board of Directors of Dr. John C. Reed, MD, PhD, Executive Vice President of Innovative Medicine R&D at Johnson & Johnson (J&J), and Dr. Donatello Crocetta, MD, MBA, Chief Medical Officer and Head of Medical Communities at UCB.
The PhRMA Foundation is a 60-year-old nonprofit that fosters biopharmaceutical innovation and value-driven health care by investing in the frontiers of research. The Foundation catalyzes the careers of promising researchers through competitive, ...
Microbiome as a potential key to better treatment: Clinical study on new therapy for Crohn's disease
2025-02-11
A special liquid diet, known as exclusive enteral nutrition, is an essential therapy for Crohn's disease. Patients consume only this formula for six to eight weeks, completely avoiding solid foods. However, the exact reasons why this is helpful were previously unclear. Researchers at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) and the LMU University Hospital Munich have now been able to decipher the mechanism behind this dietary therapy. Based on these results, they are launching a clinical study combining dietary therapy with faecal microbiome transfer to further enhance ...
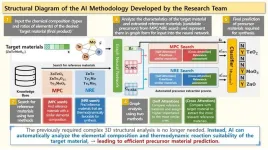
AI predicts the precursor materials needed for material synthesis
2025-02-11
Researchers in Korea have developed a technology that automatically identifies the necessary precursor materials to synthesize specific target materials.
A joint research team led by Senior Researcher Gyoung S. Na from the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology (KRICT) and Professor Chanyoung Park from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) has developed an AI-based retrosynthesis methodology that predicts the required precursor materials solely based on the chemical formula of the target material without expensive material descriptors ...
International Shark Attack File Report: Unprovoked shark bites plummeted in 2024
2025-02-11
2024 was an exceptionally calm year for shark bites. Worldwide, there were only 47 unprovoked attacks, down 22 from the previous year and well below the 10-year average of 70. Four of last year’s attacks resulted in fatalities, also a significant reduction from recent years.
The International Shark Attack File, maintained by the Florida Museum of Natural History, provides data on what are considered unprovoked bites, defined as incidents in which a person does not initiate contact with a shark. Instances in which a person intentionally or unintentionally initiates contact, including spearfishing and releasing sharks ...
Ketamine for mental health should only be provided by trained professionals
2025-02-11
CHICAGO – The anesthetic ketamine is being hailed as a breakthrough therapy for people with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), treatment-resistant depression and other mood disorders. But the drug does have side effects – some potentially life-threatening – and should only be prescribed and administered by trained health care professionals to ensure the patient’s safety, according to new guidance released by the American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA).
Long valued for its role in sedation and anesthesia during medical procedures, ...
Study takes a ‘bite’ out of shark depredation using citizen science
2025-02-11
Shark depredation is a hot-button issue in recreational fishing, as anglers face off against these stealthy ocean bandits. These underwater thieves snatch fish straight off the line, often leaving nothing but scraps – or a broken leader – as evidence of their heist.
The Southeast, a major hub for saltwater fishing, is a depredation “hot spot” due to high fishing activity. While fisheries managers in the United States monitor shark depredation in commercial fisheries, efforts to evaluate these interactions in recreational fishing have been limited.
With Florida’s recreational ...
A gender gap in using AI for research
2025-02-11
After the launch of ChatGPT male researchers’ productivity rate increased, pointing to a gender difference in how scientists use AI. Previous work has shown that men are more likely to use generative AI in their work than women. Shaobo Li and colleagues analyzed preprints uploaded to the Social Science Research Network (SSRN), one of the largest open-access repositories in the world, from May 2022 to June 2023. ChatGPT was released in late November 2022. After the release of ChatGPT, the productivity of male researchers significantly increased relative to that of female researchers, with the probability ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The Lancet: First-ever in-utero stem cell therapy for fetal spina bifida repair is safe, study finds
Nanoplastics can interact with Salmonella to affect food safety, study shows
Eric Moore, M.D., elected to Mayo Clinic Board of Trustees
NYU named “research powerhouse” in new analysis
New polymer materials may offer breakthrough solution for hard-to-remove PFAS in water
Biochar can either curb or boost greenhouse gas emissions depending on soil conditions, new study finds
Nanobiochar emerges as a next generation solution for cleaner water, healthier soils, and resilient ecosystems
Study finds more parents saying ‘No’ to vitamin K, putting babies’ brains at risk
Scientists develop new gut health measure that tracks disease
Rice gene discovery could cut fertiliser use while protecting yields
Jumping ‘DNA parasites’ linked to early stages of tumour formation
Ultra-sensitive CAR T cells provide potential strategy to treat solid tumors
Early Neanderthal-Human interbreeding was strongly sex biased
North American bird declines are widespread and accelerating in agricultural hotspots
Researchers recommend strategies for improved genetic privacy legislation
How birds achieve sweet success
More sensitive cell therapy may be a HIT against solid cancers
Scientists map how aging reshapes cells across the entire mammalian body
Hotspots of accelerated bird decline linked to agricultural activity
How ancient attraction shaped the human genome
NJIT faculty named Senior Members of the National Academy of Inventors
App aids substance use recovery in vulnerable populations
College students nationwide received lifesaving education on sudden cardiac death
Oak Ridge National Laboratory launches the Next-Generation Data Centers Institute
Improved short-term sea level change predictions with better AI training
UAlbany researchers develop new laser technique to test mRNA-based therapeutics
New water-treatment system removes nitrogen, phosphorus from farm tile drainage
Major Canadian study finds strong link between cannabis, anxiety and depression
New discovery of younger Ediacaran biota
Lymphovenous bypass: Potential surgical treatment for Alzheimer's disease?
[Press-News.org] Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute announces launch of Center for Sepsis Epidemiology and Prevention Studies (SEPSIS)New Center to enhance sepsis care and prevention through innovative research