(Press-News.org) Classic Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNs) often learn node representation holistically, which would ignore the distinct impacts from different neighbors when aggregating their features to update a node's representation. Disentangled GCNs have been proposed to divide each node's representation into several feature channels. However, current disentangling methods do not try to figure out how many inherent factors the model should assign to help extract the best representation of each node.
To solve the problems, a research team led by Chuliang WENG published their new research on 15 Jan 2025 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published by Higher Education Press and Springer Nature.
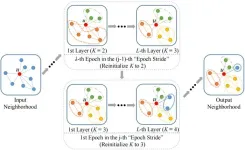
The team proposed a novel disentangled graph convolutional network named D2-GCN to dynamically adjust the number of each node’s disentangled feature channels during training, which helps obtain adaptive node representations on different datasets.
In the research, they design a two-level disentangling mechanism that integrates the epoch-level and the layer-level disentanglement during training. With this mechanism, D2-GCN could capture nuanced changes in node representations on graphs of varying topological complexities. They further leverage the expectation-maximization (EM) algorithm to demonstrate the convergence of the proposed dynamic disentanglement. Finally, they define an information entropy based evaluation metric to portray the convergence speed of the disentangling process.
Experiments show that their model outperforms all the baselines in both single- and multi-label node classification tasks in terms of test accuracies. Visualization results also indicate that D2-GCN could display clearer classification boundaries and higher intra-class similarity than the baseline disentangled methods.
Future work can combine the subgraph theory to improve their model performance in presenting more accurate local-global disentanglement and grasping long-distance dependencies in a graph .
DOI: 10.1007/s11704-023-3339-7
END
D2-GCN: a graph convolutional network with dynamic disentanglement for node classification
2025-02-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Female hoverflies beat males on long-distance migrations
2025-02-12
Male hoverflies are outflown by females when it comes to long-distance migration, new research shows.
Marmalade hoverflies leave northern Europe each autumn to escape the cold winter.
The study – by the University of Exeter – compared the number of males and females migrating at a northern point (Denmark) and further south (Spain).
At the northern point, 50% of hoverflies were male and 50% were female – but at the southern point about 90% were female, suggesting males are “poor long-distance fliers”.
“We carried out a range of tests and found females were better adapted for long-distance ...
Study finds consumer openness to smoke-impacted wines, offering new market opportunities
2025-02-12
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Certain groups of consumers appear to be open to drinking smoke-impacted wines, a finding in a new study that could provide market opportunities for winemakers increasingly dealing with the effects of wildfire smoke on grapes.
The study by researchers at Oregon State University and in New Zealand found that consumers, particularly those that like smokey flavors in food and beverages, are open to drinking smoke-impacted wines. They also found that the type of information on the label can modulate consumer acceptance.
“This ...
Why we need to expand the search for climate-friendly microalgae
2025-02-12
New research has highlighted microalgae’s capacity as a solution in the fight against climate change, but researchers warn that “smart microalgal bioprospecting” is needed to unlock its full potential.
The study highlights the vast, largely unexplored capacity of microalgae to mitigate CO2 emissions while driving sustainable industry.
“Microalgae have remarkable properties that make them an ideal tool for tackling climate change,” said lead author, PhD candidate Joan Labara Tirado from the University of Technology Sydney (UTS).
The review paper, The need for smart microalgal bioprospecting was ...
Fewer forest fires burn in North America today than in the past—and that's a bad thing
2025-02-12
Fewer wildfires burn in North American forests today than in previous centuries, increasing the risk of more severe wildfires, according to research published this week in Nature Communications. The findings may seem counterintuitive, but frequent low-lying surface fires often maintain balance in forests by reducing fuel sources across large areas.
The new study led by the Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences (CIRES) at the University of Colorado Boulder and the U.S. Forest Service’s Rocky Mountain Research Station ...
Older people in England are happier now than before the COVID pandemic, new national study suggests
2025-02-12
Older people have greater general happiness, life satisfaction and sense of purpose than they did before the Covid-19 pandemic.
That’s according to a new study which tracked 3,999 over 50s in England for 11 years, published today in the peer-reviewed journal, Aging and Mental Health.
Analysing data to understand positive psychological well-being and depression within this group, an expert team from UCL (University College London), funded by the National Institute of Ageing, a consortium of UK government departments coordinated by the National Institute ...
Texas A&M chemist wins NSF CAREER Award
2025-02-11
Dr. Alison Altman, an assistant professor in the Texas A&M Chemistry Department, has received a National Science Foundation (NSF) CAREER Award, which supports early-career faculty in research and education. The award recognizes her work on underexplored elements of the periodic table and her dedication to teaching. For Altman, it’s a launchpad for future discoveries.
“It’s an honor to receive this award, as it acknowledges not just my research program but also my teaching efforts,” ...
Micro-nano plastics make other pollutants more dangerous to plants and intestinal cells
2025-02-11
Micro- and nanoscale plastic particles in soil and water can significantly increase how much toxic chemicals plants and human intestinal cells absorb, according to two new studies from Rutgers Health that raise fresh concerns about food safety from plastic pollution.
The first study in NanoImpact found that lettuce exposed to both nanoscale plastic particles and common environmental pollutants such as arsenic took up substantially more of the toxic substances than plants exposed to the pollutants, alone confirming the risks of polycontamination of our food chain. A companion study in Microplastics journal showed ...
Study of female genital tract reveals key findings
2025-02-11
Seeking to understand what constitutes a healthy vaginal microbiome, a global research collaboration that includes a Rutgers-New Brunswick scientist has reported a series of findings, including identifying which bacteria thwart vaginal disease and determining that microbiomes vary significantly across human populations.
Authors of the study, published in Trends in Microbiology, are part of a Belgium-based initiative called the Isala Sisterhood. Members of the group aim to inspire research on microbiomes worldwide by creating a “reference map” of vaginal microbiota. Launched in 2020 at the University of Antwerp, the project has expanded to include more than 3,000 ...
Pitt Engineering Professor Fang Peng elected to National Academy of Engineering
2025-02-11
The National Academy of Engineering (NAE) today announced that University of Pittsburgh Professor Fang Peng, an internationally acclaimed power electronics researcher, is among the newest cohort elected to the academy. The NAE is recognizing Peng for “contributions to the development of high-powered electronic technologies for advanced power grid and energy conversion.”
Peng, the RK Mellon Endowed Chair Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering and Director of the Energy GRID Institute at Pitt’s Swanson School of Engineering, ...
Short-course radiation therapy effective for endometrial cancer patients
2025-02-11
In a randomized clinical trial, researchers from Huntsman Cancer Institute at the University of Utah (the U) have found that short-course, higher dose vaginal brachytherapy for endometrial cancer had similar effectiveness to more frequent, lower dose sessions.
Gita Suneja, MD, MS, physician-scientist at Huntsman Cancer Institute and professor of radiation oncology at the U, is the first author of the SAVE trial report—which stands for, Short-Course Adjuvant Vaginal Cuff Brachytherapy in Early Endometrial Cancer Compared with Standard of Care.
“There ...