DNA methylation clocks may require tissue-specific adjustments for accurate aging estimates
“Our results suggest that forensic applications of DNAm clocks using non-blood tissue types will provide age estimates that are not as accurate as predictions based on blood, especially if using clocks algorithms trained on blood samples”
2025-02-12
(Press-News.org)
“Our results suggest that forensic applications of DNAm clocks using non-blood tissue types will provide age estimates that are not as accurate as predictions based on blood, especially if using clocks algorithms trained on blood samples.”
BUFFALO, NY—February 12, 2025 — A new research paper was published in Aging (Aging-US) on January 3, 2025, in Volume 17, Issue 1, titled “Characterization of DNA methylation clock algorithms applied to diverse tissue types.”
Researchers Mark Richardson, Courtney Brandt, Niyati Jain, James L. Li, Kathryn Demanelis, Farzana Jasmine, Muhammad G. Kibriya, Lin Tong, and Brandon L. Pierce from the University of Chicago and University of Pittsburgh, studied how biological aging is measured using DNA. Their study found that while commonly used “DNA methylation clocks” work well for blood samples, they may be less reliable for other tissues like the lungs, colon, and kidneys.
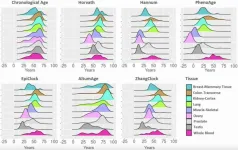
DNA methylation clocks are widely used in forensic science, epigenetics and longevity research to estimate a person’s biological age based on chemical changes in DNA. These epigenetic clocks help scientists predict age-related diseases and assess how lifestyle factors, such as smoking, impact aging. Most were originally developed using blood samples, and their effectiveness in other tissues remains unclear. This study tested eight different DNA methylation clocks across nine human tissue types, including the lungs, prostate, ovaries, skeletal muscle, and kidneys. The researchers analyzed data from 973 tissue samples collected through the Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) project.
Their analysis revealed significant differences in biological age estimates across tissues. While blood samples provided the most reliable results, other tissues showed noticeable variations. For example, testis and ovary tissues appeared younger than expected, while lung and colon tissues appeared older.
“These differences across tissue types were most apparent for clocks trained using DNAm from blood only (e.g., Hannum), but also present for clocks trained on multiple tissue types (e.g., Horvath, a clock designed for pan-tissue age prediction.”
These findings suggest that aging may not occur at the same rate in every organ, and that standard DNA methylation clocks may not always give accurate biological age estimates outside of blood samples. The authors suggest that new, organ-specific epigenetic clocks may be needed to improve biological age prediction. Creating tissue-specific aging clocks could also improve medical diagnostics, age-related disease prevention, and health monitoring.
The researchers emphasize that larger studies with more tissue-specific DNA methylation data are needed to refine these aging clocks. By improving these tools, scientists can better understand how aging affects different organs and develop more reliable methods for measuring biological age. These advancements could lead to better predictions of age-related diseases and new strategies for healthy aging.
Read the full paper: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.206182
Corresponding author: Brandon L. Pierce – brandonpierce@uchicago.edu
Keywords: aging, epigenetic aging, epigenetic clock, DNA methylation
Click here to sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article.
About Aging:
The journal Aging aims to promote 1) treatment of age-related diseases by slowing down aging, 2) validation of anti-aging drugs by treating age-related diseases, and 3) prevention of cancer by inhibiting aging. (Cancer and COVID-19 are age-related diseases.)
Aging is indexed by PubMed/Medline (abbreviated as “Aging (Albany NY)”), PubMed Central, Web of Science: Science Citation Index Expanded (abbreviated as “Aging‐US” and listed in the Cell Biology and Geriatrics & Gerontology categories), Scopus (abbreviated as “Aging” and listed in the Cell Biology and Aging categories), Biological Abstracts, BIOSIS Previews, EMBASE, META (Chan Zuckerberg Initiative) (2018-2022), and Dimensions (Digital Science).
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
Facebook
X
Instagram
YouTube
LinkedIn
Reddit
Pinterest
Spotify, and available wherever you listen to podcasts
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker St., Suite 1
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-02-12
SAN ANTONIO — February 12, 2025 —Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) scientists are studying Saturn’s moon Titan to assess its tidal dissipation rate, the energy lost as it orbits the ringed planet with its massive gravitational force. Understanding tidal dissipation helps scientists infer many other things about Titan, such as the makeup of its inner core and its orbital history.
“When most people think of tides they think of the movement of the oceans, in and out, with the passage of the Moon overhead, said Dr. Brynna Downey. “But that is just because water moves ...
2025-02-12
To effectively present the uncertainty of convective-scale weather forecasts, convective-scale ensemble prediction systems have been developed at major operational centers, whose lateral boundary conditions are usually provided by global numerical weather models. Recently, the emergence of AI weather models has provided a new approach to driving convective-scale ensemble prediction systems. AI weather models can produce forecasts for the next 7 to 10 days in just a few minutes, which is around 10,000 times faster than numerical weather models. However, the performance of using the ...
2025-02-12
WASHINGTON—Donald Patrick McDonnell, Ph.D., has been awarded the Endocrine Society’s John D. Baxter Prize for Entrepreneurship for discovering hormone therapies for treating breast and prostate cancer, the Society announced today.
The John D. Baxter Prize for Entrepreneurship was established to recognize the extraordinary achievement of bringing an idea, product, service, or process to market. This work ultimately elevates the field of endocrinology and positively impacts the health of patients.
McDonnell is a professor at Duke University School ...
2025-02-12
A new study by Silent Spring Institute and University of California, Berkeley shows how laws that promote greater transparency around harmful chemicals in products can shift markets toward safer products.
The study, published in the journal Environmental Science & Technology, focused on California’s right-to-know law called Proposition 65, or Prop 65. Under the law, the state of California maintains a list of approximately 900 chemicals known to cause cancer, birth defects, or reproductive harm. Companies that sell products in California are required to warn people if their products could expose them to harmful ...
2025-02-12
As more consumers turn to subscription-based platforms, the distribution of revenue in streaming services has become a crucial issue in the digital economy. Content creators and artists argue that the current models are opaque, frequently neglecting the needs of creators. In response, researchers at UMH have proposed a model based on three allocation rules that could be applied according to various fairness criteria.
"Our model is based on three main approaches: the equal division rule, which divides revenue equally among services; the proportional rule, which allocates revenue according ...
2025-02-12
A collaboration of researchers from Colorado State University and Denver Zoo Conservation Alliance surveyed zoo employees and volunteers across the US about their experiences of burnout and grief related to zoo animal losses.
Their latest study has found that poor grief support in some US zoos leaves staff feeling limited empathy from leadership, burned out, and unable to openly express their grief after the death of an animal to which they had formed a close emotional bond.
The research, published in the journal ...
2025-02-12
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — A cardiac surgery and heart failure team at the University of Michigan implanted a novel mechanical heart pump into a patient as part of a clinical trial that will compare it to the only device currently used to treat end-stage heart failure.
“This trial presents an opportunity to assess novel technology as we explore a potential new treatment for advanced heart failure — a life-threatening condition with extremely limited therapeutic opportunities available,” said Francis Pagani, M.D., Ph.D., national ...
2025-02-12
Picture an Antarctic animal and most people think of penguins, but there is a flightless midge, the only known insect native to Antarctica, that somehow survives the extreme climate. How the Antarctic midge (Belgica antarctica) copes with freezing temperatures could hold clues for humans about subjects like cryopreservation, but there remain many mysteries about the tiny insect.
One mystery appears to have been solved by an Osaka Metropolitan University-led international research team. Graduate School of Science Professor Shin G. Goto and Dr. Mizuki Yoshida, a graduate student at the time of the research who is now a postdoc at Ohio State University, found ...
2025-02-12
A new study explores how complex chemical mixtures change under shifting environmental conditions, shedding light on the prebiotic processes that may have led to life. By exposing organic molecules to repeated wet-dry cycles, researchers observed continuous transformation, selective organization, and synchronized population dynamics. Their findings suggest that environmental factors played a key role in shaping the molecular complexity needed for life to emerge. To simulate early Earth, the team subjected chemical mixtures to repeated wet-dry cycles. Rather than reacting randomly, the molecules organized themselves, evolved over time, and followed predictable patterns. This challenges ...
2025-02-12
Global aviation carbon dioxide emissions increased by 1% in 2023 because planes had to fly longer routes to avoid Russian airspace, according to a new study.
After Russia invaded Ukraine in February 2022, Western airlines were banned from flying over Russia. This forced them to take much longer routes between Europe or North America and East Asia, burning more fuel in the process.
Published today (Wednesday, 12 February) in Communications Earth & Environment, the study found that detours caused by the Ukraine war led to planes using 13% more fuel on average compared to their original routes. The impact was even greater for flights between Europe and Asia, which saw a 14.8% increase in ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] DNA methylation clocks may require tissue-specific adjustments for accurate aging estimates
“Our results suggest that forensic applications of DNAm clocks using non-blood tissue types will provide age estimates that are not as accurate as predictions based on blood, especially if using clocks algorithms trained on blood samples”