Loneliness and social isolation linked to increased risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, study finds
2025-02-12
(Press-News.org)
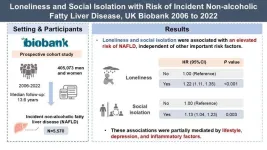
Loneliness and social isolation have been linked to an elevated risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), according to a groundbreaking study conducted by researchers from Central South University and the Army Medical University in China, in collaboration with the Karolinska Institutet in Sweden. Published in Health Data Science, the study analyzed data from over 400,000 participants in the UK Biobank, shedding light on the far-reaching impacts of social factors on liver health.
The research team, led by Professor Jiaqi Huang and Professor Jin Chai, sought to explore whether loneliness and social isolation—two critical but distinct social determinants of health—are associated with NAFLD risk. This chronic liver disease, affecting roughly 30% of the global population, has become a significant public health concern, driven by rising rates of obesity, diabetes, and aging populations. However, the role of psychosocial factors in NAFLD has remained unclear until now.
Using detailed assessments of participants' social connections and emotional well-being, the study found that loneliness increased the risk of developing NAFLD by 22%, while social isolation raised the risk by 13%, independent of traditional risk factors such as obesity, diabetes, and lifestyle behaviors. Remarkably, the associations persisted after adjusting for mutual influences between loneliness and social isolation, highlighting their independent effects.
The study’s mediation analysis revealed that unhealthy lifestyle behaviors, depression, and inflammatory responses partially explained these associations. Specifically, lifestyle factors like obesity, smoking, and irregular physical activity accounted for up to 30% of the observed risk linked to loneliness, while depression contributed an additional 33%. These findings underscore the importance of addressing both psychological and behavioral factors to mitigate NAFLD risk.
“Our findings provide robust evidence that loneliness and social isolation are not just mental health issues but also critical factors in the development of metabolic diseases like NAFLD,” said Professor Huang. “Interventions that target these social determinants, alongside promoting healthier lifestyles, could be transformative for public health.”
The researchers emphasize the need for further studies in diverse populations and longitudinal settings to confirm and expand these findings. They also call for integrated prevention strategies that address both the social and biological dimensions of health, highlighting the importance of community engagement, mental health support, and lifestyle interventions.
As the burden of NAFLD continues to grow, this study sheds new light on how fostering stronger social connections and addressing loneliness could play a pivotal role in liver disease prevention. The authors hope that their work will inspire public health initiatives aimed at alleviating the health impacts of loneliness and social isolation.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-02-12
In everyday life, we typically encounter water in one of three familiar states – solid, liquid or gas. But there are in fact many more phases, some of which – predicted to exist at high temperature and pressure – are so strange they’re referred to as exotic. State-of-the-art neutron spectrometers and sample environment infrastructures at the Institut Laue-Langevin (ILL) have enabled the first experimental observation of one of these exotic phases – plastic ice VII.
Plastic ice VII was originally predicted more than 15 years ago by molecular dynamics ...
2025-02-12
Scientists have discovered an interaction between genes that increases the risk of developing a type of alopecia.
In a new JAMA Dermatology study, scientists at King’s College London found that changes in two parts of the genome work together to influence alopecia risk.
Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA) is a highly distressing dermatological disorder which is associated with inflammation, scarring and irreversible hair loss. The disease affects an increasing number of patients worldwide and is caused by genetic and environmental factors.
The study authors conducted a meta-analysis of four cohorts ...
2025-02-12
Chinese scientists have identified two key genes responsible for sorghum's resistance to Striga, a parasitic plant that causes significant crop losses. The breakthrough, which also highlights the potential of AI to predict key amino acid sites in strigolactone (SL) transporters, could have wide-ranging applications in enhancing parasitic plant resistance across various crops.
This study, published in Cell, was conducted by Prof. XIE Qi's team at the Institute of Genetics and Developmental ...
2025-02-12
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 16:00hrs GMT Wednesday 12 February 2025
Peer reviewed
Experimental study
Animals, people and cells
Researchers from the Francis Crick Institute have found that some particularly aggressive lung cancer cells can develop their own electric network, like that seen in the body’s nervous system.
This unique property could make them less dependent on the environment surrounding the tumour and even spread more easily.
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is one of the hardest types of cancer to ...
2025-02-12
The RNA inhibitor olpasiran significantly reduces a type of “bad cholesterol” that’s associated with a high risk of cardiovascular events, according to results from an analysis by a Mount Sinai researcher of a phase 2 trial. The study reported that higher doses of olpasiran lowered the type of cholesterol called lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] by more than 95 percent in participants with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Findings were published February 12, 2025, in JAMA Cardiology.
“Our study is the first clinical trial to investigate the association between oxidized phospholipids on lipoprotein(a) and inflammatory mediators,” says ...
2025-02-12
Andrew Pines, MD, MA, a resident in the Department of Psychiatry at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and a researcher in the Center for Brain Circuit Therapeutics, is the lead author of a paper published in JAMA Psychiatry, Mapping Lesions That Cause Psychosis to a Human Brain Circuit and Proposed Stimulation Target.
Shan Siddiqi, MD, Assistant Professor of Psychiatry at Harvard Medical School and Director of Psychiatric Neuromodulation Research at the BWH Center for Brain Circuit Therapeutics, is the senior author of this ...
2025-02-12
**MEDIA ADVISORY**
UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL: Wednesday, February 12 at 11am EST
Nature article entitled:
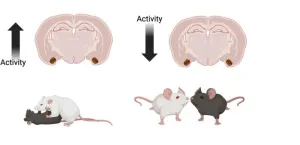
A critical role for the cortical amygdala in shaping social encounters
[https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-08540-4]
Bottom Line: Neural activity in the cortical amygdala determines whether mice engage in aggressive or pro-social behavior
Results: By performing a network analysis on whole-brain activity of male mice, we identified the cortical amygdala – an olfactory cortical structure – as a key brain region in promoting aggression. This brain region is activated by olfactory cues from male mice and by aggressive ...
2025-02-12
Recognition of telehealth as an effective strategy for delivering treatment for substance use disorder (SUD) has raised hopes for improving access to this treatment in settings with limited transportation or when time constraints compromise regular use of consistent access to in-person substance use treatment.
But the findings from a team of researchers from the Virginia Center for Health Innovation, UCLA, RAND, and MedInsight, Milliman Inc., suggest that the promise of telehealth may vary by insurance and geography.
New research suggests that people who live ...
2025-02-12
Monash research could transform how broken bones are treated, with the development of a special zinc-based dissolvable material that could replace the metal plates and screws typically used to hold fractured bones together.
Surgeons routinely use stainless steel or titanium, which stay in the body forever, can cause discomfort and may require follow-up surgeries. A new zinc alloy, designed by Monash biomedical engineers, could solve these problems by being mechanically strong but gentle enough to degrade safely over time while supporting optimal healing.
A study published today in Nature shows the research team’s innovative ...
2025-02-12
An increase in high-fat, high-fructose foods in people’s diets has contributed to a dramatic increase in type 2 diabetes. This, in turn, has led to an increase in peripheral neuropathy — nerve damage, typically in the hands and feet — that causes weakness, loss of sensation and, in some, a stabbing, burning, or tingling pain. About half of people with type 2 diabetes are affected, and of these, about half experience severe neuropathic pain.
The damage begins as axons from sensory neurons begin to retract and disappear from the tissues they innervate. New research from the lab of Clifford Woolf, MB, BCh, PhD, director ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Loneliness and social isolation linked to increased risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, study finds