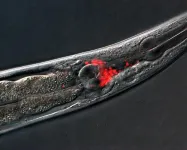
(Press-News.org) Osaka, Japan – Heart transplant is a scary and serious surgery with high cost, but for patients with heart failure it can be the only option for cure. Now, however, a multi-institutional research team led by Osaka University has found that simply taking a supplement might be all that is needed for certain patients with heart failure to recover – no surgery needed.
In a study published in Nature Cardiovascular Research, the research team found that tricaprin, a natural supplement, can improve long-term survival and recovery from heart failure in patients with triglyceride deposit cardiomyovasculopathy (TGCV).
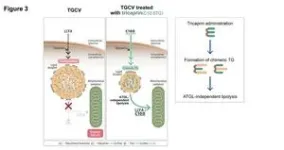
TGCV is a new type of heart disease; it results from an impaired ability of the heart and smooth muscle cells to break down triglycerides, which are a type of fat. Triglyceride accumulation in cells causes structural and functional damage in the heart and blood vessels. These changes result in clogged arteries and weakened heart muscles, which may cause debilitating symptoms and eventually heart failure, necessitating heart transplantation.
Luckily, through a series of experiments, researchers have identified how to diagnose the disease and developed a treatment that improves both disease symptoms and prognosis.
“Our previous research on the effect of tricaprin on patients with TGCV was very promising, but this time we decided to study how long the positive effects of the drug held up,” says lead author of the study Ken-ichi Hirano.
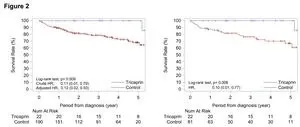
To achieve this, the researchers enrolled patients diagnosed with the condition from Japanese registries and compared the survival rates between those who had received tricaprin and those who did not. The study involved 22 patients from 12 different hospitals who had received tricaprin and 190 controls. The researchers studied the effect of tricaprin on triglyceride breakdown; to overcome differences in the compared groups, 81 of the 190 controls were matched with the tricaprin group according to their baseline characteristics for comparison of survival rates.
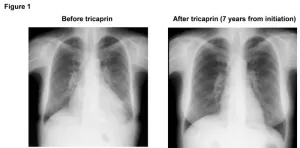
“Not only did the positive effects on patient symptoms continue, but the function of the heart muscle improved and the structural changes that had developed were reversed as well,” says Ken-ichi Hirano, the principle investigator for the Japan TGCV study group.
All the enrolled patients initially had heart failure; nevertheless, the 3- and 5-year survival rates were significantly higher in the tricaprin group (100% and 100%, respectively) compared with the control group (78.6% and 68.1%, respectively). Another favorable result was that several patients who had positive effects with tricaprin were on hemodialysis. These patients have a very poor prognosis without tricaprin.
“Spreading awareness of this disease to achieve early diagnosis and treatment offers patients the best chance for recovery,” asserts Ken-ichi Hirano.
These study findings are based on data from Japanese patients. As a next step, studies should be carried out on patients of other ethnicities to support the evidence in favor of this promising drug. This new research delivers the hope that patients can not only sustain but also recover their hearts from debilitating heart failure.
###
The article, “Long-term survival and durable recover of heart failure in patients with triglyceride deposit cardiomyovasculopathy treated with tricaprin,” was published in Nature Cardiovascular Research at DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s44161-025-00611-7
About Osaka University
Osaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and is now one of Japan's leading comprehensive universities with a broad disciplinary spectrum. This strength is coupled with a singular drive for innovation that extends throughout the scientific process, from fundamental research to the creation of applied technology with positive economic impacts. Its commitment to innovation has been recognized in Japan and around the world. Now, Osaka University is leveraging its role as a Designated National University Corporation selected by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to contribute to innovation for human welfare, sustainable development of society, and social transformation.
Website: https://resou.osaka-u.ac.jp/en
END
A simple supplement improves survival in patients with a new type of heart disease
Researchers from Osaka University find that tricaprin improves survival in patients with a novel heart disease, triglyceride deposit cardiomyovasculopathy
2025-02-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Uncovering novel transcriptional enhancers in neuronal development and neuropsychiatric disorders
2025-02-13
Neuropsychiatric disorders are becoming increasingly prevalent. Given their complex and multifactorial pathogenesis, there is an urgent need for effective and targeted therapies that can improve patients’ quality of life. Genome-wide association studies (GWASs) have identified various genetic alterations that contribute to the development and progression of neuropsychiatric disorders, ranging from mild dyslexia to more severe conditions such as schizophrenia.
While thousands of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)—changes in a single nucleotide position in the DNA—have been associated with neurological ...
IR Sant Pau study reveals immune system’s crucial role in ALS at cellular level
2025-02-13
A team of researchers from the Sant Pau Research Institute (IR Sant Pau) has published a study in the Journal of Neuroinflammation that, for the first time, examines in depth the role of the peripheral immune system in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) at the single-cell level. Their findings suggest that immune system cells—particularly two subpopulations of Natural Killer (NK) cells—may play a crucial part in the development and progression of this neurodegenerative disease.
ALS is a condition that causes the progressive degeneration of motor neurones, leading to a loss of muscle function and, eventually, affecting ...
Brain rhythms can predict seizure risk of Alzheimer’s disease patients, study finds
2025-02-13
A UCLA Health research team has identified changes in brain rhythms that indicate seizure activity in Alzheimer’s patients.
The findings, published in Brain Communications, build on UCLA neurologist and senior author Dr. Keith Vossel’s pioneering work that first linked silent epileptic activity to cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease.
Vossel’s previous studies showed that silent seizures, detected through overnight electroencephalography (EEG) and one-hour magnetoencephalography (MEG), occur in more than 40% of Alzheimer’s patients—beyond the 20% who experience overt seizures. His research has demonstrated ...
Scientists develop innovative DNA hydrogels for sustained drug release
2025-02-13
Hydrogels are polymeric materials with three-dimensional network structures containing large amounts of water. They serve as sustained-release drug delivery systems as they can encapsulate various bioactive substances, including drugs, antigens, and even cells. Hydrogels are better drug delivery alternatives than conventional systems, as they are more biocompatible, biodegradable, and easily administered as an injectable scaffold.
DNA has gained significant attention as a promising hydrogel material thanks to its customizable physicochemical properties, leading to the development of various DNA ...
Paramedics facing challenging end-of-life care demands
2025-02-13
Paramedics in England are experiencing wide-ranging challenges in responding to the increasing number of end-of-life care patients they are being called out to, according to a study from the University of Southampton.
The study published in BMC Palliative Care highlights the issues paramedics face when responding to patients at end-of-life, including a lack of patient information, barriers to administering medication, and insufficient training.
It was funded by Marie Curie and supported by National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) Applied ...
Worm study shows hyperactivated neurons cause aging-related behavioral decline
2025-02-13
A study of nematodes by researchers at Nagoya University in Japan has found that aging-related decline in brain function is caused by the excessive activation of certain neurons over time, rather than a decline in neuronal activity. This finding, published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, suggests that interventions aimed at reducing neuronal hyperactivation, such as dietary changes, could potentially mitigate age-related cognitive decline.
Proper brain function occurs when a large number of neurons are connected to each other and work ...
Combining millions of years of evolution with tech wizardry: the cyborg cockroach
2025-02-13
Osaka, Japan – From disaster zones to extreme environments, there remain areas difficult for even humans to reliably access. This poses a problem for search-and-rescue operations, research, surveillance, and more. Now, however, a research team from Osaka University and Diponegoro University, Indonesia is hard at work on one potential solution: the cyborg insect.
Cyborg insects have a lot of advantages over traditional robots. Power consumption is less of an issue, so it’s easier to miniaturize them, and they are even ‘pre-built’ in a sense. However, research on cyborg insects has been limited to simple environments, like flat surfaces supplemented ...
Discrimination can arise from individual, random difference, study finds
2025-02-13
New research from the University of Sydney has found people tend to discriminate in favour of individuals who show a similarity to them, even when the similarity arises from a random event like the flip of a coin.
Published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the research runs counter to traditional theories, in particular social identity theory, that assume discrimination occurs because we divide people into groups. It finds, instead, differences between individuals are enough to trigger discrimination.
Previous research (using the seminal ‘minimal group’ experiment) showed participants tend to financially benefit members of their own group over ...
Machine learning boosts accuracy of solar power forecasts
2025-02-13
As solar energy plays an increasing role in the global power supply, ensuring accurate forecasts of photovoltaic (PV) power generation is critical for balancing energy demand and supply. A new study published in Advances in Atmospheric Sciences explores how machine learning and statistical techniques can refine these forecasts by correcting errors in weather models.
Weather forecasts are a key input for PV power prediction models, yet they often contain systematic errors that impact accuracy. Researchers from the Institute of Statistics at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology ...
Researchers create chemotaxic biomimetic liquid metallic leukocytes with versatile behavior
2025-02-13
Scientists led by Prof. LIU Jing from the Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) have created a leukocyte-like liquid metallic entity that vividly simulates various leukocyte behaviors in nature.
Published in Matter on February 10, the researchers demonstrated how these "liquid metallic leukocytes" can autonomously perform complex actions like engulfing foreign substances, changing shape, moving in a pulsatile manner, and even climbing against gravity—showing striking similarities to the dynamic behavior of living cells.
The research ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
National Reactor Innovation Center opens Molten Salt Thermophysical Examination Capability at INL
International Progressive MS Alliance awards €6.9 million to three studies researching therapies to address common symptoms of progressive MS
Can your soil’s color predict its health?
Biochar nanomaterials could transform medicine, energy, and climate solutions
Turning waste into power: scientists convert discarded phone batteries and industrial lignin into high-performance sodium battery materials
PhD student maps mysterious upper atmosphere of Uranus for the first time
Idaho National Laboratory to accelerate nuclear energy deployment with NVIDIA AI through the Genesis Mission
Blood test could help guide treatment decisions in germ cell tumors
New ‘scimitar-crested’ Spinosaurus species discovered in the central Sahara
“Cyborg” pancreatic organoids can monitor the maturation of islet cells
Technique to extract concepts from AI models can help steer and monitor model outputs
Study clarifies the cancer genome in domestic cats
Crested Spinosaurus fossil was aquatic, but lived 1,000 kilometers from the Tethys Sea
MULTI-evolve: Rapid evolution of complex multi-mutant proteins
A new method to steer AI output uncovers vulnerabilities and potential improvements
Why some objects in space look like snowmen
Flickering glacial climate may have shaped early human evolution
First AHA/ACC acute pulmonary embolism guideline: prompt diagnosis and treatment are key
Could “cyborg” transplants replace pancreatic tissue damaged by diabetes?
Hearing a molecule’s solo performance
Justice after trauma? Race, red tape keep sexual assault victims from compensation
Columbia researchers awarded ARPA-H funding to speed diagnosis of lymphatic disorders
James R. Downing, MD, to step down as president and CEO of St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital in late 2026
A remote-controlled CAR-T for safer immunotherapy
UT College of Veterinary Medicine dean elected Fellow of the American Academy of Microbiology
AERA selects 34 exemplary scholars as 2026 Fellows
Similar kinases play distinct roles in the brain
New research takes first step toward advance warnings of space weather
Scientists unlock a massive new ‘color palette’ for biomedical research by synthesizing non-natural amino acids
Brain cells drive endurance gains after exercise
[Press-News.org] A simple supplement improves survival in patients with a new type of heart diseaseResearchers from Osaka University find that tricaprin improves survival in patients with a novel heart disease, triglyceride deposit cardiomyovasculopathy