SfN announces Early Career Policy Ambassadors Class of 2025
2025-02-13
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON — The Society for Neuroscience (SfN) has selected 10 members from a highly competitive applicant pool to participate in the Society’s annual Capitol Hill Day on March 11–13, 2025. The 10 Early Career Policy Ambassadors (ECPAs), representing many career stages and geographic locations, were chosen for their dedication to advocating for the scientific community, their desire to learn more about effective means of advocacy, and their experience as leaders in their labs and community.
The ambassadors are:
Izan Chalen, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign
Nicole D’Souza, University of California, Riverside
Lana Ruvolo Grasser, PhD, Department of Psychology Ben L. Silberstein Institute for Brain Health, Wayne State University
J. Alex Grizzell, PhD, Emory University
Joseph Hennessey, Medical College of Wisconsin
Riley Kemna, University of Kansas Medical Center Alzheimer’s Disease Research Center
Blakely Lockhart, Fralin Biomedical Research Institute at Virginia Tech
Showmick Paul, University of Rochester
Alex Rich, Yale University Interdepartmental Neuroscience Program
Kiarash Shamardani, Stanford University School of Medicine
The ECPA program is a 10-month commitment designed to create an extensive network of neuroscience advocates. Ambassadors gain the necessary skills to advocate for science funding and other issues affecting the neuroscience field, and to encourage those in their personal networks to join the conversation. Over the course of the program, ambassadors engage in at least two additional advocacy-related activities at their home institution and within their community.
###
The Society for Neuroscience (SfN) is an organization of nearly 35,000 basic scientists and clinicians who study the brain and the nervous system.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-02-13
Collecting video data is the long-established way biologists collect data to measure the behaviour of animals and humans. Videos might be taken of human subjects sitting in front of a camera while eating in a group in the University of Konstanz, or researchers using cameras to measure how often house sparrow parents visit their nests on Lundy Island, UK. All these video datasets have one thing in common: after collecting them, researchers need to painstakingly watch each video, manually mark down who, where and when each behaviour of interest happens—a process known as “annotation”. ...
2025-02-13
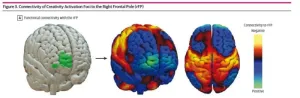
KEY TAKEAWAYS
Brigham researchers analyzed data from 857 patients across 36 fMRI brain imaging studies and mapped a common brain circuit for creativity.
They derived the circuit in healthy individuals and then predicted which locations of brain injury and neurodegenerative disease might alter creativity.
The study found that changes in creativity in people with brain injury or neurodegenerative disease may depend on the location of injury in reference to the creativity circuit.
A new study led by ...
2025-02-13
About The Study: From 2013-2014 to August 2021-August 2023, there were small increases in the percentage of children and adolescents with obesity, as well as in adults with severe obesity (but not obesity). There were no other significant changes in obesity-related measures, including waist circumference. This period included the COVID-19 pandemic; a study using electronic health records found a small increase in mean weight among adults during the pandemic.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Samuel D. Emmerich, DVM, email semmerich@cdc.gov.
To access ...
2025-02-13
About The Study: The findings of this study provide evidence that fertility rates in states with abortion bans were higher than would have been expected in the absence of these policies, with the largest estimated differences among subpopulations experiencing the greatest structural disadvantages and in states with among the worst maternal and child health and well-being outcomes.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Suzanne O. Bell, PhD, email suzannebell@jhu.edu.
To ...
2025-02-13
About The Study: U.S. states that adopted abortion bans had higher than expected infant mortality after the bans took effect. The estimated relative increases in infant mortality were larger for deaths with congenital causes and among groups that had higher than average infant mortality rates at baseline, including Black infants and those in southern states.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Alison Gemmill, PhD, email agemmill@jhu.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.28517)
Editor’s ...
2025-02-13
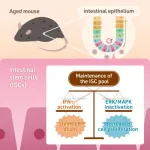
A recent study led by Associate Professor Takuya Yamamoto and Researcher May Nakajima-Koyama has revealed that maintaining a delicate balance between interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling is essential for preserving the intestinal stem cell population during aging. By comparing young and aged mouse intestinal tissues, the researchers uncovered critical insights into the interplay between these signaling pathways in supporting stem cell maintenance over time.
The intestinal epithelium exhibits the highest cell ...
2025-02-13
For fruit flies, finding the right mate is all about the right song. Now, research shows that male flies don’t just try to impress their valentine by serenading her with song—they also go to great lengths to drown out the competition. By jamming their rivals’ love songs with high-frequency wing flicks, male fruit flies boost the chances that they’ll win the female over.
The new study, published in Cell, explains how the fruit fly brain coordinates courtship and aggressive competition—a framework which could ultimately help scientists understand how humans flexibly ...
2025-02-13
With the promotion of the "the Belt and Road" initiative, the economy and society of BRI countries have developed rapidly, but they are also facing severe challenges of rising carbon emissions. Many countries rely on fossil fuels, and the process of energy transition is slow. Coupled with insufficient financial and technological support, especially low-income countries that have limited access to global climate funds, they face greater difficulties in the low-carbon transformation process.
To identify the carbon emission drivers at different development stages of BRI countries ...
2025-02-13
Geoglossomycetes is a class within the phylum Ascomycota that accommodates a single order and a single family, comprising nine genera. Geoglossomycetes is traditionally referred to as “earth tongues”. The class is characterized by tongue-shaped to clavate, stipitate, black ascomata covered with or without black setae, a swollen ascigerous portion, a cylindric stipe, filiform, septate paraphyses, cylindrical-clavate, 4–8-spored asci, and filiform or falciform, multi-septate, dark brown to hyaline ascospores.
In collaboration with ...
2025-02-13
This study is led by Dr. Zhu L. Yang (Key Laboratory of Phytochemistry and Natural Medicines, Kunming Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences). Specimens were collected by Song-Yan Zhou and Fei-Fei Liu; microscopic and phylogenetic analyses of Thaxterogaster species were conducted by Zi-Rui Wang at Kunming Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
The team used 514 (236 newly generated + 278 downloaded) sequences from 243 collections representing 112 species building a five-locus phylogenetic tree which includes most currently known lineages and newly described ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] SfN announces Early Career Policy Ambassadors Class of 2025