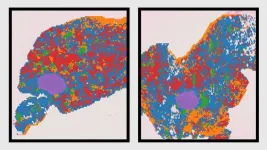
(Press-News.org) Aging is a privilege, but it also brings risks—including an increased likelihood of developing age-related diseases including cancer. Researchers at The Jackson Laboratory (JAX) have created a landmark atlas of how healthy breast tissue ages, revealing key cellular, molecular, and genetic changes that may tip the balance toward breast cancer development. Their findings, published recently in Nature Aging, provide a valuable open-access resource for the scientific community to explore aging and its role in increased cancer risk.
Rewriting the molecular story of aging cells
Using cutting-edge single-cell and spatial transcriptomics technologies, the researchers compared young virgin female mice to older mice and mapped how mammary gland cellular landscape changes over time. The team, co-led by Olga Anczukόw, Ph.D., an associate professor at JAX and co-program leader of the National Cancer Institute-designated JAX Cancer Center found that epithelial, immune, and stromal cells—which are essential for maintaining healthy breast tissue—undergo shifts not just in their numbers but also in their molecular identity.
Epithelial cells, the ones lining milk ducts and from which most breast cancers arise, lose their job descriptions, becoming more capable of dealing with change but also more prone to malignancy.
Stromal cells, which provide structural support to breast tissue, lose their specialized identity, creating a chaotic microenvironment that could promote tumor growth.
Immune cells infiltrate the aging tissue, but instead of protecting against cancer, these cells are prone to inflammation and exhaustion, potentially fueling tumor development.
But there’s more.
Anczukόw and her team, for the first time, established a direct link between aging-related gene expression changes and chromatin accessibility in the mammary gland, which refers to how tightly or loosely DNA is packed within the nucleus. This affects which genes can be turned on or off. Changes in chromatin structure, for example, might lead to dysregulation of genes involved in cell proliferation, DNA repair, and immune response – mechanisms known to contribute to tumor growth.
“For the first time, we’ve linked aging-related gene expression changes in breast tissues to alterations in chromatin accessibility, the molecular ‘script’ controlling gene activity,” said Duygu Ucar, Ph.D., a professor at JAX and the co-senior author of the study. “This implies that as breast cells age, alterations in chromatin structure may play a crucial role in regulating gene activity.”
From mice to humans: A shared cancer link
To see if these age-related molecular changes in mice reflect human breast cancer risk, Anczukόw and Ucar and their teams compared their data to genetic profiles of human breast tumors. They found that these age-related molecular signatures in mice closely mirror patterns seen in human breast cancers—suggesting that the aging breast microenvironment plays a direct role in cancer risk and can provide valuable warning signs.
“Finding these overlapping pathways was really exciting,” said Brittany Angarola, Ph.D., an associate research scientist at JAX and co-first author of the study. “It suggests that aging-related shifts in healthy tissue might create a more cancer-friendly environment before tumors even form.”
A roadmap for prevention & early detection
This open-access atlas provides a crucial resource for scientists worldwide to explore how aging influences cancer risk. The dataset allows researchers to identify potential biomarkers for early detection and develop strategies for prevention and treatment.
“This study not only advances our understanding of aging and cancer but also lays the groundwork for future research into interventions that could reduce cancer risk in aging populations,” said Anczukόw. “It provides us with a powerful tool to help cancer patients everywhere.”
This work was supported by The JAX Cancer Center, The JAX Center for Aging Research, The V Foundation, The Tallen-Kane Foundation, The Scott R. MacKenzie Foundation, and The Hevolution Foundation.
END
Landmark atlas reveals how aging breast tissue shapes breast cancer risk
Researchers at The Jackson Laboratory uncover how age-related cellular and molecular changes may contribute to breast cancer development
2025-02-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
SHEA supports key federal advisory committees
2025-02-13
The Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA) urges incoming Secretary of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Robert F. Kennedy Jr., to resume the federal advisory committees for key health-related priority issues as provided under the Federal Advisory Committees Act. Federal advisory committees are an important aspect of the deliberative process for reviewing important scientific information among federal agencies and members of the public as new evidence becomes available. The ability for members ...
Neurologic complications of flu nearly 50 times greater for children with underlying neurologic conditions
2025-02-13
Many clinicians do not consider neurologic complications of the flu when discussing vaccination or treatment of influenza with families.
A recent study that explored the neurologic impact of flu in children aims to change that.
“Serious Neurologic Events with Seasonal Influenza in Young Children,” published in Academic Pediatrics, the official journal of the Academic Pediatric Association, looked at the population-based incidence of underrecognized influenza-associated serious neurologic events in children less than 5 years of age.
While serious neurologic complications are uncommon in young children, the study showed a much higher incidence, ...
Killing H5N1 in waste milk — an alternative to pasteurization
2025-02-13
Pasteurization is the only widely recognized method of killing H5N1, the virus that causes bird flu, in milk. However, pasteurization can be expensive and fewer than 50% of large dairy farms pasteurize waste milk.
Waste milk includes colostrum, the first milk after calving; milk from cows treated with antibiotics or other drugs; or any other factor that can make milk unsuitable and unsellable for human consumption. On farms, raw waste milk poses a potential risk of spreading avian flu, which so far has been confirmed ...
NTT Research and Harvard scientists optimize biohybrid ray development with machine learning
2025-02-13
The Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) and NTT Research, Inc., a division of NTT, announced the publication of research showing an application of machine-learning directed optimization (ML-DO) that efficiently searches for high-performance design configurations in the context of biohybrid robots. Applying a machine learning approach, the researchers created mini biohybrid rays made of cardiomyocytes (heart muscle cells) and rubber with a wingspan of about 10 mm that are approximately two times more efficient at swimming than those recently ...
Mapping connections in a neuronal network
2025-02-13
Harvard researchers have mapped and catalogued more than 70,000 synaptic connections from about 2,000 rat neurons, using a silicon chip capable of recording small yet telltale synaptic signals from a large number of neurons.
The research, published in Nature Biomedical Engineering, is a major advance in neuronal recording and may help bring scientists a step closer to drawing a detailed synaptic connection map of the brain.
Higher-order brain functions are believed to be derived from the ways brain ...
Study: Air pollution exposure late in pregnancy increases NICU admission risk
2025-02-13
BUFFALO, N.Y. – Air pollution caused by auto emissions, wildfires and other sources is problematic for many people. It’s of particular concern for pregnant people due to the impact pollutants can have on the fetus, especially in the final month before birth.
A new study from the University at Buffalo offers insight into air pollution’s effects during this vulnerable time by measuring neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) admissions and satellite-based air pollution data.
The researchers focused on common pollutants, such as nitrogen dioxide (NO2), which is caused primarily by the burning of fossil fuels in vehicles, industrial processes and power plants, and PM2.5, which ...
Engineers enable a drone to determine its position in the dark and indoors
2025-02-13
CAMBRIDGE, MA – In the future, autonomous drones could be used to shuttle inventory between large warehouses. A drone might fly into a semi-dark structure the size of several football fields, zipping along hundreds of identical aisles before docking at the precise spot where its shipment is needed.
Most of today’s drones would likely struggle to complete this task, since drones typically navigate outdoors using GPS, which doesn’t work in indoor environments. For indoor navigation, some drones ...
U-M materials scientist, chemical engineer elected into National Academy of Engineering
2025-02-13
Photos
Michigan Engineering professors Elizabeth Holm and Nicholas Kotov are among the newest members of the National Academy of Engineering—one of the highest honors bestowed on engineers in the United States.
"Elizabeth Holm and Nicholas Kotov have not only distinguished themselves as leaders in their fields, they have demonstrated the impact we can have as engineers, influencing how current and future generations of engineers solve problems and do their work," said Karen Thole, the Robert J. Vlasic Dean of Engineering at the University of Michigan College of Engineering.
"We applaud this significant honor, and look forward ...
Evolutionary tradeoffs: Research explores the role of iron levels in COVID-19 infections
2025-02-13
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- Your body is ground zero for a cellular arms race.
Your mitochondria, red blood cells and immune system rely on iron to function; so do invading viruses and bacteria. As your body evolves safeguards for this most critical resource, these safeguards select for invaders that can overcome them.
“Iron is physiologically useful in catalyzing reactions, such as binding oxygen, because it both donates and accepts electrons,” explained Binghamton University Associate Professor of Anthropology ...
Ecological Society of America selects 2025 EEE Scholars
2025-02-13
The Ecological Society of America (ESA) announces the 2025 cohort of ESA Excellence in Ecology (EEE) Scholars. This prestigious scholarship program celebrates and supports outstanding early- to mid-career Ph.D. ecologists from groups traditionally underrepresented in the scientific community.
This year’s EEE Scholars are: Elvira D'Bastiani, Postdoctoral Researcher at the University of California, Los Angeles; Gabriela Garcia, Assistant Professor at Northeastern University; Camille Griffith, Assistant Professor at Oglala Lakota College; and Estelí Jiménez-Soto, Assistant Professor at the University of South Florida.
“These exceptional scholars embody ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Study: Reported crop yield gains from breeding may be overstated
Stem cells from human baby teeth show promise for treating cerebral palsy
Chimps’ love for crystals could help us understand our own ancestors’ fascination with these stones
Vaginal estrogen therapy not linked to cancer recurrence in survivors of endometrial cancer
How estrogen helps protect women from high blood pressure
Breaking the efficiency barrier: Researchers propose multi-stage solar system to harness the full spectrum
A new name, a new beginning: Building a green energy future together
From algorithms to atoms: How artificial intelligence is accelerating the discovery of next-generation energy materials
Loneliness linked to fear of embarrassment: teen research
New MOH–NUS Fellowship launched to strengthen everyday ethics in Singapore’s healthcare sector
Sungkyunkwan University researchers develop next-generation transparent electrode without rare metal indium
What's going on inside quantum computers?: New method simplifies process tomography
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
Jackdaw chicks listen to adults to learn about predators
Toxic algal bloom has taken a heavy toll on mental health
Beyond silicon: SKKU team presents Indium Selenide roadmap for ultra-low-power AI and quantum computing
Sugar comforts newborn babies during painful procedures
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
From herbal waste to high performance clean water material: Turning traditional medicine residues into powerful biochar
New sulfur-iron biochar shows powerful ability to lock up arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils
AI-driven chart review accurately identifies potential rare disease trial participants in new study
Paleontologist Stephen Chester and colleagues reveal new clues about early primate evolution
[Press-News.org] Landmark atlas reveals how aging breast tissue shapes breast cancer riskResearchers at The Jackson Laboratory uncover how age-related cellular and molecular changes may contribute to breast cancer development