(Press-News.org) AUSTIN, Texas -- McCombs’ faculty research leaped 10 spots to No. 10 worldwide in the Financial Times’ release of its Global MBA Rankings for 2025, a historic high for McCombs reaching back to 1999.
The top spot for research went to the University of Pennsylvania, with Columbia University and the University of Chicago tying for second place.
Faculty Research is the third weightiest component (10%) of the 21 used in the MBA ranking, behind percentage of salary increase (16%) and salary three years post-graduation (16%). The Texas Full-Time Hildebrand MBA Program ranked No. 17 among U.S.-based programs, which was also a historic high in the overall ranking.
The Research ranking is calculated by tallying the number of articles published by full-time faculty members in 50 academic and practitioner journals from January 2022 to May 2024. The ranking combines the absolute number of publications with the number weighted relative to faculty size. McCombs faculty members authored or co-authored 200 publications during that period.
END
Texas McCombs faculty research hits historic high
McCombs cracks top 10 in Financial Times MBA Rankings
2025-02-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Multiple sclerosis: Cell-catching implant helps identify successful treatment in mice
2025-02-18
Images
A sponge-like implant in mice helped guide a treatment that slowed or stopped a degenerative condition similar to multiple sclerosis in humans. It also gave University of Michigan researchers a first look at how primary progressive multiple sclerosis, the fastest-progressing version of the disease, attacks the central nervous system early on.
If administered early, the nanoparticle-based treatment prevented mice from developing symptoms such as paralysis. If given after the first symptoms emerged, it reduced symptom scores by half compared to untreated ...
Q&A: Is it always ‘us vs them’? Researcher explains why flexibility is key
2025-02-18
UNIVERSITY PARK , Pa. — Urban versus rural. Penn State versus Michigan. Star Wars versus Star Trek. As social beings, humans gravitate toward groups. But sometimes group living can spur an “us versus them” mentality that causes conflict, especially when two groups are competing for the same limited resources, like money or a championship trophy.
In the following Q&A, Anne Pisor, assistant professor of anthropology at Penn State and Social Science Research Institute co-funded faculty member, discussed her recently published paper on the “us versus them” mindset as well as the causes and how to overcome it.
Q: What does your research say about ...
New nanoscale technique unlocks quantum material secrets
2025-02-18
Scientists are racing to develop new materials for quantum technologies in computing and sensing for ultraprecise measurements. For these future technologies to transition from the laboratory to real-world applications, a much deeper understanding is needed of the behavior near surfaces, especially those at interfaces between materials.
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory have unveiled a new technique that could help advance the development of quantum technology. Their innovation, surface-sensitive spintronic terahertz spectroscopy (SSTS), provides an unprecedented look at how quantum ...
New study uncovers how genes influence retinal aging and brain health
2025-02-18
Vision changes are an inevitable part of aging, but why are some more susceptible to age-related eye diseases and why do some individuals experience more severe decline than others? New research from The Jackson Laboratory (JAX) reveals that genetics play a key role in how the eye ages, with different genetic backgrounds influencing retinal aging in distinct ways.
The study, published in Molecular Neurodegeneration, examined age-related changes in genes and proteins of the retinas of nine strains of mice, ...
‘False’ springs, long summers mean uncertainty for NY grape growers
2025-02-18
CORNELL UNIVERSITY MEDIA RELATIONS OFFICE
FOR RELEASE: Feb. 17, 2025
Kaitlyn Serrao
607-882-1140
kms465@cornell.edu
‘False’ springs, long summers mean uncertainty for NY grape growers
ITHACA, N.Y. – Warmer autumns and more “false” springs are disrupting the signals grapevines rely on to gain cold hardiness for the winter and blossom effectively in the spring, according to new research from Cornell University.
“In New York, we are right at the coldest ...
A treatment-resistant, severe type of asthma successfully modeled in mice
2025-02-18
A better understanding of inflammation and lung immunity over the past two decades has led to new, innovative treatments for asthma, including biologic therapies.
This is especially true for a subtype known as eosinophilic asthma—asthma that’s related to the recruitment and overactivation of white blood cells in the lungs called eosinophils.
However, a different type of asthma called neutrophilic asthma has fewer treatment options and doesn’t respond as well to first line asthma therapy.
As a result, people with this type of asthma, which ...
Cholesterol metabolism byproduct linked to Parkinson’s disease
2025-02-18
Researchers led by Zhentao Zhang at Wuhan University, China have discovered a cholesterol metabolite that plays a critical role in the development of Parkinson’s disease in mice. Published in the open-access journal PLOS Biology on February 18th, the study shows that this metabolite is responsible for the formation of Lewy bodies and the death of dopaminergic neurons in the brain—the two major hallmarks of Parkinson’s disease. Blocking its activity or preventing it from being made by the body could therefore be effective strategies for treating the disease.
Parkinson’s disease develops when the protein alpha-Syn forms clumps of tiny pathological fibers ...
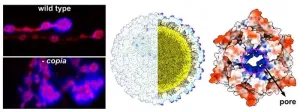
The capsid of the virus-derived retrotransposon Copia, a parasitic genome element, mediates synaptic plasticity at the Drosophila neuromuscular junction
2025-02-18
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: https://plos.io/42Ly2Pr
Article title: Capsid transfer of the retrotransposon Copia controls structural synaptic plasticity in Drosophila
Author countries: United States
Funding: This work was supported by NIH Grant R01NS112492 to TT. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. END ...
Sweet molasses feed key to understanding grazing behavior in cattle
2025-02-18
Researchers tempted grazing cattle with sweet molasses feed to discover whether cows would roam far and wide to graze or stick close to the herd, water supplies and feed stations.
The findings by animal scientists at the University of California, Davis, and published in the journal Scientific Reports, offer a low-cost way for ranchers and others to identify the best cows for their landscapes to optimize grazing while meeting the nutritional needs of cattle.
This is the third in a series of papers about research seeking to better understand the grazing personalities of cattle. The first studies ...
Fabio Boschini, first INRS researcher to receive an Alfred P. Sloan Fellowship
2025-02-18
MONTRÉAL and VARENNES, QC, Feb. 18, 2025 /CNW/ - Professor Fabio Boschini is among the 126 recipients announced today by the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation in seven fields. Sloan Fellowships support outstanding early-career scientists who demonstrate creativity, ambition, and dedication to advance discovery. These rising stars of research come from American and Canadian schools and are definitely names to watch. Many Sloan Fellows have gone on to become Nobel prize winners.
INRS Professor Fabio Boschini has just received a prestigious ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Texas McCombs faculty research hits historic highMcCombs cracks top 10 in Financial Times MBA Rankings