(Press-News.org) DALLAS, Feb. 19, 2025 — The conditions in which we are born, live, learn, work, play and age — the social drivers of health — are better predictors of health and life expectancy than our genetic code. In communities nationwide, people living in locations just a handful of miles apart can have a dramatic difference in life expectancy.
To help level the playing field, the Grubhub Community Fund awarded the American Heart Association® Social Impact Funds a $2 million grant to support food security, technology innovation and economic resiliency in New York City and Chicago.
“We are grateful for this generous support, which will help fill a critical resource gap and help communities overcome barriers to high-quality, accessible health care, food security and economic empowerment,” said Regina Benjamin, M.D., MBA, chair of the Social Impact Funds Impact Investment Committee and 18th U.S. Surgeon General. “With support from the Grubhub Community Fund and other generous funding, American Heart Association Ventures offers a unique opportunity to turn philanthropy into action that makes a real and exponential difference in peoples’ lives.”
The American Heart Association Social Impact Funds will use this new support to help up to 12 organizations and entrepreneurs with significant efforts focused in Chicago and New York City through proprietary sourcing, investment and performance management processes. Four focused on Chicago have already been identified:
CareYaya, based in North Carolina, an on-demand marketplace connecting families with more than 25,000 students in pre-health programs to be caregivers for affordable, flexible in-home care access, while helping to expand the care workforce amidst a critical caregiver shortage;
Farm Generations Corporation, based in New York, a farmer-owned cooperative that supports farm viability, food access and regenerative agriculture through technological innovation and community building. Its flagship product, GrownBy, is a SNAP-eligible, direct-to-consumer e-commerce platform connecting growers and consumers across America;
Nectar, based in Chicago, a platform that drives innovation in food security by delivering food as medicine in partnership with charitable food organizations; and
RiseKit, based in Chicago, a software platform that empowers untapped talent to find jobs and improve their economic well-being and address social drivers of health through community-based organizations and job training programs
“At Grubhub, we are committed to creating meaningful change in the communities where we operate, with a focus on supporting our largest market, New York City, and hometown, Chicago. With the American Heart Association being equally committed as us in advancing food security, technology innovation, and economic resiliency, Grubhub is proud of this ongoing work, made possible by the Grubhub Community Fund, to support organizations advancing equitable health in New York City and Chicago,” said Brianna Morris, senior manager, community impact for Grubhub. “We are excited for the four organizations that have received financial support thus far, and we look forward to seeing how their communities are positively impacted.”
Organizations are selected for funding by the Social Impact Funds based on their promising solutions to address social drivers of health and local barriers to achieving equitable health. The Funds evaluate opportunities to identify innovative, evidence-based candidates that align with the American Heart Association's mission and demonstrate the potential for lasting community impact.
Learn more about the Social Impact Funds at heart.org/socialimpactfunds.
Additional Resources:
What We Do | The Social Impact Funds | American Heart Association
###
About the American Heart Association®
The American Heart Association is a relentless force for a world of longer, healthier lives. Dedicated to ensuring equitable health in all communities, the organization has been a leading source of health information for more than one hundred years. Supported by more than 35 million volunteers globally, we fund groundbreaking research, advocate for the public’s health, and provide critical resources to save and improve lives affected by cardiovascular disease and stroke. By driving breakthroughs and implementing proven solutions in science, policy, and care, we work tirelessly to advance health and transform lives every day. Connect with us on heart.org, Facebook, X or by calling 1-800-AHA-USA1.
About the American Heart Association Social Impact Funds
The American Heart Association’s Social Impact Funds, including the Bernard J. Tyson Impact Fund, channel capital to small and medium-sized organizations that know their community best and whose ideas accelerate innovation to address local community and national health challenges. With a focus on improving health equity and expanding access to capital, the Funds support accessible, high quality health care, food security and economic empowerment. Since launching in 2018, the Funds have provided $21.5 million in financial support to more than 130 local enterprises to positively impact the well-being of nearly 5 million people. Learn more about our work at heart.org/socialimpactfunds.
END
New funding to support food security, economic resiliency
Four organizations selected by American Heart Association Social Impact Funds to fill critical resource gaps, further progress toward equitable health using $2M grant from Grubhub Community Fund
2025-02-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
All generic drugs are not equal, study finds
2025-02-19
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Generic drugs manufactured in India are linked to significantly more “severe adverse events” for patients who use them than equivalent drugs produced in the United States, a new study finds.
These adverse events included hospitalization, disability, and in a few cases, death. Researchers found that mature generic drugs, those that had been on the market for a relatively long time, were responsible for the finding.
The results show that all generic drugs are not equal, even though patients are often told that they are, said John Gray, co-author of the study and professor of operations at The Ohio State University’s ...
Enhancing shareholder accountability: Lessons from Japan’s corporate governance reforms
2025-02-19
Shareholders play a crucial role in corporate governance by voting on key decisions in the companies they invest in. To enhance transparency, regulatory bodies worldwide—such as government agencies and stock exchanges—are increasingly implementing guidelines to hold institutional investors accountable for their voting behavior and ensure they fulfill their fiduciary duties.
A study published in the journal Corporate Governance: An International Review on 22 January 2025 demonstrates that these regulations, even if non-binding, can encourage institutional investors to play a more active role and improve corporate governance. The study, conducted ...
A new treatment for post-amputation pain?
2025-02-19
Procedure is simple and could be adopted by most U.S. hospitals
Roughly 2 million people in the U.S. live with limb loss; number is expected to rise
Senior author, a retired U.S. Army colonel, traveled to Ukraine to set up the study
CHICAGO --- A reliable method to treat post-amputation pain remains elusive, but a new Northwestern Medicine study conducted in collaboration with Ukrainian physicians suggests that hydrodissection — a simple procedure that injects fluid around nerves — may reduce residual limb pain and opioid dependence.
The ...
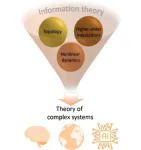
Groundbreaking study reveals how topology drives complexity in brain, climate, and AI
2025-02-19
(Embargo: 19 Feb, 10am GMT) A groundbreaking study led by Professor Ginestra Bianconi from Queen Mary University of London, in collaboration with international researchers, has unveiled a transformative framework for understanding complex systems. Published in Nature Physics, this pioneering study establishes the new field of higher-order topological dynamics, revealing how the hidden geometry of networks shapes everything from brain activity to artificial intelligence.
“Complex systems like the brain, climate, and next-generation artificial intelligence rely on interactions that extend beyond simple pairwise relationships. Our study reveals ...
Lifestyle and environmental factors affect health and ageing more than our genes
2025-02-19
A new study led by researchers from Oxford Population Health has shown that a range of environmental factors, including lifestyle (smoking and physical activity), and living conditions, have a greater impact on health and premature death than our genes.
The researchers used data from nearly half a million UK Biobank participants to assess the influence of 164 environmental factors and genetic risk scores for 22 major diseases on ageing, age-related diseases, and premature death. The study is published today in Nature Medicine.
Key findings
Environmental factors explained 17% of the variation in risk of death, compared to less than 2% explained by genetic predisposition (as ...
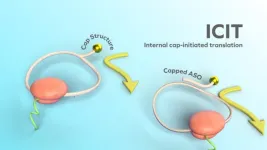
New mRNA produces 200 times more protein: Hope for treatment of cancer and protein disorders
2025-02-19
Imagine a breakthrough in cancer treatment where only malignant cells are targeted, sparing healthy host cells; or patients with abnormal protein synthesis are treated to produce a healthy protein. Hiroshi Abe and his colleagues at Nagoya University have identified two applications, among others, in a new study. Their innovative approach, reported in Nature Biotechnology, called the Internal Cap-Initiated Translation (ICIT) mechanism, introduces a novel way to 'switch on' protein synthesis ...
Magnetic semiconductor preserves 2D quantum properties in 3D material
2025-02-19
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — There is a big problem with quantum technology — it’s tiny. The distinctive properties that exist at the subatomic scale usually disappear at macroscopic scales, making it difficult to harness their superior sensing and communication capabilities for real-world applications, like optical systems and advanced computing. Now, however, an international team led by physicists at Penn State and Columbia University has developed a novel approach to maintain special quantum characteristics, even in three-dimensional (3D) materials.
The researchers published ...
Magnetic switch traps quantum information carriers in one dimension
2025-02-19
Illustration
A quantum "miracle material" could support magnetic switching, a team of researchers at the University of Regensburg and University of Michigan has shown.
This recently discovered capability could help enable applications in quantum computing, sensing and more. While earlier studies identified that quantum entities called excitons are sometimes effectively confined to a single line within the material chromium sulfide bromide, the new research provides a ...
Using light to activate treatments in the right place
2025-02-19
Acting in the right place at the right time is the key to effective medical treatment with minimal side effects. However, this feat remains difficult to achieve. Biologists and chemists at the University of Geneva (UNIGE) have succeeded in developing a tool that controls the location at which a molecule is activated by a simple pulse of light lasting only a few seconds. Tested on a protein essential for cell division, this system could be applied to other molecules. The potential applications are vast, both in basic research and in improving ...
Democracy in crisis: Trust in democratic institutions declining around the world
2025-02-19
New research from the University of Southampton has found that trust in representative institutions, such as parliaments, governments and political parties, has been declining in democratic countries around the world.
The study, published in The British Journal of Political Science, presents the largest and most comprehensive analysis of trends in political trust worldwide to date. It brings together results from 3,377 surveys covering 143 countries between 1958 and 2019, representing over five million survey respondents.
Whereas trust in representative institutions is generally in decline, trust in non-representative institutions ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
[Press-News.org] New funding to support food security, economic resiliencyFour organizations selected by American Heart Association Social Impact Funds to fill critical resource gaps, further progress toward equitable health using $2M grant from Grubhub Community Fund